- Part 1. What is a trickle charger?
- Part 2. What does "dead battery" really mean?
- Part 3. Can a trickle charger charge a dead battery?
- Part 4. How does a trickle charger work?
- Part 5. When should you use a trickle charger?
- Part 6. Signs your battery is too dead for a trickle charger
- Part 7. How to safely use a trickle charger
- Part 8. Trickle charger vs battery maintainer: What's the difference?
- Part 9. Can you leave a trickle charger on overnight?
- Part 10. Tips to bring a dead battery back to life
- Part 11. FAQs about using a trickle charger on a dead battery
Can a trickle charger charge a dead battery? This is a question many car owners ask when they find themselves with a vehicle that won’t start. The short answer is: it depends on how “dead” the battery really is. If you’ve left your lights on overnight or your car hasn’t been used in a while, there’s a chance a trickle charger can bring the battery back to life. But if the battery is completely drained or damaged, a trickle charger might not be enough.
In this guide, we’ll explore how trickle chargers work, what types of dead batteries they can revive, and how to use them safely. Whether you’re a new driver or a seasoned car enthusiast, this detailed guide will give you the honest truth about trickle chargers and dead batteries.
Part 1. What is a trickle charger?
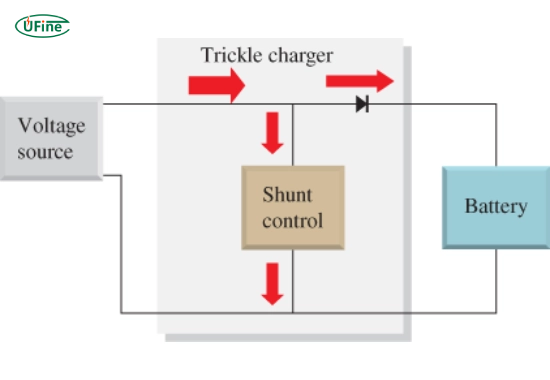
A trickle charger is a small battery charger designed to charge a battery slowly and keep it at a full charge. Unlike standard chargers, which push a high current into the battery to charge it quickly, trickle chargers use low voltage and low amperage over a long time.
They are ideal for vehicles that sit idle for long periods, like motorcycles, classic cars, boats, or RVs. By delivering a steady and continuous charge, trickle chargers help prevent the battery from going flat.
Part 2. What does “dead battery” really mean?
When people say “dead battery,” they usually mean one of two things:
- Deeply discharged: The battery still has some life, but voltage has dropped too low to start a vehicle.
- Permanently damaged: The battery has lost its ability to hold a charge due to age, sulfation, or internal failure.
A deeply discharged battery can sometimes be saved. But a damaged or old battery may be beyond recovery, even with the best charger.
Part 3. Can a trickle charger charge a dead battery?
Yes, a trickle charger can charge a dead battery—but only if the battery is not completely dead or damaged. If the battery is simply discharged, a trickle charger can slowly restore its charge over time.
However, if the battery’s voltage has dropped below 10.5 volts, many trickle chargers won’t even start the charging process. That’s because they need to detect a certain level of voltage to begin working. In such cases, a manual charger or jumpstart may be needed first.
Key takeaway: A trickle charger is best for maintaining battery charge or slowly reviving a mildly dead battery—not for emergency jumpstarts or reviving a completely flat battery.
Part 4. How does a trickle charger work?
A trickle charger works by delivering a small, controlled amount of electricity to the battery over an extended period. This slow pace reduces the risk of overheating or overcharging.
Here’s how it works:
- You connect the charger to the battery terminals.
- The charger sends a low current (usually 1 to 2 amps).
- The battery slowly absorbs the charge.
- Once full, smart trickle chargers switch to float mode to maintain the battery without overcharging.
This makes trickle chargers ideal for long-term maintenance, especially during the winter or when storing vehicles for months.
Part 5. When should you use a trickle charger?
A trickle charger is best used when:
- Your car sits unused for weeks or months.
- You own seasonal vehicles like boats or RVs.
- You want to maintain a healthy battery over time.
- Your battery is partially discharged, not completely dead.
Using a trickle charger regularly can extend your battery’s life and save you from unexpected breakdowns.
Part 6. Signs your battery is too dead for a trickle charger
Sometimes, even the best trickle charger can’t save a battery. Here are signs your battery might be too far gone:
- Battery voltage is under 10 volts
- Charger won’t recognize the battery
- Battery won’t hold a charge after hours of charging
- You see swelling, leaks, or corrosion
- Battery is over 3 to 5 years old
In these cases, it’s better to replace the battery rather than waste time trying to charge it.
Part 7. How to safely use a trickle charger
Using a trickle charger is simple, but you must follow proper steps to avoid damage or injury:
- Turn off the vehicle and make sure the battery is accessible.
- Connect the red clamp to the positive (+) terminal.
- Connect the black clamp to the negative (-) terminal or a metal ground.
- Plug in the charger and turn it on.
- Monitor the charger and battery. Most modern chargers have indicators or automatic shut-off.
Safety tips:
- Never use a trickle charger on a frozen battery.
- Avoid using indoors unless well-ventilated.
- Keep away from flammable materials.
- Use a smart charger with auto shut-off if possible.
Part 8. Trickle charger vs battery maintainer: What’s the difference?
People often confuse trickle chargers with battery maintainers. While both serve similar roles, there are differences:
| Feature | Trickle Charger | Battery Maintainer |
|---|---|---|
| Charging Speed | Slow, continuous | Smart, adaptive |
| Risk of Overcharge | Possible (if manual) | Low (auto shut-off) |
| Float Mode Support | Not always included | Yes |
| Best Use | Occasional charging | Long-term maintenance |
If you plan to leave the charger connected for weeks, a battery maintainer is safer. It monitors the battery and adjusts charging accordingly.
Part 9. Can you leave a trickle charger on overnight?
Yes, you can leave a trickle charger on overnight, but only if it’s a smart or automatic model. These chargers monitor the battery’s voltage and switch to maintenance mode once the battery is full.
Manual trickle chargers, on the other hand, keep charging until you disconnect them, which can overcharge and damage the battery if left too long.
For overnight use, always choose a smart charger with built-in safety features.
Part 10. Tips to bring a dead battery back to life
If your battery is too dead for a trickle charger to recognize, try these steps:
- Jumpstart the car using cables or a power pack. Let the engine run for 15–30 minutes.
- Once restarted, connect the trickle charger to maintain and slowly charge the battery.
- If the battery won’t start or hold a charge, have it tested at an auto parts store.
- Consider using a manual charger capable of charging at low voltages.
Sometimes, combining a jumpstart with trickle charging can bring a battery back to life, especially if it’s not badly damaged.
Part 11. FAQs about using a trickle charger on a dead battery
Can a trickle charger charge a completely dead battery?
No, most trickle chargers need the battery to have at least some voltage to start charging. If the battery is completely flat, use a manual charger or jumpstart first.
How long does it take a trickle charger to charge a dead battery?
It depends on the battery size and charger output. A trickle charger may take 24 to 72 hours to fully charge a deeply discharged battery.
Can a trickle charger damage a battery?
Yes, if it’s a manual charger and left connected too long. Overcharging can cause battery overheating and damage. Use a smart charger to avoid this risk.
Is it safe to leave a trickle charger on all winter?
Yes, if it’s a smart trickle charger with float mode. These are designed for long-term use and will maintain the battery safely over months.
What is the best trickle charger for a dead battery?
Look for a charger with:
- Smart charging features
- Low amp output (1–2 amps)
- Float mode
- Voltage detection
Brands like Battery Tender, NOCO, and Schumacher are popular among users.
Related Tags:
More Articles

18650 Battery vs AA: Which Is Better for Your Device?
Compare 18650 vs AA batteries in capacity, voltage, rechargeability, and applications. Learn which battery type fits high-drain or everyday devices.
What is the Difference Between Battery Cell, Battery Control Module, and Battery Pack?
Compare battery cells, modules, and packs. Learn functions, design differences, control modules, and selection tips for EV, ESS, and industrial use.
How to Prevent LiPo Battery Explosion?
Can LiPo batteries explode or catch fire? Learn key causes of LiPo battery fires and proven charging, storage, and handling tips to reduce explosion risk.
Aluminium Ion Battery vs Lithium-Ion: A Detailed Comparison
Compare aluminium ion battery vs lithium-ion battery in energy density, charging speed, safety, cost, and uses. A practical guide for engineers and buyers.
C vs D vs AA Battery: Size, Voltage, Capacity & Key Differences Explained
Compare AA, C, and D batteries by size, voltage, capacity, and lifespan. Learn the real difference between C and D batteries and which one you should use.