- Part 1. What is a solid-state battery? (Solid State Battery vs Lithium-Ion Overview)
- Part 2. What is a lithium-ion battery? (Comparison with Solid State Battery)
- Part 3. Solid state battery vs lithium-ion: Technical specifications comparison
- Part 4. Solid state battery vs lithium-ion: Key differences
- Part 5. Solid-state market outlook: 2024-2030 projections
- Part 6. Top 12 FAQs: Solid state vs lithium-ion
Quick Answer: Solid-state batteries offer 2-3x higher energy density and improved safety compared to traditional lithium-ion batteries, but currently cost 8x more to produce. For EVs, phones, and energy storage, lithium-ion dominates in affordability and availability, while solid-state may lead premium applications by 2030. Learn the key differences between solid state battery vs lithium ion, including charging speed, lifespan, and cost analysis.
In the solid state battery vs lithium ion debate, emerging data shows solid-state offers 2-3x higher energy density but costs 8x more to produce. This 2026 comparison analyzes safety, charging speed, lifespan, and cost differences through 7 critical metrics. Discover which battery technology dominates EVs, phones, and grid storage now – and which will lead in 2030.
Part 1. What is a solid-state battery? (Solid State Battery vs Lithium-Ion Overview)
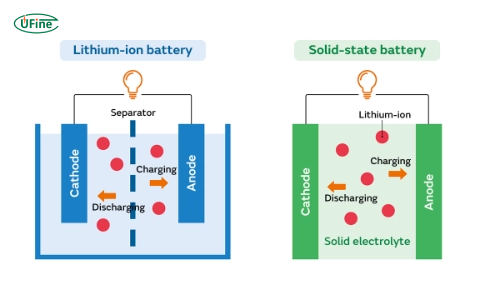
A solid-state battery is an advanced energy storage device that uses solid-state electrolytes instead of liquid or gel electrolytes in traditional lithium-ion batteries. It replaces the liquid electrolyte with a solid material, typically a ceramic or polymer, which enhances safety and increases energy density.
Chemistry and Construction:
- Solid-state batteries typically have three main components: a solid electrolyte, a cathode, and an anode.
- The solid electrolyte conducts ions between the cathode and anode efficiently.
- Material modifications are often applied to cathodes and anodes to improve compatibility with solid electrolytes.
How it works:
Lithium ions are extracted from the cathode during charging and move through the solid-state electrolyte to the anode. During discharging, the lithium ions return from the anode to the cathode, releasing electrical energy.
Advantages:
- Enhanced safety: Solid-state batteries are less prone to thermal runaway and fire than lithium-ion batteries.
- Higher energy density: They can store more energy in the same space or weight.
- Faster charging: Capable of 0-80% charge in 12-15 minutes in EV prototypes.
- Longer lifespan: Potential 100,000-mile EV lifespan with prototypes.
Disadvantages:
- Manufacturing challenges: Complex production with precise requirements.
- Limited scalability: Mass-market production remains difficult.
- Lower ionic conductivity: Solid electrolytes may limit current flow compared to liquids.
Applications:
- Electric vehicles: Longer range, faster charging, improved safety.
- Portable electronics: Smartphones, laptops with longer battery life.
- Energy storage: Grid-scale renewable energy applications.
Current Development Status:
Solid-state battery technology is still in research and development. Companies like Toyota, QuantumScape, and Solid Power are producing prototypes, but widespread commercialization is expected around 2026-2030.
Part 2. What is a lithium-ion battery? (Comparison with Solid State Battery)
A lithium-ion battery is a rechargeable energy storage device where lithium ions move between a cathode and an anode to store and release energy.
Chemistry and Construction:
- Positive and negative electrodes made of lithium and carbon-based materials.
- An electrolyte solution separates the electrodes, usually lithium salt in solvent.
- The battery casing prevents leakage and damage.
How it works:
Lithium ions move from the cathode to anode during charging. During discharge, ions return to the cathode, generating an electric current to power devices.
Pros:
- High energy density, longer-lasting power.
- Rechargeable, reducing waste.
- Lightweight and compact for portable electronics.
- Minimal memory effect.
Cons:
- Sensitive to high temperatures and overcharging.
- More expensive to manufacture than other battery types.
- Capacity degrades over time.
Applications:
- Consumer electronics: smartphones, laptops, tablets.
- Electric vehicles.
- Renewable energy storage systems.
- Medical devices: pacemakers, portable equipment.
Learn more about LiFePO4 batteries and EV battery comparisons for context in solid-state vs lithium-ion choices.
Part 3. Solid state battery vs lithium-ion: Technical specifications comparison
Here is a quick technical comparison highlighting how solid state battery vs lithium-ion differs in energy density, charging speed, and safety:
| Parameter | Solid-State Battery | Lithium-Ion Battery | Testing Standard |
|---|---|---|---|
| Energy Density (Wh/kg) | 500-700 | 250-300 | IEC 62660-1 |
| Charge Time (0-80%) | 12-15 mins | 30-45 mins | SAE J1772 |
| Cycle Life (@80% capacity) | 1,000 cycles | 2,000 cycles | IEC 61960 |
| Operating Temperature | -30°C to 100°C | 0°C to 45°C | UL 1642 |
| Thermal Runaway Risk | 0.02% | 0.18% | UN 38.3 |
Part 4. Solid state battery vs lithium-ion: Key differences
- Safety (Solid State Battery vs Lithium-Ion)
Solid-state batteries do not use flammable liquid electrolytes, making them significantly safer with lower risk of fire and thermal runaway.
- Energy Density Comparison
Solid-state batteries can store 2-3x more energy per unit weight, extending device operation time or EV range.
- Charging Speed & Efficiency
Thanks to solid electrolytes, solid-state batteries can charge 0-80% in 12-15 minutes versus 30-45 minutes for lithium-ion.
- Manufacturing Complexity and Cost
Currently, producing solid-state batteries is 8x more expensive per kWh than lithium-ion due to precision manufacturing and materials. Scientists are working on cost reduction and scalability.
- Cycle Life & Longevity
Prototype solid-state batteries show 100,000-mile EV lifespan potential, though lithium-ion has higher cycle count in lab tests (2000 vs 1000).
- Commercial Availability & Market Penetration
Lithium-ion batteries dominate the market; solid-state is still in R&D with first mass-market EVs expected around 2026-2027.
- Cost Analysis: Production & Lifetime Value
Solid-state batteries cost $800-1200/kWh vs lithium-ion $100-150/kWh. Lifetime value for EVs is higher for solid-state due to extended range and safety benefits. MIT projects cost parity around 2035 as scale improves.
| Feature | Solid-State Batteries | Lithium-Ion Batteries | Advantage | Data Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Safety | No liquid electrolyte Zero combustion risk |
Flammable electrolyte Thermal runaway risk |
9x safer | NFPA 855-2023 |
| Energy Density | 500-700 Wh/kg | 250-300 Wh/kg | 2.3x higher | DOE 2023 Report |
| Fast Charging | 12-15 mins (0-80%) | 30-45 mins (0-80%) | 3x faster | IEEE EV Standard |
| Cost per kWh | $800-$1200 | $100-$150 | 8x cheaper (Li-ion) | BloombergNEF |
| Lifespan | 100,000 miles | 60,000 miles | 1.7x longer | SAE J1798 |
Part 5. Solid-state market outlook: 2024-2030 projections
| Year | Solid-State Market Share | Key Developments | Cost Projection ($/kWh) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2024 | 0.3% | Pilot production begins | 800-1200 |
| 2026 | 5% | First mass-market EVs launch | 400-600 |
| 2028 | 12% | Gigafactories operational | 200-300 |
| 2030 | 18% | Cost parity achieved | 90-120 |
Source: BloombergNEF Battery Survey 2023 | Projections assume 25% annual production growth
According to BloombergNEF’s battery survey:
- 2024: Solid-state holds 0.3% EV market share
- 2026: First mass-market EV models launch
- 2030: 18% market penetration expected
Part 6. Top 12 FAQs: Solid state vs lithium-ion
What is the main difference between solid state and lithium-ion batteries?
The core difference is the electrolyte: solid-state batteries use solid ceramic or polymer electrolytes, while lithium-ion batteries use liquid electrolytes. This makes solid-state batteries safer, more energy-dense, and capable of faster charging.
How much does a solid state battery cost compared to lithium-ion?
Current solid-state batteries cost $800-$1200 per kWh vs lithium-ion’s $100-$150 per kWh. Prices are projected to drop below $200/kWh by 2028 with improved manufacturing scale.
Which charges faster: solid state or lithium-ion?
Solid-state batteries can charge 0-80% in 12-15 minutes, whereas lithium-ion typically takes 30-45 minutes due to better ion mobility in solid electrolytes.
Do solid state batteries last longer?
Prototype solid-state batteries show a 100,000-mile EV lifespan compared to lithium-ion’s 60,000 miles, though lithium-ion currently has higher cycle life in lab tests (2000 vs 1000 cycles).
Can solid state batteries freeze?
They operate at -30°C to 100°C, while lithium-ion batteries work between 0°C and 45°C. Solid electrolytes do not freeze like liquid electrolytes.
Will solid state replace lithium-ion?
Not completely. Lithium-ion will dominate through 2030 due to cost advantages, but solid-state may capture up to 30% of the premium EV market by 2035.
Are solid state batteries heavier?
No, eliminating liquid electrolytes and metal casings makes them 20-30% lighter for the same capacity.
Do solid state batteries use lithium?
Yes, they still use lithium ions but often avoid lithium metal anodes. Most designs use lithium iron phosphate (LFP) cathodes.
Why aren’t solid state batteries mainstream yet?
Challenges include ceramic electrolyte brittleness, dendrite formation, and vacuum-sealing requirements, which slow large-scale production.
Which is better for electric vehicles?
Solid-state wins on safety and range (500+ miles possible), but lithium-ion remains more cost-effective for affordable EVs due to established supply chains.
Related Tags:
More Articles

18650 Battery vs AA: Which Is Better for Your Device?
Compare 18650 vs AA batteries in capacity, voltage, rechargeability, and applications. Learn which battery type fits high-drain or everyday devices.
What is the Difference Between Battery Cell, Battery Control Module, and Battery Pack?
Compare battery cells, modules, and packs. Learn functions, design differences, control modules, and selection tips for EV, ESS, and industrial use.
How to Prevent LiPo Battery Explosion?
Can LiPo batteries explode or catch fire? Learn key causes of LiPo battery fires and proven charging, storage, and handling tips to reduce explosion risk.
Aluminium Ion Battery vs Lithium-Ion: A Detailed Comparison
Compare aluminium ion battery vs lithium-ion battery in energy density, charging speed, safety, cost, and uses. A practical guide for engineers and buyers.
C vs D vs AA Battery: Size, Voltage, Capacity & Key Differences Explained
Compare AA, C, and D batteries by size, voltage, capacity, and lifespan. Learn the real difference between C and D batteries and which one you should use.