A battery load test is a diagnostic method that measures a battery’s ability to deliver power under controlled conditions. How does a battery load test work? By applying a simulated electrical load (e.g., 50% of CCA for automotive batteries), technicians monitor voltage stability to determine health.
In today’s modern world, batteries power various devices, from smartphones and laptops to cars and industrial machinery. However, batteries can lose capacity and performance over time, leading to potential issues and inconveniences. That’s where battery load testing comes into play. This comprehensive guide will explore battery load testing, its importance, principles, types, equipment, procedures, and how to interpret the test results.
Part 1. What is a battery load test?
Battery load testing is a diagnostic procedure used to measure a battery’s performance and health by subjecting it to a controlled load. By applying a load to the battery, the test determines its ability to deliver power and maintain voltage levels under specific conditions. This test is crucial for assessing battery reliability, identifying potential issues, and preventing unexpected failures.
Importance of Battery Load Testing
Ensuring Battery Performance
You can evaluate their performance under real-world conditions by subjecting batteries to a load test. Identifying any shortcomings or degradation in battery capacity is essential for maintaining optimal performance.
Preventing Unexpected Failures
Regular load testing lets you identify weak or failing batteries before they cause unexpected failures. By detecting potential issues early on, you can take proactive measures such as battery replacement, reducing the risk of downtime and costly repairs.
Extending Battery Lifespan
You can implement proper maintenance and optimize charging and discharging cycles by monitoring battery health through load testing. Implementing these practices prolongs the lifespan of batteries, resulting in cost savings and improved operational efficiency.
Ensuring Safety
Battery failures can have profound safety implications in specific applications, such as automotive and industrial sectors. Load testing helps identify potential safety risks associated with battery performance, enabling timely interventions to prevent accidents or hazards.
Part 2. Principles of battery load testing
Understanding the underlying principles and factors influencing the testing process is essential for conducting a practical battery load test.
Load Testing Methodology
The load testing methodology involves subjecting the battery to a known load for a specified duration while monitoring its voltage and performance. The following steps outline a typical load-testing process:
- Prepare the battery for testing by ensuring it reaches a full charge and maintains the recommended temperature.
- Connect the battery to the load testing equipment, which applies a controlled load.
- Apply the load for a predetermined duration, typically based on the battery’s specifications or industry standards.
- Monitor the battery’s voltage and performance throughout the test.
- Analyze the test results to assess the battery’s condition and determine any necessary actions.
Factors Affecting Load Testing
Several factors can influence the accuracy and reliability of battery load testing. It’s essential to consider these factors to obtain accurate results:
Battery Temperature
Battery performance can vary significantly with temperature. Therefore, it is crucial to conduct load tests under recommended temperature conditions to obtain reliable and consistent results.
Load Applied
The load applied during testing should reflect the expected real-world usage. Using an appropriate load level can lead to accurate results and an incomplete assessment of battery performance.
Test Duration
The load test duration should align with the battery’s specifications or industry standards. Testing for an insufficient duration may not reveal specific battery issues, while testing for too long can damage the battery.
Equipment Calibration
Technicians regularly calibrate the load testing equipment to ensure accurate measurements. Proper calibration helps maintain the reliability and consistency of test results.
Part 3. Types of battery load tests
Here are some common types of load tests:
- Constant Current Load Test: This test applies a constant current load to the battery and measures its voltage response over time. It helps assess the battery’s capacity and performance under sustained current draw.
- Pulse Load Test: This test subjects the battery to intermittent high-current pulses, simulating real-life scenarios with sudden power demands. It helps evaluate the battery’s ability to handle peak loads.
- Capacity Load Test: This test determines the battery’s capacity by discharging it at a specific rate until it reaches a predefined voltage level. It provides insights into the battery’s usable capacity and helps estimate its runtime.
- Cranking Load Test: Primarily used for automotive batteries, this test assesses the battery’s ability to deliver a high current for starting the engine. It measures the voltage drop during cranking and helps evaluate the battery’s starting power.
- Car Battery Load Test: Measures Cold Cranking Amps (CCA) with 15-second load cycles.
- Solar Battery Load Test: Uses 20-hour capacity rating (C20) for deep-cycle validation.
Part 4. Battery load testing equipment
| Equipment Type | Recommended Models | Best For | Price Range |
|---|---|---|---|
| Digital Load Tester | Midtronics MDX-650 | Automotive Batteries | $300-$400 |
| Industrial Analyzer | Fluke 500 Series | Solar/Deep Cycle | $450-$600 |
| Basic Multimeter | INNOVA 3320 | Quick Voltage Checks | $20-$50 |
Professional-grade testers cost $150-$500, while basic multimeter tests start at $20.
Load Tester
A load tester applies a controlled load to the battery and measures its voltage response. It also provides readings for current, resistance, and other parameters relevant to the test.
Multimeter
A multimeter measures voltage, current, and resistance during the load test. It helps ensure accurate readings and provides additional diagnostic information.
Data Logger
A data logger records and stores data throughout the load test, allowing for detailed analysis and comparison of test results. It enables the identification of trends and patterns in battery performance.
Safety Equipment
Safety should always be a priority during battery load testing. To minimize the risk of accidents or injuries, safety equipment, such as gloves, goggles, and protective clothing, should be used.
Part 5. Battery load testing procedure
- Preparation
- Charge to 12.6V (lead-acid) or 3.65V/cell (lithium)
- Wear ANSI-approved gloves & goggles
- Connection
- Red clamp to (+) terminal, black to (-)
- Ensure contacts are corrosion-free
- Load Application
- Automotive: Apply 50% CCA for 15 seconds
- Deep-cycle: 3x Ah rating for 3 hours
- Voltage Monitoring
- Record initial/5s/15s readings
- Stop if voltage drops below 9V (12V battery)
Part 6. Interpreting load test results
Interpreting load test results requires a comprehensive understanding of battery performance characteristics and specifications. Here are some key aspects to consider:
- Voltage Response: Monitor the battery’s voltage during the load test. A healthy battery should maintain a stable voltage within acceptable limits. Significant voltage drops may indicate capacity issues or internal resistance problems.
- Capacity Assessment: Assess the battery’s capacity based on the load test results. Compare the actual capacity observed during the test with the battery’s rated capacity. If the observed capacity is significantly lower, it may indicate aging, degradation, or other issues.
- Performance Analysis: Analyze the battery’s performance under the applied load. Look for signs of excessive voltage drops, inability to sustain the load, or irregular voltage patterns. Such observations can provide insights into the battery’s overall health and suitability for specific applications.
- Trends and Historical Data: If available, compare the current test results with previous load test data. Monitor trends over time to identify any progressive degradation or improvements in battery performance.
Pass/Fail Voltage Thresholds
- 12V Automotive Battery: ≥9.6V @ 15s load = Healthy
- 6V Golf Cart Battery: ≥5.5V @ 30min = Replace if below
- Solar Lithium Battery: ≤3% voltage drop @ 1C rate
Part 7. 5 Critical battery load test mistakes
❌ Testing a discharged battery
Causes false “bad battery” readings. Always charge to 100% SOC first.
❌ Ignoring temperature compensation
Add 0.01V/°F above 80°F, subtract below (per SAE J537).
❌ Wrong load settings
Use 50% CCA for cars, 3x Ah for deep-cycle batteries.
❌ Testing immediately after charging
Wait 2 hours for surface charge dissipation.
❌ Using damaged cables
Worn clamps cause voltage drop errors. Replace if resistance >0.2Ω.
Part 8. FAQs about battery load testing
How long does a battery load test take?
Typically 15-30 seconds for automotive batteries, 1-3 hours for deep-cycle systems.
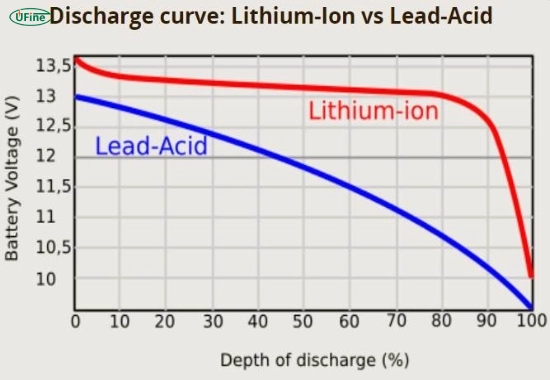
Can you load test a lithium battery?
Yes, but use CC/CV mode instead of traditional resistive load. Never exceed 1C rate.
Is a load test better than a voltage test?
Load tests reveal actual performance under stress, while voltage only shows surface charge.
Can I do a load test without special equipment?
Basic tests can use headlights (auto) or inverters (solar), but professional tools give accurate results.
How often should load testing be done?
Every 6 months for critical systems (UPS/medical), annually for automotive batteries.
Part 9. Conclusion
Battery load testing is crucial for evaluating battery performance and preventing unexpected failures. By understanding the principles, types, equipment, and interpretation of load test results, you can make informed decisions to optimize battery maintenance and ensure long-term reliability in diverse applications.Proper maintenance combined with regular load testing can extend battery life by up to 40%. Learn more about how to recondition a dead battery to maximize your power solutions.
Related Tags:
More Articles

High‑Capacity 3S LiPo Batteries: 5000 mAh vs. 10000 mAh
Compare 3S LiPo 5000mAh vs 10000mAh batteries by weight, power, and use. Find the best fit for your drone, RC car, or boat setup.
Top 5 Applications for Small 3S LiPo Batteries
Small 3S LiPo batteries power drones, RC gear, wearables, and robotics with high energy and low weight. Making them ideal for compact electronics projects.
Building and Charging Your Own 3S LiPo Pack: A Step‑by‑Step Guide
Learn how to build, balance, and charge a 3S LiPo battery pack safely at home with this complete DIY guide for hobbyists and beginners.
How to Choose the Right LiPo Battery Plug Type?
Discover the best LiPo battery plug types, how to choose them, and expert tips for safe usage, soldering, and maintenance.
Choosing the Right Connector for Your 3S LiPo Battery
Choosing the right 3S LiPo connector depends on current, space, and use. Learn the pros and cons of XT60, JST, EC3, and more.