- Part 1. What is a 3S LiPo battery?
- Part 2. 3S LiPo voltage chart
- Part 3. What affects the voltage of a 3S LiPo battery?
- Part 4. 3S LiPo fully charged voltage
- Part 5. 3S LiPo storage voltage
- Part 6. 3S LiPo minimum voltage
- Part 7. What is the discharge voltage of a 3S LiPo battery?
- Part 8. How to charge a 3S LiPo battery?
- Part 9. 3S LiPo charging amps
- Part 8. FAQs
When it comes to maintaining and maximizing the performance of your 3S LiPo battery, understanding the proper voltage for charging, storing, and using it is crucial. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll delve into everything you need to know about 3S LiPo voltage. From what a 3S LiPo battery is, to the factors that affect its voltage, and the specific voltages for charging, storage, and usage, we’ve got you covered. Whether you’re new to LiPo batteries or looking to deepen your knowledge, this article will provide the insights you need.
Part 1. What is a 3S LiPo battery?
A 3S LiPo battery is a type of lithium polymer battery that consists of three cells connected in series. Each cell has a nominal voltage of 3.7 volts, so a 3S battery has a nominal voltage of 11.1 volts (3.7V x 3). These batteries are widely used in applications that require high performance, such as remote-controlled cars, drones, and other hobbyist electronics. The “S” in 3S stands for “series,” indicating that the cells are connected in a sequence to produce a higher voltage.
The structure of a 3S LiPo battery is designed to provide a high energy density, meaning it can store a lot of energy relative to its weight. This makes them ideal for applications where weight is a critical factor. Additionally, LiPo batteries offer a flat discharge curve, which means they can deliver consistent power output until they are almost depleted.
The Ultimate Guide to 3S LiPo Batteries
Part 2. 3S LiPo voltage chart
Understanding the voltage levels at different states of charge is essential for the proper use and maintenance of your 3S LiPo battery. Here’s a detailed voltage chart:
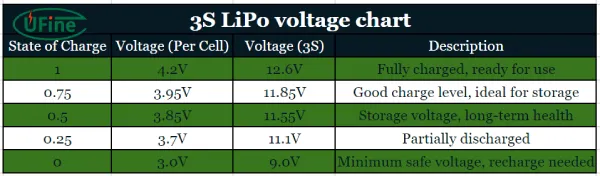
By monitoring these voltage levels, you can ensure that your 3S LiPo battery is always within the safe operating range. This not only helps maintain the battery’s performance but also enhances its lifespan.
Part 3. What affects the voltage of a 3S LiPo battery?
How to Read Lithium Battery Discharge Curve and Charging Curve?
Several factors can influence the voltage of a 3S LiPo battery. Understanding these factors can help you maintain the battery’s health and performance.
State of Charge (SOC): The voltage of a LiPo battery changes depending on its state of charge. A fully charged 3S LiPo battery will have a higher voltage compared to a partially charged or fully discharged one.
Temperature: Temperature plays a significant role in the performance of LiPo batteries. Higher temperatures can increase the voltage, while lower temperatures can decrease it. It’s essential to store and use LiPo batteries within the recommended temperature range to ensure optimal performance.
Load: The voltage can drop when the battery is under a heavy load. This is because the internal resistance of the battery causes a voltage drop when current flows through it. Once the load is removed, the voltage will recover.
Age and Condition: As LiPo batteries age, their capacity and ability to hold voltage can degrade. Regular use, improper charging, and extreme temperatures can accelerate this degradation. It’s important to monitor the condition of your batteries and replace them when necessary.
Part 4. 3S LiPo fully charged voltage
The fully charged voltage of a 3S LiPo battery is 12.6 volts, which means each cell is charged to 4.2 volts. Charging beyond this voltage can lead to overcharging, which can damage the battery and pose a safety risk. Overcharging can cause the cells to swell, generate heat, and in extreme cases, catch fire. Therefore, it’s crucial to use a charger that is specifically designed for LiPo batteries and has built-in safety features to prevent overcharging.
To achieve a full charge, it’s recommended to use a balance charger. A balance charger ensures that each cell in the battery pack is charged to the same voltage, which helps maintain the battery’s health and performance. Charging with a standard charger that does not balance the cells can lead to imbalances, where some cells are overcharged while others are undercharged, reducing the overall lifespan of the battery.
Part 5. 3S LiPo storage voltage
Proper storage of your 3S LiPo battery is key to extending its lifespan. The recommended storage voltage for a 3S LiPo battery is between 11.4 and 11.6 volts, which equates to about 3.8 to 3.85 volts per cell. Storing the battery at this voltage helps prevent degradation and maintains its health when not in use.
LiPo batteries should be stored in a cool, dry place away from direct sunlight and extreme temperatures. Using a LiPo-safe storage bag or container can add an extra layer of safety. It’s also important to check the voltage of the battery periodically during storage and recharge it to the storage voltage if it drops below the recommended level.
Part 6. 3S LiPo minimum voltage
The minimum safe voltage for a 3S LiPo battery is around 9.0 volts, which is 3.0 volts per cell. Discharging the battery below this voltage can cause permanent damage and significantly reduce its capacity and performance. Running a LiPo battery down to zero volts can result in cell imbalance and may render the battery unusable.
To avoid over-discharging, it’s recommended to use a low-voltage alarm or cutoff device. These devices can be set to alert you when the battery voltage drops to a specified level, giving you enough time to recharge the battery before it reaches the minimum safe voltage. It’s also a good practice to recharge the battery as soon as possible after use to prevent deep discharge.
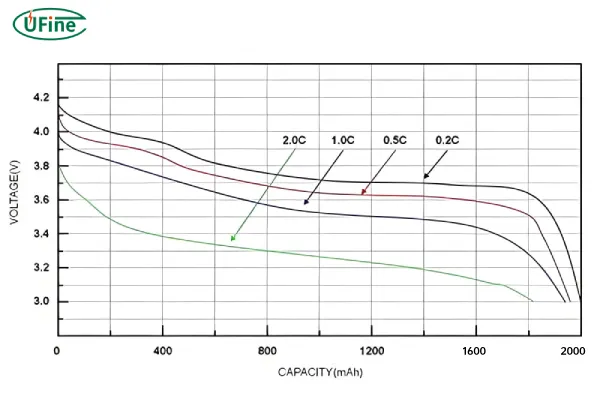
Part 7. What is the discharge voltage of a 3S LiPo battery?
A 3S LiPo battery consists of three cells in series, with a nominal voltage of 11.1V (3.7V × 3). The discharge voltage refers to how much the battery voltage drops as it is used.
Here’s how 3S LiPo voltage typically behaves during discharge:
| State of Charge | Voltage per Cell | Total Voltage (3S) |
|---|---|---|
| Fully Charged | 4.2V | 12.6V |
| Nominal Voltage | 3.7V | 11.1V |
| 50% Capacity | ~3.85V | ~11.55V |
| Minimum Safe Limit | 3.0V | 9.0V |
| Danger Zone | <3.0V | <9.0V |
Discharging below 3.0V per cell (9.0V total for a 3S pack) is not recommended, as it can cause permanent damage and reduce cycle life. Most ESCs (electronic speed controllers) and battery monitors allow users to set a low-voltage cutoff, typically around 3.3–3.5V per cell, to protect the battery.
Part 8. How to charge a 3S LiPo battery?
Charging a 3S LiPo battery requires a LiPo-compatible balance charger that supports 3-cell packs. Improper charging can lead to swelling, capacity loss, or even fire hazards, so it’s crucial to follow the right procedure.
Charging Steps for a 3S LiPo:
- Use a balance charger that can detect and individually monitor all 3 cells.
- Set charger to LiPo mode and select “3S” (or allow auto-detect).
- Set the charge current — typically 1C (e.g., for a 2200mAh battery, set 2.2A).
- Connect both balance and main leads to the charger.
- Start charging and monitor until it reaches 12.6V (4.2V per cell).
Charging Safety Tips:
- Always charge in a fireproof LiPo bag.
- Never leave a charging LiPo battery unattended.
- Allow the battery to cool to room temperature before recharging.
- Do not charge a damaged or swollen battery.
Storage Charging:
If you won’t use your 3S LiPo for a week or more, charge or discharge it to storage voltage — around 3.8V per cell or 11.4V total. This helps maintain long-term health and prevents swelling or degradation.
Part 9. 3S LiPo charging amps
Quickly Learn About Charging Amps
When it comes to charging amps, it’s essential to understand the terminology and guidelines to ensure safe and efficient charging of your 3S LiPo battery. The charging current, measured in amps (A), determines how quickly your battery will charge. Here’s a quick overview:
Charging Rate (C-rate): This term represents the speed at which you charge your battery relative to its capacity. For instance, a 1C rate means charging the battery at a current equal to its capacity. If you have a 2200mAh battery, charging it at 1C would be 2.2 amps.
Higher Charging Rates: Some advanced LiPo batteries can handle higher C-rates, such as 2C, 3C, or even 5C. This means you can charge your 2200mAh battery at 4.4A (2C), 6.6A (3C), or 11A (5C). However, charging at higher rates can generate more heat and reduce the battery’s lifespan if not managed properly.
- Manufacturer Specifications: Always refer to the manufacturer’s guidelines for the maximum recommended charging rate. Exceeding this rate can lead to overheating, swelling, or even fire hazards.
- Smart Chargers: Investing in a smart charger with adjustable amp settings and safety features like temperature monitoring and overcharge protection can help ensure your battery charges safely and efficiently.
- Balance Charging: When charging LiPo batteries, it’s crucial to use a balance charger. This type of charger ensures each cell within the battery pack charges evenly, preventing overcharging of individual cells and maintaining the overall health of the battery.
When it comes to charging a 3S LiPo battery, using the correct charging current is crucial. The recommended charging rate for a LiPo battery is 1C, which means charging at a current equal to the battery’s capacity. For example, if you have a 2200mAh 3S LiPo battery, you should charge it at 2.2 amps. Charging at a higher rate can shorten the battery’s lifespan and increase the risk of overheating.
Some LiPo batteries are designed to handle higher charging rates, such as 2C or even 5C. However, it’s important to check the manufacturer’s specifications before charging at these higher rates. Using a charger with adjustable current settings and a built-in safety timer can help ensure that the battery is charged safely and efficiently.
Part 8. FAQs
What connector does a 3S LiPo battery use?
It depends on the application, but common connectors include XT60, Deans (T-plug), and EC3. Always match your device’s connector type.
How long does a 3S LiPo battery last?
Typically 150–300 charge cycles, depending on usage, charge rate, and how well it’s maintained.
What is the 80% rule for LiPo batteries?
It means discharge only up to 80% of the battery’s capacity (stop at ~3.7V/cell) to extend lifespan and avoid over-draining.
Related Tags:
More Articles
What is the Difference Between Battery Cell, Battery Control Module, and Battery Pack?
Compare battery cells, modules, and packs. Learn functions, design differences, control modules, and selection tips for EV, ESS, and industrial use.
How to Prevent LiPo Battery Explosion?
Can LiPo batteries explode or catch fire? Learn key causes of LiPo battery fires and proven charging, storage, and handling tips to reduce explosion risk.
Aluminium Ion Battery vs Lithium-Ion: A Detailed Comparison
Compare aluminium ion battery vs lithium-ion battery in energy density, charging speed, safety, cost, and uses. A practical guide for engineers and buyers.
C vs D vs AA Battery: Size, Voltage, Capacity & Key Differences Explained
Compare AA, C, and D batteries by size, voltage, capacity, and lifespan. Learn the real difference between C and D batteries and which one you should use.
What is a battery MSDS? Learn what a lithium battery MSDS certificate includes, why it’s required for shipping and compliance, and how to read it correctly.