- Important clarification: Lithium vs alkaline batteries
- Part 1. What is a lithium-ion battery?
- Part 2. Lithium-ion battery advantages
- Part 3. Lithium-ion battery disadvantages
- Part 4. What is an alkaline battery?
- Part 5. Alkaline battery advantages
- Part 6. Alkaline battery disadvantages
- Part 7. Lithium vs alkaline batteries: 7 Key differences you must know
- Part 8. How to choose lithium or alkaline batteries by use case
- Part 9. FAQs about lithium vs alkaline batteries
Choosing between lithium and alkaline batteries affects how long your devices last, especially in cameras, security sensors, and everyday household electronics. Understanding which battery type fits your usage scenario helps you avoid frequent replacements and performance issues.
Important clarification: Lithium vs alkaline batteries
In everyday consumer electronics, “lithium batteries” usually refer to lithium primary batteries (non-rechargeable), such as lithium AA or AAA cells. Lithium-ion batteries are rechargeable and are mainly used in smartphones, laptops, power banks, and electric vehicles.
This article primarily compares alkaline batteries vs lithium primary batteries for AA/AAA devices, while also explaining how lithium-ion batteries differ when relevant.
Quick Answer: Lithium vs Alkaline Batteries
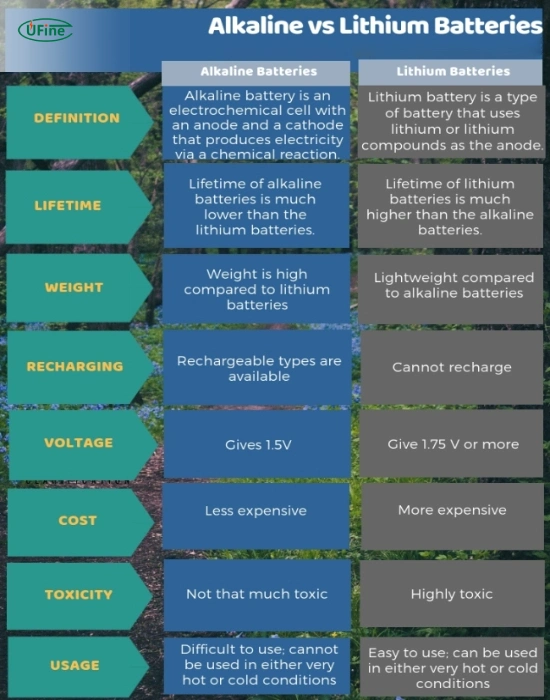
The main difference between lithium and alkaline batteries is lifespan and performance. Lithium batteries last 3–7 times longer, perform better in extreme temperatures, and deliver more stable voltage. Alkaline batteries cost less upfront and work well in low-drain devices like TV remotes and clocks.
Part 1. What is a lithium-ion battery?
A lithium-ion battery is a rechargeable battery widely used in smartphones, laptops, medical devices, power tools, and electric vehicles. It works by moving lithium ions between the negative electrode (anode) and positive electrode (cathode) during charging and discharging.
Lithium-ion batteries are known for their high energy density, lightweight design, and stable voltage output. Unlike alkaline batteries, lithium-ion batteries are designed for repeated charging cycles and are not typically used as AA or AAA disposable cells.
Part 2. Lithium-ion battery advantages
Lightweight Design
Lithium-ion batteries are significantly lighter than alkaline batteries with similar capacity, making them ideal for portable electronics and mobility-focused devices.
High Energy Density
Lithium-ion batteries store more energy per unit weight than alkaline batteries, enabling longer runtimes without increasing battery size.
Low Self-Discharge
Lithium-ion batteries lose only about 2–3% of their charge per month when stored, allowing devices to remain ready for use even after long periods of inactivity.
Stable Voltage Output
They maintain a relatively flat discharge curve, delivering consistent voltage until near depletion, which improves device performance and reliability.
Rechargeable and Cost-Effective Over Time
Although lithium-ion batteries cost more upfront, their ability to be recharged hundreds or thousands of times makes them more economical and environmentally friendly than disposable alkaline batteries.
Part 3. Lithium-ion battery disadvantages
Limited Lifespan
Lithium-ion batteries have a finite lifespan measured in charge cycles. Over time, chemical aging reduces their capacity, eventually requiring replacement.
Temperature Sensitivity
High temperatures accelerate lithium-ion battery degradation, while extremely low temperatures can temporarily reduce performance and output.
Safety Risks
Damaged or improperly charged lithium-ion batteries may overheat, swell, or catch fire. Quality battery management systems are essential for safe operation.
Complex Charging Requirements
Lithium-ion batteries require precise charging control. Overcharging, deep discharging, or using incompatible chargers can shorten lifespan and increase safety risks.
Environmental and Resource Impact
Lithium-ion batteries rely on materials such as lithium, cobalt, and nickel. Mining and improper disposal can negatively impact the environment if not responsibly managed.
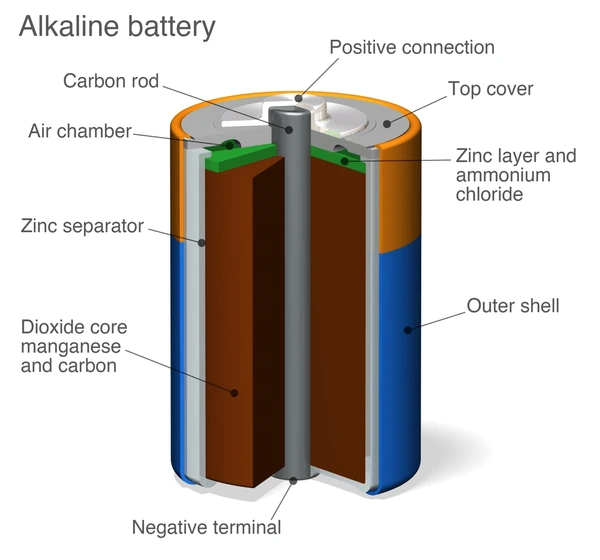
Part 4. What is an alkaline battery?
An alkaline battery is a disposable, non-rechargeable battery commonly used in low-drain household electronics. It generates electricity through a chemical reaction between zinc and manganese dioxide.
Alkaline batteries are widely available in standard sizes such as AA, AAA, C, D, and 9V. They are best suited for devices that require steady, low power over long periods, including remote controls, wall clocks, toys, and smoke detectors.
Unlike lithium-ion batteries, alkaline batteries are designed for single use and must be replaced once depleted.
Part 5. Alkaline battery advantages
Low Upfront Cost
Alkaline batteries are inexpensive and widely available, making them a convenient choice for everyday household use.
Long Shelf Life
When stored properly, alkaline batteries can retain usable charge for up to 5–10 years, ideal for emergency and backup devices.
Stable Power for Low-Drain Devices
They provide consistent voltage in low-drain applications, ensuring reliable performance for devices like clocks and TV remotes.
Wide Compatibility
Most consumer electronics are designed to work with alkaline batteries, ensuring easy replacement and compatibility.
Convenience
No charging equipment is required—simply replace depleted batteries with new ones when needed.
Part 6. Alkaline battery disadvantages
Single-Use Design
Alkaline batteries cannot be recharged. Once depleted, they must be disposed of, contributing to long-term waste.
Poor Performance in High-Drain Devices
In devices that draw high current, alkaline batteries drain quickly and may cause reduced performance or frequent replacement.
Voltage Drops Over Time
As alkaline batteries discharge, their voltage gradually declines, which can negatively affect sensitive electronics.
Leakage Risk
Old or fully depleted alkaline batteries are more prone to leakage, which can damage devices.
Higher Long-Term Cost
Although inexpensive upfront, repeated replacement can make alkaline batteries more expensive than lithium batteries over time in frequent-use devices.
Part 7. Lithium vs alkaline batteries: 7 Key differences you must know
1. Energy Density
Lithium batteries have a much higher energy density than alkaline batteries. This allows lithium batteries to store more energy in the same size, resulting in longer runtimes.
2. Lifespan
Lithium batteries typically last 3–7 times longer than alkaline batteries, especially in high-drain devices such as digital cameras and security sensors.
3. Voltage Stability
Lithium batteries maintain a stable voltage throughout most of the discharge cycle, while alkaline batteries experience a gradual voltage drop that can reduce device performance.
4. Temperature Performance
Lithium batteries operate reliably in extreme temperatures, from −40°F to 140°F. Alkaline batteries perform best at room temperature and struggle in cold environments.
5. Cost Over Time
Although lithium batteries have a higher upfront cost, their longer lifespan often makes them more cost-effective than alkaline batteries in frequent-use devices.
6. Leakage and Reliability
Lithium batteries have a significantly lower leakage risk compared to alkaline batteries, making them safer for long-term use in valuable electronics.
7. Best Use Cases
Lithium batteries are ideal for high-drain and outdoor devices, while alkaline batteries are better suited for low-drain indoor electronics.
- 📸 Cameras & GPS → Lithium
- 🔐 Smart locks & sensors → Lithium
- 📺 TV remotes & clocks → Alkaline
According to the 2023 Battery Industry Report by TÜV Rheinland:
- 📈 Lithium battery adoption increased by 42% in consumer electronics
- 🌍 Alkaline batteries still account for 68% of single-use battery sales
- 🔥 Lithium failure rate: 0.03% vs 0.15% for alkaline
| Criteria | Lithium Batteries | Alkaline Batteries |
|---|---|---|
| Lifespan | 3–7× longer | Shorter, frequent replacement |
| Temperature Range | −40°F to 140°F | 32°F to 77°F |
| Voltage Stability | Very stable | Gradual decline |
| Leakage Risk | Very low | Moderate to high |
| Best For | High-drain & outdoor devices | Low-drain indoor devices |
Lithium vs Alkaline AA Batteries: Which Should You Choose?
Choose lithium AA batteries for high-drain or outdoor devices such as cameras, smart locks, GPS units, and security sensors. Choose alkaline AA batteries for low-power indoor devices like TV remotes, wall clocks, and smoke detectors.
Part 8. How to choose lithium or alkaline batteries by use case
Choosing between lithium and alkaline batteries depends on how much power your device needs, how often it is used, and the environment in which it operates.
Always Choose Lithium Batteries For:
- 📸 Digital cameras and action cameras
- 🔐 Smart door locks and sensors
- 📡 GPS devices and handheld radios
- ❄️ Outdoor or cold-weather devices
- 📷 Security cameras and motion detectors
Alkaline Batteries Are Better For:
- 📺 TV remote controls
- 🕰️ Wall clocks
- 🚨 Smoke detectors
- 🧸 Low-power electronic toys
Quick buying rule: If your device drains batteries quickly or works outdoors, choose lithium. If your device uses batteries slowly and stays indoors, alkaline batteries are usually sufficient.
Looking for high-performance lithium batteries for demanding applications? Explore our premium battery solutions designed for reliability and efficiency. Shop Now.
Part 9. FAQs about lithium vs alkaline batteries
Which battery is better: lithium or alkaline?
Lithium batteries are better in most situations. They last longer, perform better in extreme temperatures, and provide more stable voltage than alkaline batteries. Alkaline batteries remain suitable for low-drain devices such as TV remotes and wall clocks.
What is the longest-lasting battery: lithium or alkaline?
Lithium batteries are the longest-lasting option. In AA size, lithium batteries can last up to 7 times longer than alkaline batteries in high-drain devices like digital cameras and security sensors.
This is because lithium batteries have higher energy density, maintain stable voltage during discharge, and lose less energy through self-discharge.
Are lithium batteries safer than alkaline batteries?
Both battery types are safe when used correctly. Lithium batteries have a lower leakage risk, while alkaline batteries are less prone to fire. Never use damaged or swollen lithium batteries.
Can I mix lithium and alkaline batteries in the same device?
No. Mixing lithium and alkaline batteries can cause uneven discharge, overheating, or device damage. Always replace all batteries in a device with the same type and brand.
Do lithium batteries work better in cold weather?
Yes. Lithium batteries perform reliably in cold temperatures down to −40°F, while alkaline batteries lose capacity quickly below freezing.
How should lithium and alkaline batteries be recycled?
Lithium batteries should be recycled at approved battery recycling centers. Alkaline batteries can be disposed of with household waste in most U.S. states, except where local regulations require recycling.
Related Tags:
More Articles
Capacitor vs Battery: What is the Difference?
Capacitor vs battery explained in detail. Learn the difference between capacitor and battery in energy storage, charging speed, lifespan, and real applications.
18650 Battery vs AA: Which Is Better for Your Device?
Compare 18650 vs AA batteries in capacity, voltage, rechargeability, and applications. Learn which battery type fits high-drain or everyday devices.
What is the Difference Between Battery Cell, Battery Control Module, and Battery Pack?
Compare battery cells, modules, and packs. Learn functions, design differences, control modules, and selection tips for EV, ESS, and industrial use.
How to Prevent LiPo Battery Explosion?
Can LiPo batteries explode or catch fire? Learn key causes of LiPo battery fires and proven charging, storage, and handling tips to reduce explosion risk.
Aluminium Ion Battery vs Lithium-Ion: A Detailed Comparison
Compare aluminium ion battery vs lithium-ion battery in energy density, charging speed, safety, cost, and uses. A practical guide for engineers and buyers.