- Key Takeaways
- Part 1. What is a lithium-ion battery electrolyte?
- Part 2. What does the electrolyte do inside a lithium battery?
- Part 3. Lithium-ion battery electrolyte composition
- Part 4. Types of lithium battery electrolytes
- Part 5. How the electrolyte affects battery performance
- Part 6. Final thoughts
- Part 7. FAQs
Key Takeaways
- The electrolyte is what allows lithium ions to move inside a lithium-ion battery.
- A typical lithium battery electrolyte is made of lithium salts, organic solvents, and small amounts of additives.
- While it doesn’t get much attention, the electrolyte strongly affects battery performance, lifespan, temperature range, and safety.
- Most lithium-ion batteries today still use liquid electrolytes, but gel and solid electrolytes are gaining interest.
- Simply put, if the electrolyte isn’t well designed, even the best electrode materials won’t perform well.
Part 1. What is a lithium-ion battery electrolyte?
When people ask “what is in lithium batteries?”, they’re often surprised to learn how important the electrolyte really is.
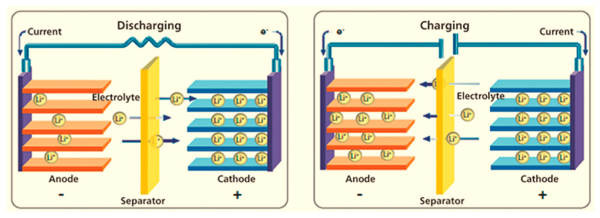
A lithium-ion battery electrolyte is the internal medium that allows lithium ions (Li⁺) to move between the cathode and the anode during charging and discharging. Because everything inside the battery depends on this movement, the electrolyte is often called the “blood” of a lithium-ion battery.
Here’s an easy way to think about it:
electrons power your device by flowing through the external circuit, while lithium ions travel inside the battery through the electrolyte. These two movements happen together. If either one is blocked, the battery stops working.
Even though the electrolyte usually accounts for only about 10–15% of total battery cost, it has a much bigger impact on how the battery actually behaves in real life.
Reading is helpful, but seeing the process makes it much clearer—watch the video below to see how lithium batteries are produced in real factories.
If you’d like a clearer picture of the full charging and discharging process, this guide on how does a battery work explains the basics step by step.
Part 2. What does the electrolyte do inside a lithium battery?
The electrolyte isn’t just a passive liquid. In fact, it performs several critical tasks at the same time.
1 It Enables Lithium-Ion Movement
First and most importantly, the electrolyte provides a pathway for lithium ions to move freely between the electrodes.
When you charge the battery, lithium ions leave the cathode and move through the electrolyte toward the anode. When you use the battery, they travel back again. This back-and-forth motion is what makes energy storage possible.
2 It Helps Create a Stable SEI Layer
At the anode surface, the electrolyte reacts slightly to form a thin protective layer known as the solid electrolyte interphase (SEI).
This layer might sound like a side effect, but it’s actually essential. A stable SEI protects the electrode while still allowing lithium ions to pass through, which directly affects cycle life and long-term stability.
3 It Influences Temperature Behavior and Safety
Because most electrolytes are liquid, they help absorb and release heat generated during battery operation.
At the same time, the chemical stability of the electrolyte determines how the battery behaves at high temperatures, low temperatures, or under stress conditions. In other words, electrolyte design plays a major role in battery safety.
Part 3. Lithium-ion battery electrolyte composition
If you’re specifically searching for lithium ion battery electrolyte composition, this is the part you’re looking for.
A typical lithium-ion battery electrolyte is made up of three main components, each with a very specific role.
1 Lithium Salts
Lithium salts are what supply the electrolyte with mobile lithium ions. To work well, a lithium salt needs to dissolve easily, conduct ions efficiently, and remain stable across the battery’s operating voltage range.
Some common lithium salts include:
- LiPF₆ (Lithium hexafluorophosphate) – the industry standard
- LiBF₄ (Lithium tetrafluoroborate)
- LiTFSI (Lithium bis(trifluoromethanesulfonyl)imide)
Among these, LiPF₆ is by far the most widely used. It offers a good balance of conductivity, cost, and compatibility with electrode materials—even though it has known weaknesses like moisture sensitivity.
2 Organic Solvents
Organic solvents make up most of the liquid electrolyte. Their job is to dissolve the lithium salt and provide a low-resistance environment for lithium ions to move through.
In theory, you’d want a solvent that has:
- High dielectric constant
- Low viscosity
- Wide operating temperature range
- Strong chemical stability
In reality, no single solvent can do all of that well. That’s why lithium-ion batteries almost always use a mixture of solvents.
Commonly used solvents include:
- EC (Ethylene Carbonate) – great for dissolving lithium salts
- DMC (Dimethyl Carbonate) – lowers viscosity
- DEC (Diethyl Carbonate) – improves low-temperature performance
A very typical electrolyte formulation uses EC combined with DMC and/or DEC, allowing the strengths of each solvent to balance out the others.
3 Electrolyte Additives
Electrolyte additives are used in very small amounts, but they can dramatically change how a battery performs.
By carefully choosing additives, manufacturers can improve:
- Cycle life
- Rate performance
- Overcharge protection
- Thermal and fire safety
Some additives are designed to help form a better SEI layer, while others reduce flammability or protect the cathode at high voltages. In many cases, additives are what turn a “working battery” into a reliable, long-lasting battery.
Typical Lithium-Ion Battery Electrolyte Composition
| Component | Common Materials | Primary Function |
|---|---|---|
| Lithium Salt | LiPF₆ | Provides mobile lithium ions |
| Organic Solvent | EC, DMC, DEC | Dissolves salt and transports ions |
| Additives | VC, FEC | Improve SEI stability and safety |
Part 4. Types of lithium battery electrolytes
Not all lithium batteries use the same type of electrolyte. Depending on the application, different approaches make more sense.
Liquid Electrolytes
Liquid electrolytes are still the most common choice today. They offer excellent ionic conductivity and work well with existing battery designs. The downside is that they can be flammable and may leak if the battery is damaged.
Gel Electrolytes
Gel electrolytes use a polymer matrix to hold the liquid electrolyte in place. This reduces leakage risk while maintaining good conductivity. You’ll often see gel electrolytes in lithium polymer batteries.
Solid Electrolytes
Solid electrolytes eliminate liquid solvents entirely. They promise higher safety and potentially higher energy density, but challenges remain in ion conductivity, interface resistance, and large-scale production.
Part 5. How the electrolyte affects battery performance
Even if two batteries use the same cathode and anode materials, different electrolytes can lead to very different results.
The electrolyte directly affects:
- Energy density: how efficiently lithium ions move
- Cycle life: how fast the battery degrades over time
- Operating temperature range: especially low-temperature performance
- Safety: resistance to thermal runaway and fire
That’s why electrolyte design is such a big focus in modern battery research.
Part 6. Final thoughts
Electrodes usually get most of the attention, but without the right electrolyte, a lithium-ion battery simply can’t perform well.
From ion transport to safety and lifespan, the electrolyte quietly controls many of the most important battery characteristics. As battery technology continues to evolve, improvements in electrolyte formulation and solid-state designs will play a huge role in what batteries can do next.
Part 7. FAQs
1. Is lithium battery electrolyte always liquid?
Most commercial lithium-ion batteries use liquid electrolytes, but gel and solid electrolytes also exist.
2. Why is LiPF₆ used so widely?
LiPF₆ offers high ionic conductivity and good compatibility with common electrode materials at a reasonable cost.
3. Can changing the electrolyte improve battery life?
Yes. A more stable electrolyte can reduce side reactions and significantly extend cycle life.
4. Are lithium battery electrolytes dangerous?
Some liquid electrolytes are flammable, which is why additives, separators, and battery management systems are essential for safety.
5. Do different lithium-ion batteries use different electrolyte formulas?
Absolutely. Electrolyte composition varies based on voltage, temperature range, and application.
Related Tags:
More Articles

How to Calculate Battery Run Time?
Learn how to calculate battery run time using mAh, Wh, and watts. Covers battery run time formulas, derating factors, and lithium battery examples.
LiFePO4 Battery Price in 2026: Cost per kWh, per kg & Real Examples
Discover LiFePO4 battery prices in 2026, from cost per kWh to per kg. Learn how to save money while getting long-lasting, safe lithium batteries.
Cylindrical Battery Sizes Explained: 18650, 21700 & More
Confused by cylindrical battery sizes? Learn how 18650, 21700, and other lithium cells differ in size, power, safety, and real-world use.
NMC Battery Explained: Pros, Cons, Lifespan, and Safety
Learn how NMC batteries work, their real specifications, NMC 811 vs LFP differences, lifespan limits, and when NMC is the right choice for you.
Understanding Deep Cycle Battery Size Options
Learn deep cycle battery sizes, BCI group standards, capacity matching, battery types, and key questions for RV, marine, solar, and backup power systems.