How do solar batteries work? Solar batteries store energy from the sun, allowing us to use solar power anytime. In this article, we’ll explain the basics, key components, and the working principles of solar batteries. We’ll also look at what affects their performance and the benefits they offer.
Part 1. Working principle of solar batteries
Photovoltaic Effect
The photovoltaic effect is the process that makes solar panels work. It starts when sunlight hits the solar panels. These panels consist of tiny units called photovoltaic (PV) cells.
Here’s how it works:
- Sunlight Hits the PV Cell: When light hits the cell, it excites electrons in the material.
- Electron Movement: The excited electrons start to move, creating an electric current.
- Energy Conversion: This electric current is the primary form of electricity solar panels produce.
At the atomic level, the energy from sunlight knocks electrons loose in the PV cell. These free electrons flow through the cell, creating a current we can harness as electricity.
Energy Conversion Process
Solar panels convert sunlight into direct current (DC) electricity. Here’s a step-by-step look at how this happens:
- Sunlight Hits the Panels: Solar panels absorb sunlight.
- Photovoltaic Cells Activate: PV cells in the panels start to work.
- Electron Movement: The PV cells convert sunlight into a flow of electrons.
- Creation of DC Electricity: This flow of electrons is DC electricity.
- Flow to Battery: The DC electricity flows from the panels to the battery storage system.
This process captures the sun’s energy and turns it into electricity stored in batteries for later use.
Charge Regulation
The charge controller is crucial in managing the flow of electricity to the battery. It has several vital roles:
- Regulates Charging: It ensures the battery charges at a safe rate.
- Prevents Overcharging: It stops too much electricity from damaging the battery.
- Prevents Deep Discharging: It protects the battery from losing too much charge, which can shorten its life.
The controller helps keep the battery healthy and efficient by managing the charge.
Energy Storage Mechanism
Inside the battery, chemical reactions store electricity. Here’s how it works for different types:
- Lead-Acid Batteries: Use lead plates and sulfuric acid. When charging, lead sulfate converts to lead dioxide. When discharging, it reverses.
- Lithium-Ion Batteries: Use lithium compounds. When charging, lithium ions move to the anode. When discharging, they move back to the cathode.
- Saltwater Batteries: Use saltwater solutions. They store energy in a safe, eco-friendly way through saltwater reactions.
These reactions store and release energy as needed.
Energy Discharge Process
The discharge process involves converting stored energy back to electricity:
- Stored Energy is Released: The battery releases stored energy as DC electricity.
- Inverter Converts DC to AC: The inverter changes DC electricity to AC electricity used in homes.
- Energy Powers Appliances: The AC electricity powers lights, appliances, and devices.
The inverter plays a crucial role in making stored energy usable. Discharge patterns affect battery life. Regular, shallow discharges extend lifespan, while deep discharges can shorten it.
Part 2. Basics of solar batteries
Solar batteries store energy from the sun. They capture sunlight using solar panels and save this energy for later use. This means you can have power even when it’s dark or cloudy.
Solar batteries help people use more green energy. They reduce the need for electricity from the grid. This saves money and helps the planet by reducing pollution.
The history of solar batteries goes back to the 1970s. Early solar batteries were big and expensive. Over time, they have become smaller, cheaper, and better at storing energy. Today, they are essential to many homes and businesses that use solar power.
Types of Solar Batteries
There are several types of solar batteries. Each type has its benefits. Here are the main types:
Lead-Acid Batteries
- Used For: Homes, small systems
- Efficiency: Lower than other types
- Lifespan: 3-5 years
- Cost: Cheapest option
- Pros: Affordable, reliable
- Cons: Heavy, needs regular maintenance
Lithium-Ion Batteries
- Used For: Homes, businesses, electric cars
- Efficiency: High
- Lifespan: 10-15 years
- Cost: More expensive than lead-acid
- Pros: Lightweight, long-lasting, requires little maintenance
- Cons: Higher initial cost
Saltwater Batteries
- Used For: Homes, off-grid systems
- Efficiency: Medium
- Lifespan: 5-10 years
- Cost: Moderate
- Pros: Eco-friendly, safe, non-toxic
- Cons: Newer technology, less common
Each type of battery fits different needs. Lead-acid batteries are suitable for people on a budget. Lithium-ion batteries are great if you need high performance and long life. Saltwater batteries are the best choice if you want an eco-friendly option.
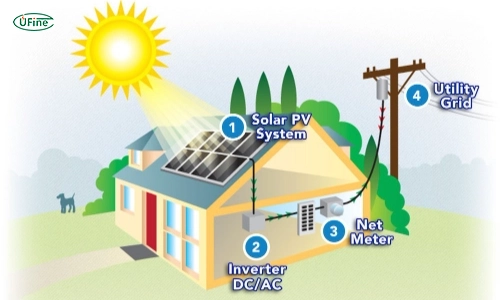
Part 3. Critical components of solar battery systems
Solar Panels
Solar panels are the starting point of a solar battery system. They convert sunlight into electricity. This process begins when sunlight hits the solar panels. These panels comprise many small units called photovoltaic (PV) cells.
Each PV cell works like a tiny solar factory. When sunlight strikes the cell, it knocks electrons loose. This creates an electric current. This current flows from the panel and into your home’s solar system.
In simple terms, solar panels turn sunshine into usable electricity. They are vital for collecting energy to store in your solar batteries.
Inverter
The electricity from solar panels is called direct current (DC). Most of our home appliances use alternating current (AC). This is where the inverter comes in.
The inverter changes DC electricity into AC electricity. This ensures your lights, fridge, TV, and other devices can utilize the power from your solar panels.
Inverters are crucial because they make solar energy compatible with our daily needs. With an inverter, the electricity from the solar panels would be usable in most homes.
Charge Controller
The charge controller is like a traffic cop for your solar battery system. It manages the flow of electricity from the solar panels to the batteries.
Here’s what it does:
- Regulates Charging: It ensures the batteries charge at the correct rate.
- Prevents Overcharging: Too much charge can damage the batteries. The charge controller stops this from happening.
- Prevents Excessive Discharge: It also ensures the batteries are not too empty. This helps prolong battery life.
By protecting the batteries, the charge controller ensures your system works efficiently and lasts longer.
Battery Storage Unit
The battery storage unit is the heart of a solar battery system. This is where the system stores the electricity for later use.
Inside the battery, chemical reactions take place to store energy. When you need electricity, the system converts the stored energy into electrical power.
Different batteries use different chemicals to store energy:
- Lead-Acid: Uses lead plates and sulfuric acid. These are cheaper but heavier.
- Lithium-Ion: Uses lithium compounds. These are lighter and last longer.
- Saltwater: Uses saltwater and other safe materials. These are eco-friendly but newer and less common.
The battery storage unit is essential for saving the energy your solar panels collect. It ensures you have power even when the sun isn’t shining.
Part 4. Factors influencing solar battery performance
Several factors can affect how well solar batteries work. Understanding these can help you get the most out of your solar energy system.
Depth of Discharge (DoD)
Depth of Discharge (DoD) represents the amount of the battery’s energy consumed. For instance, a 60% DoD means the battery uses 60% of its power, leaving 40% unused.
- Impact on Lifespan: Higher DoD means more use, which can wear out the battery faster. Lower DoD helps the battery last longer.
- Optimal DoD: Different batteries have different optimal DoD. Lithium-ion batteries can handle higher DoD than lead-acid batteries.
Charge Cycles
A charge cycle is one full charge and discharge of the battery. The number of cycles affects the battery’s life.
- Cycle Count: More cycles mean more wear and tear. Batteries have a limited number of cycles before they degrade.
- Battery Type: Lithium-ion batteries usually have more charge cycles than lead-acid batteries.
Temperature and Environmental Conditions
Temperature dramatically affects battery performance. Extreme temperatures can harm the battery.
- Optimal Temperature: Batteries work best at moderate temperatures. Too hot or too cold can reduce efficiency and lifespan.
- Protection: Use shelters or cooling systems to protect batteries from extreme conditions.
Maintenance
Regular maintenance keeps batteries working well.
- Lead-Acid Batteries: Need regular checks and water top-ups.
- Lithium-Ion Batteries: Require less maintenance but still need periodic checks.
Battery Age
Over time, batteries naturally degrade and lose capacity.
- Regular Monitoring: Monitor battery performance to know when it needs replacement.
Part 5. Benefits of solar batteries
Solar batteries offer many advantages. They make solar power more valuable and efficient.
Energy Independence
With solar batteries, you can store your energy. This means less reliance on the power grid.
- Power Anytime: Use stored energy at night or during power outages.
- Lower Bills: Reduce or eliminate electricity bills by using stored solar power.
Environmental Benefits
Solar batteries help protect the environment.
- Reduce Emissions: Using solar energy reduces the need for fossil fuels, cutting greenhouse gas emissions.
- Sustainable Energy: Solar power is renewable, unlike finite fossil fuels.
Reliability and Backup Power
Solar batteries provide a reliable power source.
- Backup Power: Keep your lights and appliances running during outages.
- Steady Supply: Store extra energy for cloudy days or nighttime use.
Part 6. FAQs
-
How long do solar batteries last?
Solar batteries typically last 5 to 15 years, depending on the type and usage. Lithium-ion batteries usually last up to 15 years, while lead-acid batteries last around 5 to 7 years. Proper maintenance and optimal usage can extend their lifespan. -
Can solar batteries work during a power outage?
Yes, solar batteries can provide power during outages. When the grid is down, the battery system automatically switches to battery power. This keeps your lights and appliances running until the grid restores power or the batteries run out. -
How do I know when to replace my solar battery?
Look for signs like reduced power storage, frequent charging, and discharging cycles, or if your solar system’s performance drops. Most solar batteries have a lifespan indicator. Check the manufacturer’s guidelines and monitor battery health regularly. -
What is the best type of solar battery for home use?
Lithium-ion batteries are often the best choice for home use. They are efficient, have a long lifespan, and require less maintenance than other types. Lead-acid batteries are cheaper but heavier and need more maintenance. Saltwater batteries are eco-friendly but less common.
Related Tags:
More Articles

Gravity Battery vs. Traditional Battery: A Comparative Analysis
Gravity batteries use gravitational energy for storage. This article compares them to traditional batteries, exploring mechanisms, advantages, and applications.
What Is a Gravity Battery?
A gravity battery stores electricity using gravitational energy. This article explores its mechanics, benefits, and real-world applications in renewable energy.
How to Choose the Right Battery Relay for Your Vehicle?
Choosing the right battery relay ensures optimal performance. This article explores key factors and answers common questions for selecting a reliable relay.
What to Know Before Buying a Riding Mower Battery
Ready to buy a riding mower battery? Learn the key factors to consider. Discover what you need to choose the best battery today!
Understanding Battery Relay: A Comprehensive Guide
Battery relays are essential for managing power efficiently. This guide covers their functions, types, and applications for DIY enthusiasts and vehicle owners.