- Quick Answer
- Key Takeaways
- Part 1. What does “18650 capacity” actually mean?
- Part 2. Typical 18650 capacity range
- Part 3. Maximum capacity in 2026: reality check
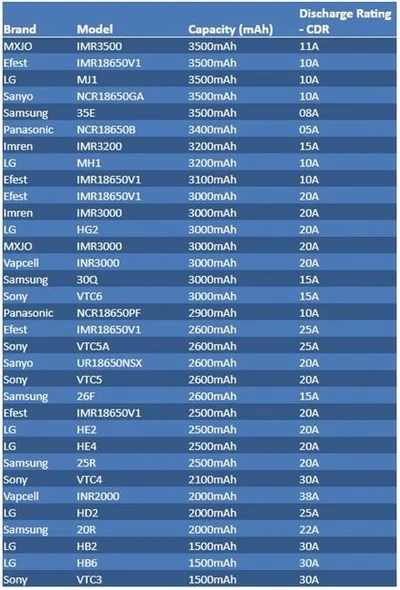
- Part 4. Top 3 highest capacity 18650 batteries
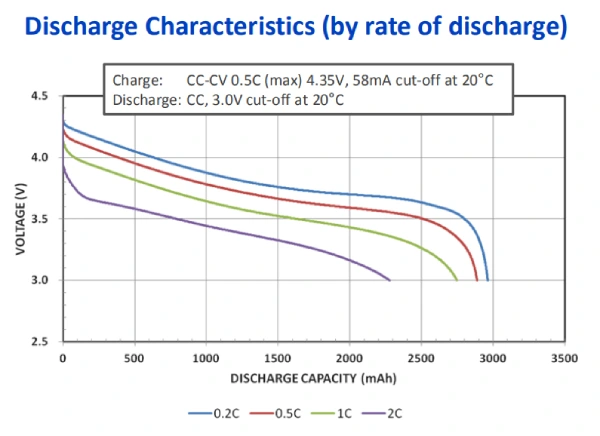
- Part 5. Why higher capacity often means lower discharge power
- Part 6. Commercial vs. marketing capacities: spotting fakes
- Part 7. How to choose the right capacity 18650 for you
- Part 8. Why the 18650 form factor isn’t increasing much more
- Part 9. FAQs
Quick Answer
Right now (as of 2026), the **real maximum capacity you can expect from a commercially available 18650 battery is around 3500–3600 mAh. Anything above that — like 4000 mAh or 5000 mAh — is almost certainly exaggerated or fake.
Key Takeaways
- Maximum real-world 18650 capacity: ~3500–3600 mAh
- Claims above 4000 mAh are often false or unsafe
- Higher capacity generally means lower discharge current
- Capacity isn’t the only spec that matters — discharge rate, safety, and quality matter too
- Always buy from reputable manufacturers
Part 1. What does “18650 capacity” actually mean?
When folks talk about 18650 battery capacity, they mean how much charge a single cell can store, typically measured in milliamp-hours (mAh).
In simple terms:
More mAh = longer runtime (in the same conditions)
but, importantly, it doesn’t always mean “better” if the discharge rate or safety is compromised.
Part 2. Typical 18650 capacity range
The 18650 battery capacity range can vary depending on the specific chemistry, manufacturer, and intended use.
Generally, the 18650 capacity range falls within the range of approximately 1000mAh to 3600mAh. However, it’s important to note that there are exceptions, and some specialty or high capacity 18650 batteries can exceed this range.
18650 batteries come in several lithium-ion chemistries, each with unique properties tailored for different applications. Here’s a breakdown of the most common types:
Comparison Table
| Chemistry | Capacity (mAh) | Voltage | Max Discharge | Lifespan (Cycles) | Safety | Use Case Examples |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LCO | 2000–3600 | 3.7V | 1C–2C | ~500 | Low | Laptops, cameras |
| NMC | 2500–3500 | 3.6V | 5C–10C | ~1000 | Medium | EVs, power tools |
| LFP | 1200–1500 | 3.2V | 10C–30C | ~2000+ | High | Solar storage |
| NCA | 3000–3600 | 3.6V | 1C–3C | ~800 | Medium | Tesla cars |
| LTO | 500–1100 | 2.4V | 10C+ | ~20,000 | Very High | Industrial |
Curious how battery chemistry affects capacity? Check out our detailed guide on 18650 battery capacity across different materials to see which cells deliver the most energy.
Here’s a snapshot of what you’ll find in mainstream, trustworthy cells:
| Battery Model | Nominal Capacity | Nominal Voltage | Typical Use |
|---|---|---|---|
| Panasonic NCR18650G | 3600 mAh | 3.6 V | Long runtime, low-medium drain |
| LG INR18650-M36 | 3600 mAh | 3.6 V | Balanced capacity + decent current |
| Samsung INR18650-36G | 3600 mAh | 3.6 V | All-around performer |
| Panasonic NCR18650B | 3400 mAh | 3.6 V | Older high-capacity cell |
| LG MJ1 | 3500 mAh | 3.63 V | Popular high-capacity option |
| Samsung 30Q | 3000 mAh | 3.6 V | Higher power than big capacity |
Note: These represent commercially mass-produced, verifiable cells — not sketchy listings online.
Part 3. Maximum capacity in 2026: reality check
Despite what some sellers hype, true maximum capacity for a standard 18650 cell hasn’t moved far past the early 3500–3600 mAh range.
Multiple authoritative industry references agree:
- Mass-produced 18650 cells top out around 3600 mAh as of 2025–2026.
- Claims of 4000 mAh+ on marketplaces are often overstated, misleading, or fake.
Why doesn’t it keep getting higher?
Because in the tiny 18 mm × 65 mm format, the physical energy density limits get hit long before you can safely shoehorn more capacity. Manufacturers like Panasonic, Samsung SDI, and LG have squeezed what they can out of the chemistry within those constraints.
Part 4. Top 3 highest capacity 18650 batteries
There are three main manufacturers that produce and manufacture the highest capacity 18650 batteries. These battery manufacturers are Panasonic, LG, and Samsung SDI.
| Brand | Type | Dimension | Nominal Capacity | Nominal Voltage | Maximum Voltage | Discharge Current |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Panasonic | NCR18650G | 18650 | 3600mAh | 3.6V | 4.2V | Maximum continuous 4.87A |
| LG | INR18650-M36 | 18650 | 3600mAh | 3.6V | 4.2V | Maximum continuous 10A |
| Samsung SDI | INR18650-36G | 18650 | 3600mAh | 3.6V | 4.2V | Maximum continuous 10A |
Part 5. Why higher capacity often means lower discharge power
It’s tempting to think “bigger mAh = better,” but that’s only part of the story.
In 18650 cells, higher capacity cells usually:
- Have higher internal resistance
- Deliver lower peak current
- Perform best in low-to-medium drain devices (e.g., flashlights, laptops)
If your device demands quick bursts of power, our comprehensive guide to 18650 high-drain batteries explains which cells can handle heavy loads safely.
Whereas lower capacity cells (like Samsung 30Q) usually provide higher discharge currents, making them better for high-drain tools or vaping gear.
Part 6. Commercial vs. marketing capacities: spotting fakes
It’s unfortunately common to see 18650 listings claiming insane numbers like “5000 mAh” or even “9000 mAh.”
Here’s the truth:
- Industry experts and measurement tests repeatedly find these claims don’t match actual cell performance.
- Some of these are counterfeit, rewrapped, or misrepresented cells.
- Real testing often shows actual capacities far lower than advertised.
- Buying fake cells isn’t just disappointing — it can be unsafe.
So again: if you see a genuine OEM cell above 3600 mAh in real tests, it’s either extremely new/impractical or misrepresented.
Part 7. How to choose the right capacity 18650 for you
Use Case Guide
| Application | Recommended Capacity | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Flashlights & drones | 3000–3600 mAh | Good balance of runtime + power |
| High-drain devices (tools, vaping) | 2500–3000 mAh | Lower capacity but higher discharge |
| Power banks | 3500–3600 mAh | Maximizes energy storage |
| E-bikes or packs | Depends on config | Packs combine cells for both power and capacity |
Tip: Always match voltage, capacity, and discharge rate to your device’s requirements.
Part 8. Why the 18650 form factor isn’t increasing much more
It’s natural to wonder: Why can’t we just make bigger 18650 cells?
Here’s the deal:
- Fixed physical size limits how much active material you can pack into the cell
- More material usually means higher heat and safety concerns
- Engineering always balances capacity vs. power vs. longevity
This is why newer formats like 21700 and others have taken over in many high-energy applications — they offer more volume + safety margin than traditional 18650 cells.
Part 9. FAQs
Can cheap 18650 batteries damage my device?
Yes — especially if internal resistance is high or discharge current is inadequate.
Do high-capacity 18650 cells have shorter lifespan?
Often they age faster under heavy cycling because they’re optimized for energy density, not power.
Why do some batteries show lower measured capacity than rated?
Real testing conditions (load, temp, discharge rate) affect how capacity is measured versus nominal ratings.
Is battery capacity the same as energy?
No — real usable energy also depends on voltage and discharge profile.
Should I pay more for branded 18650 cells?
In most cases, yes — reputable manufacturers consistently deliver more reliable and safer performance.
Related Tags:
More Articles

8 Volt Golf Cart Batteries: Tips, Types & Lifespan
Explore 8 volt golf cart batteries, types, lifespan, and maintenance tips. Find out which battery suits your cart best in 2026.
What Is the Charge Voltage of the AGM Battery?
Discover the ideal charge voltage for AGM batteries. Ensure optimal performance and longevity. Learn more about maintaining your battery today!
Bad Battery Cell Symptoms: How to Tell If a Battery Cell Is Dead
Learn how bad battery cells behave, how to test them, and when replacement is the safest option.
Lithium Battery Sizes Guide: 18650, 21700, LiPo & Coin
Learn about lithium battery sizes, form factors, and uses. Compare dimensions and capacities for cylindrical, pouch, prismatic, and more.
What’s the Difference Between Lithium Metal AA Battery and Lithium Ion Battery?
Learn the difference between lithium metal AA batteries and other types. Find out if AA batteries are lithium and which type performs best for your devices.