- Part 1. Why is the lithium battery hot?
- Part 2. Why does the lithium battery get hot when charging?
- Part 3. What happens if the lithium battery overheats?
- Part 4. Safe temperature range for lithium batteries
- Part 5. What to do when your battery is hot
- Part 6. Checklist: 7 Steps to prevent battery overheating
- Part 7. FAQs
Lithium batteries sometimes get hot — and that’s not always normal. Overheating can reduce battery life, cause swelling, or even start a fire. In this guide, we’ll explain why lithium batteries overheat, what to do when they get hot, and how to keep them safe.
Part 1. Why is the lithium battery hot?
Several factors can cause a lithium battery to overheat. Understanding these can help you identify and mitigate the risks.
1 High Current Discharge — Why it Heats the Battery
When a lithium battery discharges high current, it generates heat. Devices that quickly require a lot of power, like electric vehicles or high-performance gadgets, can cause this issue. The battery’s internal resistance plays a role here; higher resistance leads to more heat generation during high current discharge.
2 Hot Environment — How External Temperature Affects Lithium Batteries
Batteries are sensitive to their surroundings. High ambient temperatures can cause the battery to overheat as the external heat adds to the internal heat generated during use. Prolonged exposure to heat, such as leaving a device in a hot car, can exacerbate this problem.
3 Aging and Internal Resistance — Why Old Batteries Get Hot Faster
Over time, batteries degrade. An aged or damaged battery is more prone to heating because its internal components break down, increasing internal resistance. Regularly using an old battery beyond its optimal performance range can lead to excessive heat generation.
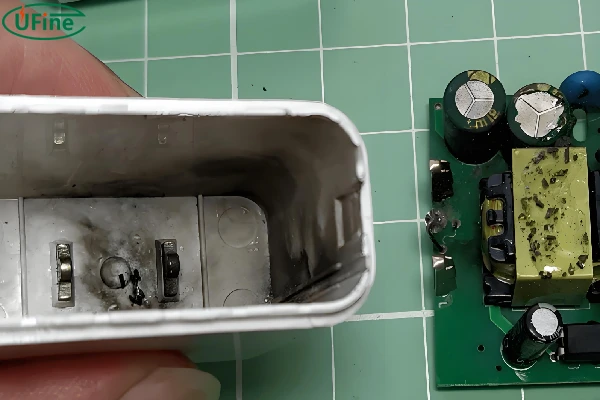
4 Manufacturing Defects — The Hidden Risk
Sometimes, the cause of overheating lies in the battery’s design or manufacturing flaws. Poorly made batteries can have internal short circuits or other defects that lead to overheating during normal use.
5 Intensive Use — Continuous Load and Poor Cooling
Continuous or heavy battery usage without breaks can also cause it to heat up. Devices that continuously draw a lot of power, such as drones or electric bikes, can cause batteries to overheat if used for extended periods.
Part 2. Why does the lithium battery get hot when charging?
Charging a lithium battery generates heat, and there are several reasons why this might happen more intensely during charging.
1 High Charging Current
Fast charging methods, while convenient, push a lot of current into the battery quickly, generating heat. This is especially true for quick and high-wattage chargers designed to reduce charging times.
2 Chemical Reactions
The process of charging a battery involves complex chemical reactions. As the battery stores energy, these reactions release heat. While some heat is normal, excessive heat indicates that the reactions are happening too rapidly or inefficiently.
3 Overcharging
Charging the battery beyond its capacity, though less common with modern smart chargers, can still happen. Overcharging leads to increased internal pressure and heat as the battery attempts to store more energy than it can handle.
4 Poor Ventilation
Charging a battery in an enclosed space or without adequate ventilation can cause heat buildup. Ensuring proper airflow around the device and charger can help dissipate this heat more effectively.
5 Faulty Charging Equipment
Using incompatible or low-quality chargers can cause batteries to heat up. Chargers that don’t match the battery’s specifications can overload it, leading to overheating.
Here is a simple table summary:
| Cause | Description | Prevention |
|---|---|---|
| Fast charging | High current flow increases heat | Use manufacturer-approved charger |
| Overcharging | Causes internal pressure buildup | Unplug after full charge |
| Poor ventilation | Heat accumulates | Charge in open space |
Part 3. What happens if the lithium battery overheats?
Overheating can have several serious consequences for lithium batteries:
- Reduced Lifespan: Consistent overheating can significantly shorten a battery’s life. Heat accelerates the degradation of the internal components, leading to faster wear and tear.
- Capacity Loss: A battery that overheats frequently may lose its ability to hold a charge effectively. This happens because the heat damages the internal cell structure, reducing its overall capacity.
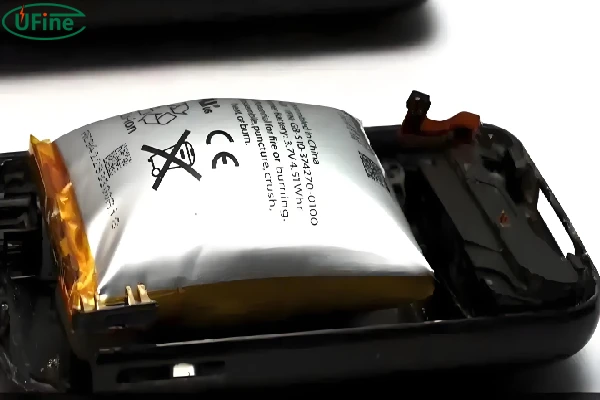
- Swelling: Excessive heat can cause the battery to swell. This is due to the buildup of gases inside the battery as the internal components break down. Swelling is a serious warning sign that the battery is close to failing.
- Fire Hazard: In extreme cases, overheating can lead to thermal runaway, where the battery’s internal temperature increases uncontrollably. This can result in the battery catching fire or even exploding, posing significant safety risks.
- Performance Issues: Overheating can also cause immediate performance issues, such as the device shutting down to protect itself, reduced power output, and erratic behavior.
| Symptom | What It Means | Risk |
|---|---|---|
| Swelling | Gas buildup inside the cells | Imminent battery failure |
| Reduced Capacity | Heat damages cell structure | Shorter battery life |
| Thermal Runaway | Temperature rises uncontrollably | Fire or explosion |
| Performance Drop | Power output becomes unstable | Device shuts down unexpectedly |
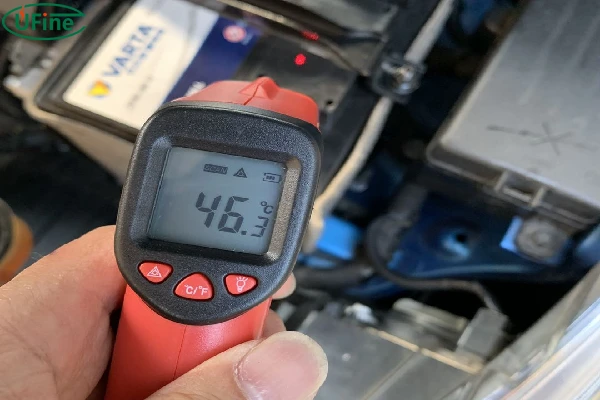
Part 4. Safe temperature range for lithium batteries
Maintaining lithium batteries within a safe temperature range is crucial for their performance and safety:
- Operating Range: Typically, lithium batteries operate safely between 0°C and 45°C (32°F to 113°F). Operating outside this range can cause performance issues and increase the risk of overheating.
- Storage Range: For storage, the safe temperature range is usually -20°C to 25°C (-4°F to 77°F). Storing batteries in temperatures beyond this range can lead to self-discharge and potential damage.
| Condition | Recommended Temperature |
|---|---|
| Operation | 0°C – 45°C (32°F – 113°F) |
| Charging | 5°C – 35°C (41°F – 95°F) |
| Storage | -20°C – 25°C (-4°F – 77°F) |
Operating or storing batteries outside these limits can lead to faster degradation or internal damage.
✅ Summary: The ideal lithium battery operating temperature range is between 0°C and 45°C. Beyond this range, overheating risk increases rapidly.
Part 5. What to do when your battery is hot
To prevent your lithium battery from overheating, follow these practical safety tips:
- Use Quality Chargers: Always use the charger recommended by the battery or device manufacturer. Cheap or counterfeit chargers can damage your battery and increase the risk of overheating.
- Avoid Extreme Temperatures: Keep batteries away from direct sunlight or heat sources. Avoid leaving them in hot environments, such as inside a car on a sunny day.
- Monitor Charging: Do not leave batteries charging unattended for long periods. Remove the battery from the charger once it is fully charged to prevent overcharging.
- Ensure Proper Ventilation: Ensure good airflow around the battery during use and charging. Avoid charging batteries in enclosed or poorly ventilated areas.
- Regular Inspection: Check your batteries for signs of damage, swelling, or unusual heat. Replace any batteries that show signs of wear or damage immediately.
- Avoid Overloading: Do not exceed the recommended usage limits for your battery. High loads can generate excessive heat and strain the battery.
- Safe Storage: Store batteries in a cool, dry place. Use protective cases if necessary to prevent damage and keep them at a stable temperature.
- Battery Management Systems (BMS): Invest in devices with built-in Battery Management Systems. These systems help monitor and regulate the battery’s temperature, charging, and discharging cycles.
- Educate Yourself: Stay informed about the latest battery safety guidelines and technologies. Understanding how to properly care for and use your batteries can prevent overheating.
By following these tips, you can maintain the safety and efficiency of your lithium batteries, ensuring they serve you well for their entire lifespan.
Part 6. Checklist: 7 Steps to prevent battery overheating
Follow these seven practical steps to keep your lithium batteries cool, safe, and efficient:
Use Quality Chargers
Always use chargers recommended by the device or battery manufacturer. Avoid cheap or counterfeit chargers.
Avoid Extreme Temperatures
Keep batteries away from direct sunlight, heaters, or hot environments like cars on sunny days.
Monitor Charging
Do not leave batteries charging unattended for long periods. Unplug once fully charged.
Ensure Proper Ventilation
Charge and use devices in well-ventilated areas. Avoid enclosed spaces that trap heat.
Regular Inspection
Check batteries for swelling, leaks, or unusual heat. Replace any damaged or worn-out batteries immediately.
Avoid Overloading
Do not exceed recommended usage limits. High-power draws can generate excessive heat.
Safe Storage
Store batteries in a cool, dry place. Use protective cases if necessary and keep them at stable temperatures.
⚡ Tip: Keeping a small checklist like this near your workspace or device charging area can help prevent overheating accidents.
Part 7. FAQs
Why do lithium batteries get hot when charging?
Fast charging, overcharging, or poor ventilation can cause excessive heat during charging.
Is it normal for lithium batteries to get warm?
A slight warmth is normal. But if it becomes uncomfortably hot to touch, stop using it.
How can I cool down a hot battery safely?
Turn off the device, move it to a cool area, and let it cool naturally. Do not use water or cooling sprays.
What temperature is unsafe for lithium batteries?
Anything above 45°C (113°F) during operation or 35°C (95°F) during charging is unsafe.
What should I do with an overheated battery?
Stop using it, let it cool, and safely dispose of it if swollen or damaged.
Related Tags:
More Articles
Tracker Lithium Batteries: A Comprehensive Guide
Learn about tracker lithium battery types, applications, advantages, and how to choose the right manufacturer for GPS and IoT tracking devices.
8 Volt Golf Cart Batteries: Tips, Types & Lifespan
Explore 8 volt golf cart batteries, types, lifespan, and maintenance tips. Find out which battery suits your cart best in 2026.
What Is the Charge Voltage of the AGM Battery?
Discover the ideal charge voltage for AGM batteries. Ensure optimal performance and longevity. Learn more about maintaining your battery today!
Bad Battery Cell Symptoms: How to Tell If a Battery Cell Is Dead
Learn how bad battery cells behave, how to test them, and when replacement is the safest option.
18650 Maximum Capacity in 2026: What’s Real and What’s Hype?
Discover the real 18650 battery capacity limits in 2026, top high-capacity cells, and how to avoid fake claims.