- Part 1. Top rated lithium battery types comparison
- Part 2. Nominal voltage of various lithium battery types
- Part 3. Lithium battery charging and discharging parameters
- Part 4. Influence of lithium battery voltage
- Part 5. Lithium battery voltage considerations for device compatibility
- Part 6. FAQs about lithium battery voltage
Lithium ion battery voltage typically ranges from 3.0V (discharged) to 4.2V (fully charged) per cell. This voltage determines device compatibility, energy capacity, and safe charging practices. Understanding lithium battery voltage is critical for selecting the right power source for your devices. It affects not only energy capacity but also charging requirements and overall device safety. This comprehensive guide explains key voltage characteristics of major lithium battery types, including Li-ion, LiPo, LiFePO4, and 18650 batteries, with detailed voltage comparison charts and practical compatibility advice.
Part 1. Top rated lithium battery types comparison
The table below summarizes typical voltages of popular lithium battery types, including nominal, minimum, and maximum voltages for each cell type, along with cycle life, energy density, and top uses.
| Feature | Li-ion | LiPo | LiFePO4 | 18650 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nominal Voltage | 3.6–3.7V | 3.7V | 3.2V | 3.6–3.7V |
| Min Voltage | 3.0V | 3.0V | 2.8V | 3.0V |
| Max Voltage | 4.2–4.3V | 4.2–4.3V | 3.6–3.8V | 4.2V |
| Cycle Life | 300–500 | 200–300 | 2000+ | 500–1000 |
| Energy Density | High | Very High | Medium | High |
| Top Rated Uses | Smartphones, Laptops | Drones, RC Vehicles | Solar Storage, EVs | Flashlights, Power Banks |
Part 2. Nominal voltage of various lithium battery types
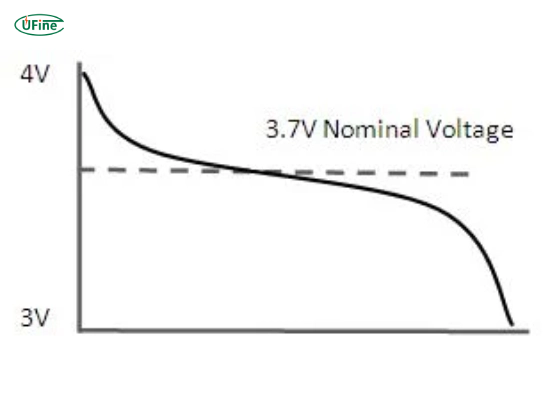
What is lithium battery nominal voltage?
The nominal voltage of a battery refers to the average voltage that a battery cell is expected to operate within during its discharge cycle. It’s an approximate value used to characterize a battery’s voltage for general understanding and compatibility with electronic devices. For instance, a battery labeled as having a nominal voltage of 3.7 volts means that it typically operates around that voltage level during its discharge.
Li-ion Batteries Nominal Voltage
A single Li-ion cell typically has a nominal voltage of 3.6–3.7V, while fully charged voltage reaches 4.2V and discharged voltage drops to about 3.0V. Series connection increases total voltage proportionally. For example, three Li-ion cells in series (3.7V each) produce 11.1V total.
LiPo Batteries Nominal Voltage
LiPo batteries generally have a nominal voltage of 3.7V per cell. When cells are connected in series, the voltage sums up. For instance, two 3.7V LiPo cells in series yield 7.4V total.
LiFePO4 Batteries Nominal Voltage
LiFePO4 batteries maintain a nominal voltage of around 3.2V per cell. Four cells in series produce 12.8V total (3.2V x 4).
18650 Batteries Nominal Voltage
18650 batteries, usually Li-ion chemistry, have a nominal voltage of 3.6–3.7V per cell. Certain LiFePO4 18650 cells have 3.2V per cell. Series connections scale the total voltage. For example, five 3.2V cells yield 16V total.
Part 3. Lithium battery charging and discharging parameters
Different types of lithium batteries have specific charging and discharging voltage ranges. Proper adherence ensures safety, prolongs cycle life, and maintains device compatibility.
Charge Voltage
Maximum charge voltages for popular lithium battery types:
| Battery Type | Max Charge Voltage | Discharge Cutoff Voltage |
|---|---|---|
| Li-ion | 4.2–4.3V | 2.5–3.0V |
| LiPo | 4.2–4.3V | 2.5–3.0V |
| LiFePO4 | 3.6–3.8V | 2.8–3.2V |
For example, a Li-ion battery might have a maximum charge voltage of 4.2V per cell, while a LiFePO4 battery in the same device would have a maximum charge voltage of 3.6V per cell.
How to Measure Lithium Battery Voltage?
Using a digital multimeter is the most accurate method. Set the meter to DC voltage measurement, connect the red probe to the positive terminal and black to negative. Healthy lithium battery voltage readings range from 3.0V (discharged) to 4.2V (fully charged).
Part 4. Influence of lithium battery voltage
Several factors influence lithium battery voltage behavior, including chemistry, temperature, load, and internal resistance.
- Lithium Battery Chemistry: LiFePO4 batteries typically have lower nominal voltage (3.2V) than Li-ion batteries (3.6–3.7V).
- Voltage Range: Fully charged batteries reach up to 4.2V per cell, discharged batteries may drop to around 3.0V per cell.
- Temperature Impact: Cold reduces voltage (0.3–0.5V at freezing), while heat can increase it. Voltage normalizes at room temperature.
- Voltage Sag: Under high loads, batteries may show temporary voltage drops due to current demand.
- Internal Resistance: Aging increases internal resistance, leading to voltage drops under high-demand usage.
- Cell-to-Cell Variability: Manufacturing differences can cause slight voltage differences among cells of the same batch.
Part 5. Lithium battery voltage considerations for device compatibility
Matching a power source’s voltage to device requirements is critical for safe and efficient operation.
Matching Voltage to Device Requirements
Consumer Electronics: Smartphones and laptops require specific voltages. For example, a smartphone charger output must match device voltage, typically 5V, to prevent damage.
Automotive Applications: Electric and hybrid vehicles require battery systems compatible with specified voltages for performance and safety.
Industrial Machinery: CNC machines, robotics, and other industrial equipment need precise voltage levels for stable operation.
Voltage Adaptations for Specialized Applications
Medical Devices: MRI machines and pacemakers require precise voltage delivery.
Aerospace Technology: Aircraft avionics need stabilized voltage to operate reliably under variable conditions.
Telecommunications: Network equipment depends on regulated voltage to ensure reliable data transmission.
Renewable Energy Systems: Solar panels and wind turbines require voltage converters to match grid or storage system requirements.
Looking for specific battery solutions? Check our guide on how to choose lithium batteries or compare 18650 battery specifications.
Part 6. FAQs about lithium battery voltage
What is the standard voltage of lithium battery?
Standard lithium ion battery voltage ranges 3.6–3.7V nominal, with fully charged voltage at 4.2V per cell. LiFePO4 batteries have 3.2V nominal voltage.
Are all lithium batteries 3.7 volts?
No. Li-ion and LiPo batteries are usually 3.7V, LiFePO4 is 3.2V, and some specialty lithium cells may have different voltages.
What voltage is too high for lithium batteries?
Voltages above 4.2V per Li-ion cell are unsafe and may cause damage. Always follow the manufacturer’s specifications for maximum voltage limits.
How do I check lithium battery voltage?
Use a digital multimeter set to DC voltage. Connect red to positive and black to negative. Healthy lithium batteries read between 3.0V (discharged) and 4.2V (fully charged).
What voltage is 50% charge for lithium batteries?
For 3.7V Li-ion batteries, 50% charge is around 3.6–3.7V. For 3.2V LiFePO4 cells, 50% charge is about 3.25V.
Can I mix different voltage lithium batteries?
No. Mixing different voltage lithium batteries can lead to improper charging, reduced performance, and safety hazards. Always use batteries with matching voltages.
How does temperature affect lithium battery voltage?
Cold temperatures reduce voltage temporarily (by 0.3–0.5V at freezing), while high temperatures may increase voltage. Voltages return to normal at room temperature.
Related Tags:
More Articles

Top 10 Lithium Motorcycle Batteries for Optimal Performance
Compare the best lithium motorcycle batteries for 2026, including LiFePO4 vs lead-acid, lifespan, CCA ratings, cold-start performance, and expert buying tips.
Group 35 Battery Size, Type & Best Options for Your Car (2026 Guide)
Discover the complete group 35 battery guide with detailed size charts, battery types, pricing, applications, and recommended brands for your car in 2026.
Understanding D Battery: A Quick Guide
Discover D battery types, voltage, capacity, and lifespan. Learn how to choose the best D battery for flashlights, tools, and emergency gear.
Tracker Lithium Batteries: A Comprehensive Guide
Learn about tracker lithium battery types, applications, advantages, and how to choose the right manufacturer for GPS and IoT tracking devices.
8 Volt Golf Cart Batteries: Tips, Types & Lifespan
Explore 8 volt golf cart batteries, types, lifespan, and maintenance tips. Find out which battery suits your cart best in 2026.