- Part 1. Lithium battery temperature range overview
- Part 2. Lithium-ion battery temperature range vs temperature limits
- Part 3. Why lithium battery temperature ranges matter for performance and safety
- Part 4. Optimal lithium-ion battery operating temperature & maximum limits
- Part 5. How extreme temperatures affect lithium-ion battery performance
- Part 6. Recommended lithium-ion battery storage temperature
- Part 7. Charging and discharging lithium batteries at extreme temperatures
- Part 8. Strategies for managing lithium battery temperature
- Part 9. Summary: lithium battery temperature range explained
- Part 10. FAQs about lithium-ion battery temperature range
Lithium Battery Temperature Range Guide: Lithium-ion batteries perform best only within specific temperature ranges. Operating, charging, or storing lithium batteries outside these limits can lead to capacity loss, accelerated aging, or serious safety risks. Understanding lithium battery temperature range, operating limits, and storage conditions is essential for applications exposed to extreme environments.
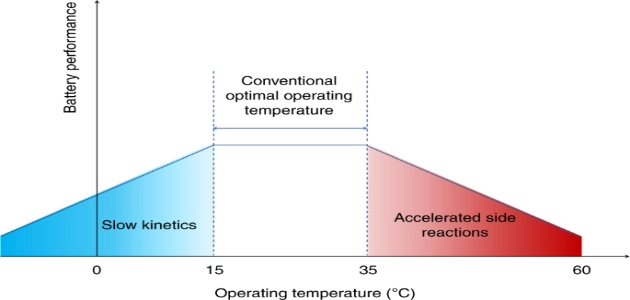
Part 1. Lithium battery temperature range overview
Lithium battery temperature range varies by usage:
- Operating temperature: 15°C–35°C (59°F–95°F) for optimal performance
- Charging temperature: 0°C–45°C (32°F–113°F)
- Storage temperature: -20°C–25°C (-4°F–77°F)
- Maximum safe temperature: 60°C (140°F)
Operating or storing lithium-ion batteries outside these temperature limits increases the risk of performance degradation, shortened lifespan, and thermal safety hazards.
Part 2. Lithium-ion battery temperature range vs temperature limits
Temperature range refers to conditions where lithium-ion batteries operate efficiently and safely. Temperature limits define absolute boundaries beyond which irreversible damage or safety failure may occur.
| Category | Temperature | Meaning |
|---|---|---|
| Optimal operating range | 15°C–35°C | Best efficiency, longest lifespan |
| Charging range | 0°C–45°C | Stable and safe charging conditions |
| Storage range | -20°C–25°C | Preserves capacity during long-term storage |
| Maximum temperature limit | 60°C | Above this, safety risks rise sharply |
Part 3. Why lithium battery temperature ranges matter for performance and safety
Short answer: Temperature directly controls lithium-ion battery efficiency, internal resistance, aging speed, and safety stability.
When lithium batteries operate outside their recommended temperature range, chemical reactions inside the cell become unstable. At low temperatures, reactions slow down and usable capacity drops. At high temperatures, reactions accelerate, causing faster degradation and increased safety risks.
Key impacts of improper temperature control include:
- Reduced runtime and sudden voltage drop
- Accelerated capacity fade and shorter cycle life
- Increased internal resistance and heat generation
- Higher risk of swelling, leakage, or thermal runaway
For applications exposed to outdoor, industrial, or mobile environments, maintaining a stable lithium battery operating temperature is essential for reliability and safety.
Part 4. Optimal lithium-ion battery operating temperature & maximum limits
Optimal lithium-ion battery operating temperature: 15°C to 35°C (59°F to 95°F). Within this range, batteries deliver maximum efficiency, stable output voltage, and the longest service life.
Below 15°C (59°F), electrochemical reactions slow down, increasing internal resistance and reducing available capacity. Above 35°C (95°F), excessive heat accelerates electrolyte breakdown and electrode degradation.
How temperature affects lithium battery performance:
- 15°C–35°C: Optimal performance and longest lifespan
- 0°C–15°C: Reduced capacity and lower power output
- 35°C–60°C: Accelerated aging and increased safety risk
- Above 60°C: High risk of permanent damage or thermal runaway
Lithium battery temperature effects on performance
| Temperature Range | Performance Impact | Engineering Recommendation |
|---|---|---|
| -20°C to 0°C | Severe capacity loss, high internal resistance | Avoid use; apply insulation or battery preheating |
| 15°C to 35°C | Maximum efficiency and stable output | Best range for operation and charging |
| 35°C to 60°C | Accelerated degradation and heating | Use cooling systems and thermal monitoring |
| Above 60°C | Severe damage and safety failure risk | Avoid completely; redesign thermal system |
Real-world scenarios affected by operating temperature
- Electric vehicles: Reduced driving range in winter due to low-temperature capacity loss
- Medical devices: Unexpected shutdowns caused by cold environments
- Drones and outdoor equipment: Overheating and shortened cycle life during summer operation
- Industrial systems: Thermal stress from continuous high-load operation
In these scenarios, selecting lithium batteries designed for extended temperature ranges or integrating thermal management systems is critical to ensure stable operation.
Part 5. How extreme temperatures affect lithium-ion battery performance
Short answer: Low temperatures reduce lithium-ion battery capacity and power output, while high temperatures accelerate aging and increase safety risks.
Performance at low temperatures
At temperatures below 0°C (32°F), lithium-ion batteries may lose up to 30% or more of their usable capacity due to increased internal resistance and slowed electrochemical reactions.
- Slower lithium-ion diffusion reduces power output
- Higher internal resistance causes voltage drop under load
- Devices may shut down unexpectedly in cold environments
Typical cold-temperature scenarios:
- Outdoor energy storage systems in winter
- Medical and monitoring devices used in cold climates
- Drones, GPS trackers, and portable equipment
Performance at high temperatures
At temperatures above 35°C (95°F), chemical reactions inside lithium batteries accelerate, leading to faster degradation and increased thermal stress.
- Accelerated electrolyte decomposition
- Faster capacity fade and shorter cycle life
- Increased risk of swelling, leakage, or thermal runaway
High-temperature risk scenarios:
- Electric vehicles parked in direct sunlight
- Industrial equipment operating under continuous load
- Battery packs installed in poorly ventilated enclosures
Prolonged exposure to temperatures above the lithium battery maximum temperature of 60°C (140°F) can cause irreversible damage and serious safety hazards.
Part 6. Recommended lithium-ion battery storage temperature
Best lithium-ion battery storage temperature: -20°C to 25°C (-4°F to 77°F), stored at 30%–50% state of charge (SOC).
Storing lithium batteries within this temperature range minimizes self-discharge, slows chemical aging, and preserves long-term capacity. Excessive heat during storage accelerates degradation, while extreme cold may cause internal damage.
Storage temperature impact on lithium batteries
| Storage Condition | Impact on Battery | Recommendation |
|---|---|---|
| Below -20°C | Risk of electrolyte damage | Avoid long-term storage |
| -20°C to 25°C | Minimal aging and stable chemistry | Ideal storage range |
| Above 25°C | Accelerated capacity loss | Reduce temperature or storage time |
Storage and transportation in extreme climates
- Cold climates: Use insulated or heated storage to prevent freezing
- Hot climates: Store batteries in shaded, ventilated, or climate-controlled areas
- Transportation: Use insulated packaging to reduce temperature fluctuations
- Vehicles: Avoid leaving lithium batteries inside parked cars
Proper storage temperature management is especially important for lithium batteries used in energy storage systems, medical equipment, and industrial applications.
Part 7. Charging and discharging lithium batteries at extreme temperatures
Short answer: Lithium batteries should only be charged and discharged within specified temperature limits to avoid permanent damage and safety risks.
Safe charging temperature for lithium-ion batteries
Recommended charging temperature: 0°C–45°C (32°F–113°F).
- Charging below 0°C may cause lithium plating on the anode
- Lithium plating leads to irreversible capacity loss and internal short circuits
- High-temperature charging increases the risk of overheating and thermal runaway
Safe discharging temperature for lithium batteries
Recommended discharging temperature: -20°C–60°C (-4°F–140°F).
- Low temperatures increase internal resistance and reduce power output
- High temperatures accelerate chemical degradation
- Extreme conditions shorten battery lifespan significantly
Temperature limits for charging and discharging
| Operation | Safe Temperature Range | Risk if Exceeded |
|---|---|---|
| Charging | 0°C–45°C | Lithium plating, thermal runaway |
| Discharging | -20°C–60°C | Capacity loss, accelerated aging |
Part 8. Strategies for managing lithium battery temperature
Thermal management systems
Thermal management systems keep lithium-ion battery operating temperature within safe limits, improving reliability and extending service life.
- Heat sinks and thermal pads to dissipate excess heat
- Cooling fans or liquid cooling for high-power systems
- Insulation materials for cold-temperature environments
- Temperature sensors integrated with BMS for real-time monitoring
Environmental and design controls
- Maintain ambient temperature between 15°C–35°C when possible
- Avoid installing batteries in sealed or poorly ventilated enclosures
- Design enclosures to allow airflow and heat dissipation
- Use climate-controlled storage for long-term battery warehousing
For applications operating outside standard temperature ranges, custom battery packs with enhanced thermal protection and intelligent BMS are often required.
Part 9. Summary: lithium battery temperature range explained
Maintaining lithium batteries within recommended temperature ranges is essential for safety, performance, and lifespan.
- Optimal operating temperature: 15°C–35°C (59°F–95°F)
- Safe charging temperature: 0°C–45°C (32°F–113°F)
- Recommended storage temperature: -20°C–25°C (-4°F–77°F)
- Maximum temperature limit: 60°C (140°F)
Proper temperature management reduces degradation, prevents safety incidents, and ensures reliable battery performance across diverse applications.
Part 10. FAQs about lithium-ion battery temperature range
What is the safe operating temperature for lithium-ion batteries?
Lithium-ion batteries operate best between 15°C and 35°C (59°F–95°F), where efficiency, output stability, and lifespan are maximized.
What is the maximum temperature lithium batteries can handle?
The maximum safe temperature for lithium batteries is around 60°C (140°F). Exceeding this limit can cause permanent damage and serious safety risks.
Can lithium batteries work in freezing temperatures?
Lithium batteries can discharge at low temperatures but suffer significant capacity loss below 0°C. Charging below 0°C is not recommended without preheating.
What is the best storage temperature for lithium-ion batteries?
The ideal storage temperature is -20°C to 25°C (-4°F–77°F), with batteries stored at 30%–50% state of charge to minimize aging.
Why does temperature affect lithium battery performance?
Temperature influences chemical reaction rates, internal resistance, and electrolyte stability. Extreme heat or cold disrupts these processes and degrades performance.
How can lithium batteries be used safely in extreme environments?
Using batteries designed for wide temperature ranges, combined with thermal management systems and intelligent BMS, ensures safe operation in extreme conditions.
Ufine Battery provides lithium battery solutions with extended temperature ranges and advanced thermal management systems to meet your specific environmental requirements — whether for extreme cold, high heat, or fluctuating conditions.
Find A Solution NowRelated Tags:
More Articles
What is the Difference Between Battery Cell, Battery Control Module, and Battery Pack?
Compare battery cells, modules, and packs. Learn functions, design differences, control modules, and selection tips for EV, ESS, and industrial use.
How to Prevent LiPo Battery Explosion?
Can LiPo batteries explode or catch fire? Learn key causes of LiPo battery fires and proven charging, storage, and handling tips to reduce explosion risk.
Aluminium Ion Battery vs Lithium-Ion: A Detailed Comparison
Compare aluminium ion battery vs lithium-ion battery in energy density, charging speed, safety, cost, and uses. A practical guide for engineers and buyers.
C vs D vs AA Battery: Size, Voltage, Capacity & Key Differences Explained
Compare AA, C, and D batteries by size, voltage, capacity, and lifespan. Learn the real difference between C and D batteries and which one you should use.
What is a battery MSDS? Learn what a lithium battery MSDS certificate includes, why it’s required for shipping and compliance, and how to read it correctly.