- Part 1. What is a 3.6V lithium battery?
- Part 2. 3.6V vs 3.7V vs 3.2V (LiFePO4) — voltage explained
- Part 3. Common size (18650, AA, 14500, coin cells)
- Part 4. What’s the life of a 3.6V battery?
- Part 5. Performance data and specifications
- Part 6. Are all 3.6V batteries rechargeable?
- Part 7. What type of battery can replace a 3.6V battery?
- Part 8. Charging and safety guidelines
- Part 9. Best 3.6V batteries in 2026 (Top brands & models)
- Part 10. FAQs
In 2026, the demand for compact and high-energy lithium batteries continues to surge. Among the many voltage configurations, the 3.6V lithium battery remains one of the most widely used and versatile power sources — from IoT sensors and flashlights to medical and industrial equipment.
This complete guide covers everything you need to know about 3.6V lithium batteries — their chemistry, voltage differences, common types, lifespan, specifications, charging tips, and the best models available today.
Part 1. What is a 3.6V lithium battery?
According to IEC 62133, the nominal voltage of lithium-ion rechargeable cells is defined between 3.6V and 3.7V
A 3.6V lithium battery is a rechargeable or primary (non-rechargeable) lithium cell designed with a nominal voltage of approximately 3.6 volts. This voltage represents the optimal balance between energy density, safety, and lifespan.
It’s the “sweet spot” used across multiple lithium chemistries — most notably Li-ion (Lithium-ion) and Li-SOCl₂ (Lithium-thionyl chloride) — to power electronics efficiently while maintaining compact size and long-term reliability.
3.6V Lithium Battery Chemistry Explained
The voltage of 3.6V comes from the electrochemical potential between the cathode and anode materials used in lithium cells:
- Lithium-Ion (LiCoO₂, NCM, etc.) – Typical nominal voltage 3.6–3.7V; rechargeable; used in laptops, tools, and portable devices.
- Lithium-Thionyl Chloride (Li-SOCl₂) – Nominal voltage 3.6V; non-rechargeable; extremely long shelf life (10–20 years); used in metering and IoT.
- LiFePO₄ (Lithium Iron Phosphate) – Nominal voltage around 3.2V; slightly lower energy density but excellent safety and cycle life.
Each chemistry defines how the battery behaves in terms of cycle life, discharge curve, and temperature tolerance, which are key considerations for different industries.
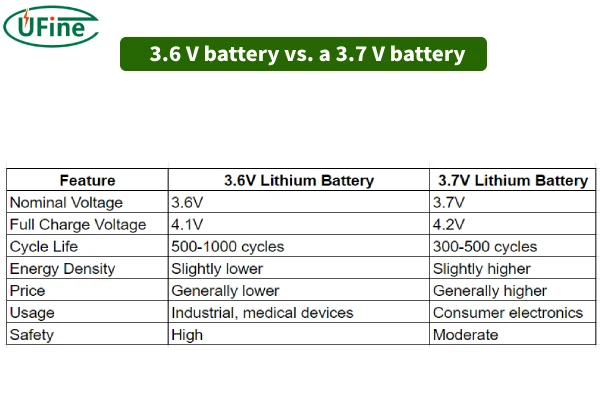
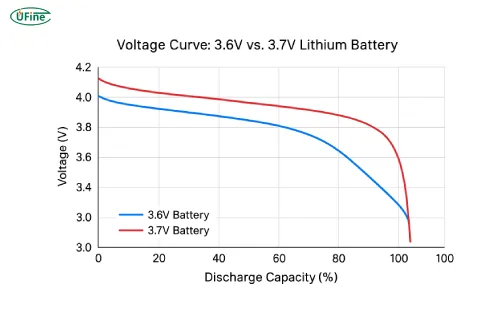
Part 2. 3.6V vs 3.7V vs 3.2V (LiFePO4) — voltage explained
While 3.6V and 3.7V batteries may sound interchangeable, their chemical makeups differ slightly:
| Feature | 3.6V Li-ion | 3.7V Li-ion | 3.2V LiFePO₄ |
|---|---|---|---|
| Nominal Voltage | 3.6V | 3.7V | 3.2V |
| Full Charge Voltage | 4.1V | 4.2V | 3.65V |
| Cycle Life | 500–1000 | 300–500 | 2000+ |
| Energy Density | High | Slightly Higher | Moderate |
| Safety | Good | Good | Excellent |
| Common Use | Industrial, Sensors | Consumer Electronics | EVs, Solar Storage |
➡Key takeaway: 3.6V cells emphasize stability and longevity, while 3.7V types deliver slightly higher power output. LiFePO₄ (3.2V) batteries are favored in electric vehicles and solar systems for their unmatched cycle life and safety.
Part 3. Common size (18650, AA, 14500, coin cells)
3.6V lithium batteries come in several standard sizes, each suited for different applications.
1 3.6V 18650 Lithium Battery
- Dimensions: 18mm × 65mm
- Capacity: 2000–3500mAh
- Applications: Laptops, flashlights, power tools, e-bikes
- Highlights: Rechargeable, high energy density, long cycle life
2 3.6V AA Lithium Battery
- Dimensions: 14.5mm × 50.5mm
- Capacity: 1200–2000mAh
- Applications: Remote controls, toys, wireless sensors
- Highlights: Lightweight, easy replacement, often rechargeable
3 3.6V 14500 Lithium Battery
- Dimensions: 14mm × 50mm (similar to AA)
- Capacity: 600–1000mAh
- Applications: Cameras, flashlights, small electronics
- Highlights: Compact with stable voltage output
4 3.6V Coin Cell (CR123A, CR2, etc.)
- Dimensions: Vary by model (e.g., 16mm × 34mm for CR123A)
- Applications: Cameras, security devices, IoT sensors
- Highlights: Often non-rechargeable; excellent for long-term, low-drain use
Part 4. What’s the life of a 3.6V battery?
The lifespan of a 3.6V lithium battery depends on its chemistry and usage pattern:
| Battery Type | Cycle Life | Shelf Life | Typical Lifespan |
|---|---|---|---|
| Rechargeable Li-ion | 500–1000 cycles | 2–3 years | 3–5 years |
| LiFePO₄ | 2000+ cycles | 5–7 years | 5–10 years |
| Li-SOCl₂ (Primary) | N/A | 10–20 years | 10–20 years |
Usage tips for longer life:
- Store partially charged (40–60%) if unused for long periods.
- Avoid deep discharge and overcharging.
- Keep in a cool, dry environment (15–25°C).
Part 5. Performance data and specifications
| Parameter | Typical Range |
|---|---|
| Nominal Voltage | 3.6V |
| Full Charge Voltage | 4.1V |
| Cut-off Voltage | 2.75V |
| Capacity | 500–3500mAh (depending on size) |
| Operating Temperature | -20°C to 60°C |
| Energy Density | 180–250 Wh/kg |
| Recharge Cycles | 500–1000 |
These specifications vary across brands and chemistries, but they illustrate why 3.6V batteries are the preferred balance of performance, safety, and compact design.
Part 6. Are all 3.6V batteries rechargeable?
Not all.
There are two main categories:
- Rechargeable 3.6V lithium-ion batteries (Li-ion, LiFePO₄) – used in tools, electronics, and power packs.
- Non-rechargeable lithium batteries (Li-SOCl₂, Li-MnO₂) – used in medical, metering, and long-term standby devices.
⚠️ Always check the label before charging. Charging a non-rechargeable lithium cell can cause leakage, overheating, or explosion.
Part 7. What type of battery can replace a 3.6V battery?
- 3.7V Li-ion: In most devices, a 3.7V battery can replace a 3.6V one because their voltage difference is minimal.
- 3.2V LiFePO₄: Possible substitute if the device tolerates slightly lower voltage.
- NiMH (1.2V) packs: Not a suitable replacement unless multiple cells are connected in series.
When replacing, always verify device voltage tolerance, battery size, and BMS compatibility.
Part 8. Charging and safety guidelines
Charging voltage: Typically 4.1V (for 3.6V nominal batteries).
Recommended method: CC–CV (Constant Current–Constant Voltage) charging.
Best practices:
- Use a dedicated lithium charger with overcharge and temperature protection.
- Avoid charging above 45°C or below 0°C.
- Do not mix new and old batteries in series or parallel packs.
- Stop charging immediately if the battery becomes hot or swollen.
Tips: A “smart charger” automatically adjusts voltage and current, extending the battery’s lifespan significantly.
Part 9. Best 3.6V batteries in 2026 (Top brands & models)
Here are some popular and reliable 3.6V lithium batteries on the market in 2026:
| Brand | Model | Type | Capacity | Application |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Saft LS14500 | Li-SOCl₂ | Non-rechargeable | 2600mAh | Smart meters, alarms |
| Panasonic NCR18650B | Li-ion | Rechargeable | 3400mAh | Flashlights, laptops |
| Ufine 3.6V 18650 Pack | Li-ion | Rechargeable | 2600–3000mAh | Custom battery packs |
| Energizer ER18505 | Li-SOCl₂ | Primary | 3500mAh | Industrial sensors |
| EVE ER14250 | Li-SOCl₂ | Primary | 1200mAh | IoT, meters |
When selecting a battery, prioritize reliability, safety certification (UL, IEC62133), and supplier credibility.
Part 10. FAQs
Can I use a 3.7V battery instead of a 3.6V one?
Yes, most devices are compatible. However, check your device specifications first to avoid overvoltage issues.
How long does a 3.6V lithium battery last?
Typically 3–5 years for rechargeable types, or up to 20 years for primary lithium cells.
How do I charge a 3.6V lithium battery?
Use a charger with a 4.1V maximum output and follow CC–CV charging protocols.
What’s the best 3.6V lithium battery for IoT devices?
Li-SOCl₂ batteries (like Saft LS14500) are ideal for long-term, low-drain IoT or metering applications.
Is a 3.6V lithium battery the same as a 18650?
Not exactly — 18650 refers to the size (18×65mm). Many 18650 cells have a nominal voltage of 3.6V, but “3.6V battery” can refer to other sizes too.
Related Tags:
More Articles

Master Your 24V Power Supply: Tips, Tricks & Expert Advice
Get practical insights on selecting, using, and troubleshooting 24V power supplies. Avoid common mistakes and optimize your setup today.
A Simple Guide to 3.7V 2000mAh Li Ion Batteries
Is a 3.7V 2000mAh battery enough for your device? Learn runtime, replacement rules, connector types, and how to avoid common battery mistakes.
How Much Does a Golf Cart Battery Weigh?
Learn how golf cart batteries affect total golf cart weight and size, with average weight ranges and standard dimensions for electric golf carts.
Top 20 Lithium Ion Battery Manufacturers
2026 guide to top 10 lithium-ion battery manufacturers, covering small & large companies, applications, technology strengths, and selection tips.
How to Charge a LiPo Battery Safely and Correctly
Learn how to safely charge your LiPo batteries, avoid overcharging, and choose the best chargers for longer battery life and safety.