- Part 1. What is a lithium-ion battery?
- Part 2. How does a lithium-ion battery work?
- Part 3. Li-ion battery discharging process
- Part 4. Li-ion battery charging process
- Part 5. Lithium-ion battery types, prices and applications
- Part 6. What factors affect the lithium-ion battery working?
- Part 7. Advantages and limitations of lithium-ion batteries
- Part 8. Conclusion
Lithium-ion Batteries are now getting popular because of their reliability and high performance. They are used in different electronic devices and automobiles. So, it is important to understand how the lithium-ion battery works. So, in this article, we will discuss the components, working principle, and a wide range of applications, along with how a lithium-ion battery works.
Part 1. What is a lithium-ion battery?
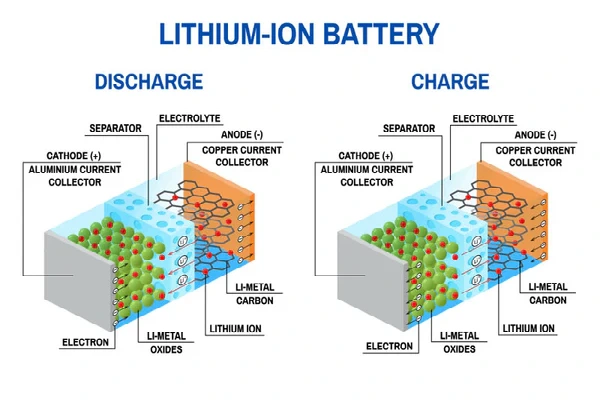
A lithium-ion battery works like other batteries. It is rechargeable and uses lithium ions to store energy. The other batteries go through chemical reactions for recharging. But in the case of the lithium-ion battery, it just reverses the flow of ions and gets recharged. It usually consists of two electrodes, called cathode and anode. So, these electrodes are separated with an electrolyte. When the lithium-ion battery connects with an external source, it allows the flow of electrons or ions from the anode to the cathode. This is known as recharging, But when the battery is discharged, it simply reverses the flow of ions, i.e., from cathode to anode.
Part 2. How does a lithium-ion battery work?
Let’s discuss “How does lithium-ion battery work?” in detail. But before this, let’s explore the components.
Components of Lithium-Ion Batteries
The following are the main components of Li-ion Batteries.
- The anode (Negative Electrode) mainly comprises graphite material and offers high conductance. Here, the electrons or ions leave the anode and start to move towards the lower potential, i.e., the cathode (+ve charge).
- Cathode (Positive Electrode): It is mainly comprised of lithium metal oxide, i.e., lithium cobalt oxide (LiCoO2) or lithium iron phosphate (LiFePO4). It takes the electrons or ions that derive from the anode.
- Electrolyte and Separator: It usually consists of electrodes. The electrolysis is generally composed of lithium salt dissolved in an organic solvent. They help in the flow of electrons.
Part 3. Li-ion battery discharging process
How a Lithium-Ion Battery Works During Discharge
When a lithium-ion battery discharges (i.e., supplies power), lithium ions move from the anode (negative electrode) to the cathode (positive electrode) through the electrolyte, while electrons flow through the external circuit to power devices.
At the Anode (Negative Electrode):
The anode is typically made of graphite (carbon). During discharge, lithium atoms in the graphite are ionized and release electrons:
LiC₆ → C₆ + Li⁺ + e⁻
This means lithium leaves the graphite structure as a lithium ion and an electron.
At the Cathode (Positive Electrode):
The cathode is commonly made of lithium cobalt oxide (LiCoO₂). During discharge, lithium ions and electrons are inserted into the cathode:
Li⁺ + e⁻ + CoO₂ → LiCoO₂
The lithium ion enters the structure of cobalt oxide to form lithium cobalt oxide.
Overall Net Discharging Reaction:
By combining the half-reactions, the net cell reaction during discharge is:
LiC₆ + CoO₂ → C₆ + LiCoO₂
Part 4. Li-ion battery charging process
How a Lithium-Ion Battery Works During Charging
During charging, an external power source forces the reverse of the discharge reactions. Lithium ions move from the cathode back to the anode, and electrons are pushed through the external circuit into the anode.
At the Anode (Negative Electrode):
Lithium ions are re-inserted into the graphite layers:
C₆ + Li⁺ + e⁻ → LiC₆
At the Cathode (Positive Electrode):
Lithium cobalt oxide releases lithium ions and electrons:
LiCoO₂ → CoO₂ + Li⁺ + e⁻
Overall Net Charging Reaction:
The combined overall charging reaction is:
C₆ + LiCoO₂ → LiC₆ + CoO₂
So, when the battery discharges, the following chemical reaction occurs:
At anode:
The general reaction at the anode is:
Li1+C6 ⇌ LiC6 + Li+ + e-
At Cathode:
The following reaction occurs at the cathode is:
LiCoO2 ⇌ Li1-CoO2 + Li+ + e-
Net Discharging Reaction:
So, the net reaction during the discharging process is:
LiC6 + LiCoO2 ⇌ Li1+C6 + Li1-CoO2
Part 5. Lithium-ion battery types, prices and applications
The following table describes different types of lithium-ion batteries available in the market. Moreover, we will get to know their range of prices as well.
| Lithium-ion Battery Type | Price (per kWh) | Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Lithium Cobalt Oxide (LiCoO2) | $150-$250 | Smart devices (smartphones, laptops), electric vehicles (Tesla Model S, Nissan Leaf) |
| Lithium Manganese Oxide (LiMn2O4) | $100-$200 | Power tools, electric bicycles, medical devices |
| Lithium Iron Phosphate (LiFePO4) | $200-$300 | Solar energy storage, electric buses, stationary energy storage |
| Lithium Nickel Manganese Cobalt Oxide (NMC) | $150-$250 | Electric automobiles (Chevrolet Bolt, BMW i3), grid energy storage |
| Lithium Nickel Cobalt Aluminum Oxide (NCA) | $200-$300 | Electric transport (Tesla Model 3, Model Y), aerospace applications |
| Lithium Titanate (Li4Ti5O12) | $300-$400 | High-power vehicles (electric buses, grid stabilization), renewable energy storage |
Part 6. What factors affect the lithium-ion battery working?
After discussing How a Lithium-Ion Battery works, let’s discuss a few factors that can reduce the working capabilities of lithium-ion batteries.
1. Temperature
Lithium-ion batteries are sensitive to temperature. So, they work in specific ranges, i.e., high temperatures can lead to their degradation. Thus, it reduces its capacity and overall lifespan. On the other hand, lower temperatures also affect its performance.
2. Depth of Discharge (DOD)
It is the extent of depth to which the lithium battery discharges. This factor also affects how a Lithium-Ion Battery works. DOD can be estimated during each cycle. So, it also directly impacts the lifespan of the battery. We can understand this by saying that shallow discharges use a small portion
of capacity. So, it increases the battery life. On the other hand, deep discharges use most of the battery capacity and reduce longevity.
3. Charging Rate
It also impacts the battery life. If the battery charges at a fast charging rate, it heats the battery. So, in the case of lithium batteries, slow charging rates are preferable to fast rates. Moreover, slow charging rates also improve the battery’s performance over time.
4. Overcharging and discharging
Always take care of overcharging and discharging when you charge your battery. Because it may cause damage and ultimately decrease the capacity of the battery. You can use an appropriate battery management system for this.
5. Charge Cycling
The number of charge cycles in the overall battery’s life may affect how a lithium-ion battery works, so if you charge the battery regularly within the recommended depth of discharge limits. It will increase the battery’s health and operating conditions.
Part 7. Advantages and limitations of lithium-ion batteries
Lithium-ion batteries have many advantages. However, it also comes up with some limitations. So, let’s discuss both here in detail.
Benefits of Li-ion Batteries
- High Energy Density: These Lithium-ion batteries have high capacities. So they can store more energy than other alternatives. Moreover, these batteries are smaller in size and are relatively lightweight.
- Long Cycle Life: The lithium-ion batteries may have hundreds to thousands of charge-discharge cycles rate. Thus, they face more capacity loss.
- Low Self-Discharge: The lithium batteries show a minimal self-discharge rate. So they can store energy for a long time. This is why these lithium-ion batteries are suitable for wide applications that need long-term storage.
Limitations of Li-ion Batteries
- Safety Limitations: The lithium-ion batteries have safety limitations. When they overcharge, they tend to experience short circuits. Moreover, they cannot bear high temperatures because they can catch fire.
- High Cost: The Li-ion batteries require advanced technology. They need complex manufacturing materials as well. So, its manufacturing cost is quite high.
Part 8. Conclusion
In conclusion, how a lithium-ion battery works. The lithium-ion batteries are made using advanced technologies. These batteries have many applications in portable electronic, electrical vehicles, and renewable energy resources. Lithium batteries are fast and perform well. Moreover, they offer a high discharge cycle. Additionally, multiple well-known brands are manufacturing efficient lithium-ion batteries. So, this article is the best guide to dealing with how a lithium-ion battery works.
Related Tags:
More Articles
Capacitor vs Battery: What is the Difference?
Capacitor vs battery explained in detail. Learn the difference between capacitor and battery in energy storage, charging speed, lifespan, and real applications.
18650 Battery vs AA: Which Is Better for Your Device?
Compare 18650 vs AA batteries in capacity, voltage, rechargeability, and applications. Learn which battery type fits high-drain or everyday devices.
What is the Difference Between Battery Cell, Battery Control Module, and Battery Pack?
Compare battery cells, modules, and packs. Learn functions, design differences, control modules, and selection tips for EV, ESS, and industrial use.
How to Prevent LiPo Battery Explosion?
Can LiPo batteries explode or catch fire? Learn key causes of LiPo battery fires and proven charging, storage, and handling tips to reduce explosion risk.
Aluminium Ion Battery vs Lithium-Ion: A Detailed Comparison
Compare aluminium ion battery vs lithium-ion battery in energy density, charging speed, safety, cost, and uses. A practical guide for engineers and buyers.