In today’s world, where sustainability and renewable energy are becoming increasingly important, 3.2V solar batteries are gaining significant attention. These batteries are pivotal in solar power systems, offering a reliable and efficient way to store energy harnessed from the sun. This comprehensive guide will delve into everything you need to know about 3.2V solar batteries, from their basic principles to their applications and maintenance.
Part 1. What is a 3.2V solar battery?
A 3.2V solar battery is a rechargeable battery designed to store energy generated by solar panels. The “3.2V” refers to the nominal voltage of the battery. Manufacturers commonly make these batteries from lithium iron phosphate (LiFePO4) for their stability, safety, and long cycle life.
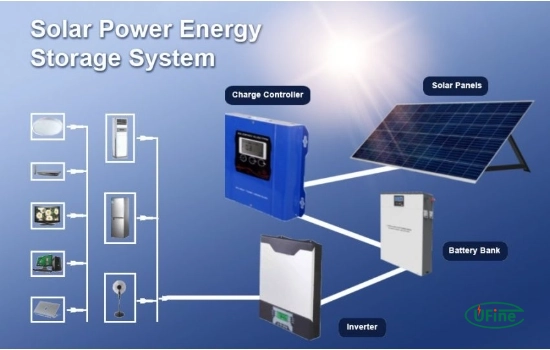
Critical Components of a 3.2V Solar Battery System
1. Solar Panels
The primary component that captures sunlight and converts it into electricity. The solar panels’ efficiency directly impacts the entire system’s performance.
2. Charge Controller
A charge controller regulates the voltage and current from the solar panels to the battery. It prevents overcharging and ensures the longevity of the battery.
3. Inverter
An inverter converts the DC electricity stored in the battery into alternating current (AC) electricity used by most household appliances.
4. Battery Management System (BMS)
The BMS monitors and manages the battery’s performance, ensuring it operates within safe parameters. It protects against overcharging, deep discharge, and overheating.
Part 2. How do 3.2V solar batteries work?
3.2V solar batteries work by storing electrical energy produced by solar panels. When sunlight hits the solar panels, it generates direct current (DC) electricity. This electricity is then converted to a suitable voltage and stored in the battery for later use. Here is a detailed breakdown of the process:
1. Solar Energy Collection
Solar panels, also known as photovoltaic (PV) panels, comprise many solar cells that convert sunlight into electricity. When sunlight strikes the solar cells, it excites electrons, creating an electric current.
2. Direct Current (DC) Generation
The electricity generated by solar panels is direct current (DC). This type of electricity exhibits a constant flow of electric charge in one direction.
3. Charge Controller Regulation
The DC electricity produced by the solar panels flows into a charge controller. The charge controller primarily regulates the voltage and current coming from the solar panels to ensure the battery charges safely and efficiently. It prevents overcharging and deep discharging, which can damage the battery.
4. Battery Storage
The 3.2V solar battery then stores the regulated DC electricity. The battery accumulates energy during the day when sunlight is available and stores it for use during periods when sunlight is unavailable, such as at night or during cloudy days.
5. Inverter Conversion
Most household appliances and electronic devices run on alternating current (AC). Therefore, an inverter converts the stored DC electricity in the battery into AC electricity. This conversion allows standard home and business electrical systems to utilize the stored energy.
6. Energy Utilization
Finally, the converted AC electricity powers various devices and appliances. The battery ensures a continuous and reliable power supply, even without sunlight.
Part 3. Advantages of 3.2V solar batteries
1. High Energy Density
3.2V solar batteries are known for their high energy density, which can store significant energy in a relatively small space. This makes them ideal for applications where space is limited.
2. Long Lifespan
Lithium iron phosphate batteries have a long lifespan, often exceeding 2000 charge-discharge cycles. This longevity translates to fewer replacements and lower maintenance costs over time.
3. Safety
LiFePO4 batteries are inherently safer than other types of lithium batteries. They have a stable chemical composition, which reduces the risk of overheating, explosion, or fire.
4. Eco-Friendly
These batteries are more environmentally friendly compared to other battery types. They do not contain harmful heavy metals and are recyclable, contributing to a greener planet.
Part 4. Disadvantages of 3.2V solar batteries
1. Higher Initial Cost
One of the main drawbacks of 3.2V solar batteries is their higher initial cost than other battery types. The advanced materials and technology used in LiFePO4 batteries make them more expensive to produce.
2. Size and Weight
While these batteries offer high energy density, they can still be bulkier and heavier than other battery types, such as lithium-ion polymer batteries. This can be a disadvantage in applications where space and weight are critical factors.
3. Temperature Sensitivity
3.2V solar batteries can be sensitive to extreme temperatures. High temperatures can reduce the battery’s lifespan, while extremely low temperatures can affect its performance. Proper thermal management is essential to ensure optimal operation.
4. Charging time
Although these batteries charge faster than many others, they may still require several hours to charge fully. This can be a limitation in situations where rapid recharging is necessary.
Part 5. Applications of 3.2V solar batteries
1. Residential Solar Systems
One of the primary uses of 3.2V solar batteries is in residential solar power systems. Homeowners use these batteries to store excess energy generated during the day, which they can use at night or during power outages.
2. Off-Grid Systems
For those living in remote areas without access to the grid, 3.2V solar batteries are a lifesaver. They provide a reliable power source, ensuring that essential devices and appliances can operate without interruption.
3. Commercial and Industrial Applications
Businesses and industries also adopt 3.2V solar batteries to reduce energy costs and carbon footprint. These batteries help ensure a steady power supply, even during peak usage.
4. Portable Solar Chargers
3.2V batteries are used in portable solar chargers and power banks, providing a convenient way to charge electronic devices on the go. This is especially useful for outdoor enthusiasts and travelers.
Part 6. How do I choose the suitable inverter for my 3.2V solar battery system?
Choosing the suitable inverter for your 3.2V solar battery system is essential. Here’s a simple guide:
1. Determine Your Power Needs
List all the devices you want to power. Check their wattage and add them up.
Example:
- Refrigerator: 150-200 watts
- LED TV: 60-100 watts
- Laptop: 50-75 watts
- Light Bulb: 10-60 watts
2. Choose the Right Inverter Type
Pure Sine Wave Inverters
- Best for sensitive electronics.
- It’s more expensive but efficient.
Modified Sine Wave Inverters
- It is suitable for essential appliances.
- It’s cheaper but less efficient.
3. Check Voltage Compatibility
Ensure the inverter matches your 3.2V battery. Most inverters are for 12V, 24V, or 48V systems, so you may need a particular setup.
4. Look at Capacity
The inverter should handle more than your total power needs. Add 20-30% extra capacity.
Example: If you need 1000 watts, get a 1300-watt inverter.
5. Consider efficiency
Choose an inverter with high efficiency (90% or above) to save energy.
6. Check Safety Features
Ensure the inverter has:
- Overload protection
- Short circuit protection
- Over-temperature protection
- Low battery alarm
Part 7. Installation and setup of 3.2V solar battery systems
1. Choosing the Right Location
Select a location with maximum sunlight exposure for your solar panels. Ensure no obstructions like trees or buildings could cast shadows on the panels.
2. Mounting the Solar Panels
Install the solar panels on a sturdy structure, such as a rooftop or a ground-mounted frame. You should optimize the angle and orientation of the panels for your location.
3. Connecting the Components
Connect the solar panels to the charge controller, then connect the charge controller to the battery. Finally, connect the battery to the inverter. Ensure all connections are secure and follow the manufacturer’s instructions.
4. Testing the System
Once everything is connected, test the system to ensure it works correctly. Check that the battery is charging properly and that the inverter provides AC power.
Part 8. Maintenance tips for 3.2V solar batteries
1. Regular Inspections
Periodically inspect the entire system for any signs of wear or damage. Check the solar panels, wiring, and battery for any issues.
2. Cleaning the Solar Panels
Keep the solar panels clean and free of debris to maintain their efficiency. Dust, dirt, and bird droppings can reduce the amount of sunlight reaching the panels.
3. Monitoring Battery Performance
Use the battery management system to monitor the battery’s performance. Keep an eye on charge levels, temperature, and overall health.
4. Proper Storage
If you need to store the battery for an extended period, store it in a cool, dry place. Fully charge the battery before storage and periodically recharge it to maintain health.
Part 9. Common issues and troubleshooting for 3.2V solar batteries
1. Battery Not Charging
Check the connections between the solar panels, charge controller, and battery if the battery is not charging. Ensure the charge controller is functioning correctly and that there is sufficient sunlight.
2. Reduced Battery Capacity
Over time, the battery’s capacity may decrease. This can be due to aging or improper use. Ensure the battery is not frequently overcharged or deeply discharged.
3. System Overheating
If the system overheats, check the ventilation around the battery and inverter. Ensure they are exposed to direct sunlight or placed in an enclosed space with proper airflow.
Part 10. FAQs
-
How long do 3.2V solar batteries last?
These batteries can last over 2000 charge-discharge cycles, which usually translates to several years of use, depending on the frequency of cycling and maintenance. -
Are 3.2V solar batteries safe?
Yes, 3.2V solar batteries, especially those using LiFePO4 chemistry, are considered very safe due to their stable chemical composition that reduces the risks of overheating and fire. -
Can 3.2V solar batteries be recycled?
Yes, these batteries are recyclable, which makes them an environmentally friendly option compared to other battery types that may contain harmful heavy metals. -
Can I use 3.2V solar batteries in cold climates?
Yes, but they may require additional insulation or heating solutions to maintain optimal performance in very low temperatures.
Related Tags:
More Articles

LiPo Battery Discharge Rate Guide & Calculation Tips
Understand LiPo battery discharge rates, C-ratings, and how to calculate max current. Essential guide for RC, drones, and electronics users.
High‑Capacity 3S LiPo Batteries: 5000 mAh vs. 10000 mAh
Compare 3S LiPo 5000mAh vs 10000mAh batteries by weight, power, and use. Find the best fit for your drone, RC car, or boat setup.
Top 5 Applications for Small 3S LiPo Batteries
Small 3S LiPo batteries power drones, RC gear, wearables, and robotics with high energy and low weight. Making them ideal for compact electronics projects.
Building and Charging Your Own 3S LiPo Pack: A Step‑by‑Step Guide
Learn how to build, balance, and charge a 3S LiPo battery pack safely at home with this complete DIY guide for hobbyists and beginners.
How to Choose the Right LiPo Battery Plug Type?
Discover the best LiPo battery plug types, how to choose them, and expert tips for safe usage, soldering, and maintenance.