- Part 1. What is a sand battery?
- Part 2. How does a sand battery work?
- Part 3. Why use sand for thermal energy storage?
- Part 4. The technology behind sand batteries
- Part 5. Sand battery vs molten salt and water tank storage
- Part 6. Sand battery vs lithium-ion battery
- Part 7. Benefits of sand batteries
- Part 8. Where are sand batteries currently being used?
- Part 9. Challenges and limitations
- Part 10. The future of sand battery technology
- Part 11. FAQs about sand batteries
What is a sand battery? A sand battery is a thermal energy storage system that uses sand to store heat generated from renewable electricity. This heat can be retained for days or weeks and later used to power industrial processes, heating systems, or even generate electricity. Sand batteries provide a cost-effective, safe, and sustainable solution to the biggest challenge in green energy: how to store energy when the sun isn’t shining or the wind isn’t blowing.
This article provides a deep dive into the technology, working principle, benefits, and comparisons of sand batteries with other thermal storage solutions and lithium-ion batteries. Whether you are a green tech enthusiast, an energy professional, or simply curious about the future of energy storage, this guide is for you.
Part 1. What is a sand battery?
A sand battery is a thermal energy storage system that stores excess energy as heat in a large volume of sand. Unlike traditional batteries that store energy chemically, a sand battery stores thermal energy by heating sand to high temperatures using surplus electricity, typically from renewable sources like solar and wind.
The sand, contained in a large insulated tank or silo, holds the heat for long durations. When energy is needed, the stored heat is extracted for district heating and industrial processes or potentially converted to electricity using a steam turbine.
This storage method is environmentally friendly, low-cost, and highly scalable.
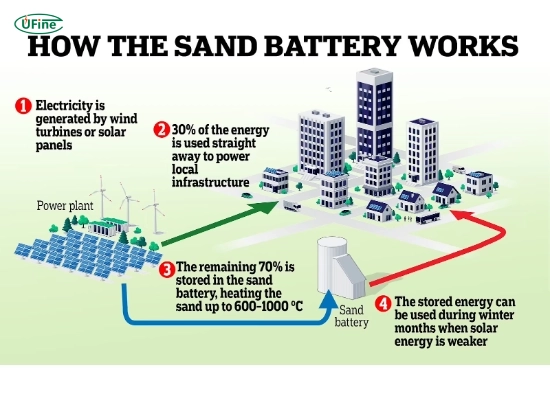
Part 2. How does a sand battery work?
The operation of a sand battery can be broken down into the following key steps:
- Electricity generation: Renewable energy sources such as solar panels or wind turbines generate electricity.
- Heat generation: This electricity powers resistive heaters or air heaters that heat air from 500°C to 1,000°C.
- Heat transfer to sand: The hot air is circulated through a heat exchanger embedded in or around a large insulated tank filled with sand.
- Thermal storage: The sand absorbs and stores the heat. Due to its high heat capacity and insulating properties, sand can retain this heat for days or even weeks.
- Heat extraction: When energy is needed, the hot air is circulated back out of the sand and used to heat water, warm buildings, or drive steam turbines for electricity generation.
The entire system involves no chemical reactions, making it safe and low-maintenance.
Part 3. Why use sand for thermal energy storage?
Sand is an ideal material for thermal energy storage for several reasons:
- Abundant and inexpensive: Sand is widely available and costs very little compared to other energy storage materials.
- High thermal capacity: Sand can store large amounts of heat energy.
- Durability: Sand does not degrade even when exposed to high temperatures.
- Non-toxic and eco-friendly: There are no environmental risks or toxic chemicals involved.
- Long-term storage: Properly insulated sand batteries can retain heat for extended periods.
These properties make sand a strong candidate for grid-scale energy storage, especially in colder regions that require large amounts of heat.
Part 4. The technology behind sand batteries
Sand battery systems are high-temperature thermal energy storage (HT-TES). The main components include:
- Resistive heating unit: Converts electricity into thermal energy.
- Insulated silo: A large steel or concrete tank filled with dry sand, often placed underground.
- Heat exchanger: Transfers thermal energy into and out of the sand.
- Control system: Manages temperature, airflow, and energy input/output.
Most sand battery systems are modular. They can be scaled up or down depending on the energy storage requirements. In some cases, waste heat from industrial processes is also used to charge the sand battery, enhancing overall system efficiency.
Part 5. Sand battery vs molten salt and water tank storage
Let’s compare sand batteries with two other popular thermal energy storage systems: molten salt tanks and water tank storage.
| Feature | Sand Battery | Molten Salt Storage | Water Tank Storage |
|---|---|---|---|
| Temperature range | 500°C to 1,000°C | 250°C to 600°C | Up to 100°C |
| Heat retention duration | Days to weeks | Days | Hours |
| Thermal storage capacity | High | High | Low to Moderate |
| Material cost | Very low | Moderate | Low |
| Safety | Very safe | Risk of corrosion and leaks | Very safe |
| Environmental impact | Very low | Moderate | Very low |
| Best use cases | Industrial heat, district heating | CSP power plants, industrial use | Residential heating, small-scale |
| System complexity | Moderate | High | Low |
Sand batteries offer better storage capacity and higher temperature operation than water tanks, and they are safer and cheaper than molten salt systems. This makes them ideal for long-term, high-temperature storage in regions with variable renewable energy production.
Part 6. Sand battery vs lithium-ion battery
Based on current technologies and data, here is a realistic comparison between sand and lithium-ion batteries.
| Feature | Sand Battery | Lithium-Ion Battery |
|---|---|---|
| Type of energy stored | Thermal | Electrical |
| Storage efficiency | 50-70% | 90-95% |
| Cost per kWh (installed) | $20-50 | $150-350 |
| Lifespan | 20-40 years | 5-15 years |
| Temperature tolerance | Up to 1,000°C | Sensitive to high heat |
| Environmental impact | Very low | Moderate to high |
| Use cases | Heating, industrial processes | EVs, electronics, grid balancing |
| Scalability | Very high | Moderate |
| Safety | Very safe | Risk of fire and thermal runaway |
While lithium-ion batteries are better for electrical applications, sand batteries excel in thermal storage, especially in industrial settings where heat is needed.
Part 7. Benefits of sand batteries
- Low Cost and High Scalability
- Sand is affordable and widely available, making sand battery systems cost-effective to build and scale.
- Long-Duration Storage
- Sand can retain heat for days, ideal for seasonal energy storage in cold climates.
- Environmentally Friendly
- No toxic chemicals, rare earth materials, or harmful emissions are involved in operation.
- Long Lifespan
- Unlike chemical batteries, sand batteries can last for decades with minimal degradation.
- Compatible with Renewables
- Ideal for storing surplus solar and wind energy, helping stabilize renewable-powered grids.
- Low Maintenance
- Few moving parts and no chemical reactions lead to minimal wear and low maintenance needs.
Part 8. Where are sand batteries currently being used?
One of the most well-known sand battery installations is located in Kankaanpää, Finland, developed by Polar Night Energy. This system uses 100 tons of sand stored in a 7-meter silo and can reach temperatures of 500°C. It is integrated with the local district heating system, helping to keep buildings warm during winter using stored solar power.
Other pilot projects are in development in:
- Germany (industrial-scale heating)
- Netherlands (greenhouse heating)
- Australia (remote mining operations)
Governments and energy companies closely watch these early systems to assess scalability and grid integration.
Part 9. Challenges and limitations
Although sand batteries are promising, they face several challenges:
- Energy conversion efficiency: Converting electricity to heat and back to electricity (if needed) results in energy losses.
- Heat loss over time: Some heat is inevitably lost even with insulation.
- Limited to thermal applications: Sand batteries are unsuitable for mobile or portable devices.
- Infrastructure requirements: Large tanks and heating systems require space and capital investment.
However, ongoing research addresses these issues, especially in improving insulation and integrating with Combined Heat and Power (CHP) systems.
Part 10. The future of sand battery technology
Sand batteries are still in their early stages, but their potential is significant. As the world shifts toward 100% renewable energy, thermal storage systems like sand batteries will play a major role in:
- Grid balancing during peak demand
- Decarbonizing heating in residential and industrial sectors
- Improving energy resilience in remote and off-grid areas
- Enhancing energy independence for countries with limited fossil fuel access
Future innovations may combine sand batteries with AI-powered energy management systems and hybrid battery setups for maximum efficiency.
Part 11. FAQs about sand batteries
What is the main purpose of a sand battery?
A sand battery stores excess renewable energy as heat, which can later be used for district heating or industrial processes.
How long can sand hold heat?
With proper insulation, sand can hold heat for up to several weeks, depending on external temperature and silo design.
Can sand batteries generate electricity?
Yes, but indirectly. Stored heat can be used to produce steam, which drives a turbine and generates electricity.
Are sand batteries safe?
Yes. Sand batteries are among the safest energy storage systems available. They are not at risk of explosion or toxic leaks.
Are sand batteries commercially available?
They are currently in the pilot and early commercial stage, with more systems expected to roll out globally in the next few years.
Related Tags:
More Articles
Capacitor vs Battery: What is the Difference?
Capacitor vs battery explained in detail. Learn the difference between capacitor and battery in energy storage, charging speed, lifespan, and real applications.
18650 Battery vs AA: Which Is Better for Your Device?
Compare 18650 vs AA batteries in capacity, voltage, rechargeability, and applications. Learn which battery type fits high-drain or everyday devices.
What is the Difference Between Battery Cell, Battery Control Module, and Battery Pack?
Compare battery cells, modules, and packs. Learn functions, design differences, control modules, and selection tips for EV, ESS, and industrial use.
How to Prevent LiPo Battery Explosion?
Can LiPo batteries explode or catch fire? Learn key causes of LiPo battery fires and proven charging, storage, and handling tips to reduce explosion risk.
Aluminium Ion Battery vs Lithium-Ion: A Detailed Comparison
Compare aluminium ion battery vs lithium-ion battery in energy density, charging speed, safety, cost, and uses. A practical guide for engineers and buyers.