- Part 1. What are battery cycles?
- Part 2. Why is it important to prevent battery cycles?
- Part 3. What is battery cycle count?
- Part 4. 9 Tips to reduce battery cycles and extend lifespan
- Part 5. How does charging to 80% instead of 100% affect battery lifespan?
- Part 6. Understanding depth of discharge (DoD)
- Part 7. The role of battery management systems (BMS)
- Part 8. Charging habits that help extend battery life
- Part 9. Storing batteries properly
- Part 10. FAQs about reducing battery cycles and extending battery life
How do I prevent battery cycles? This question is crucial for anyone who relies on rechargeable batteries in their devices. Batteries are essential for powering smartphones, laptops, tablets, and electric vehicles. However, we contribute to its cycle count every time we charge and discharge a battery. Understanding how to minimize these cycles can significantly extend the life of your battery. This article will explore practical strategies to prevent battery cycles and ensure your devices remain powered for as long as possible.
Quick Answer
A battery cycle means using 100% of a battery’s charge (for example, two 50% discharges = 1 cycle). To prevent battery cycles and extend lifespan, follow these 9 tips:
- Keep charge between 20%–80%
- Avoid extreme hot or cold temperatures
- Use smart charging settings (limit to 80%)
- Update device software regularly
- Limit resource-heavy apps
- Avoid overnight charging
- Use quality/original chargers
- Turn off or reduce features while charging
- Store batteries at ~50% charge in a cool, dry place
Part 1. What are battery cycles?
Battery cycles refer to the complete process of charging and discharging a battery. Each time you use your device and charge it back up, you contribute to its cycle count. For example, using 50% of your battery’s capacity and then wholly recharging it counts as half a cycle. Understanding this concept is crucial because most batteries have limited cycles before their capacity diminishes significantly.
Key Points About Battery Cycles
- Cycle Count: The total number of complete charge-discharge cycles a battery can undergo before its capacity drops to around 80% of its original state.
- Impact on Lifespan: The more cycles a battery goes through, the shorter its lifespan. Manufacturers design most lithium-ion batteries for approximately 300 to 500 cycles.
- Partial Discharges: Using only part of your battery’s capacity before recharging can help extend its lifespan.
In simple terms, a battery cycle means one full discharge of 100% capacity and recharge back to full, whether done at once or in parts.
Part 2. Why is it important to prevent battery cycles?
Preventing unnecessary battery cycles is vital for several reasons:
- Cost Efficiency: Replacing batteries can be expensive. By extending the life of your current battery, you save money.
- Environmental Impact: Fewer batteries mean less electronic waste, contributing to ecological sustainability.
- Device Performance: A well-maintained battery ensures your device runs efficiently without unexpected shutdowns or performance issues.
Part 3. What is battery cycle count?
Battery cycle count refers to the total number of complete charge and discharge cycles a battery has undergone. For example, if you use 30% of your battery today, recharge, then use 70% tomorrow and recharge again, that equals one full cycle. Most lithium-ion batteries last about 300–500 cycles before their capacity drops to 80% of the original.
This metric is important because the higher the cycle count, the closer the battery is to the end of its useful lifespan.
Part 4. 9 Tips to reduce battery cycles and extend lifespan
To minimize cycle count and maximize battery life, follow these best practices:
| Practice | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Charge 20%–80% | Reduces stress & cycles |
| Avoid extreme temps | Prevents thermal degradation |
| Use smart charging | Limits max voltage |
| Software updates | Optimizes power management |
| Quality chargers | Stable current & voltage |
Here are 9 proven tips to reduce battery cycle count and extend battery lifespan:
- Maintain charge between 20%–80% – Avoid full discharges and overcharging, which put stress on the battery.
- Use smart charging settings (limit to 80%) – Many devices let you cap charging at 80% to reduce cycle wear.
- Avoid extreme temperatures – Keep devices between 20°C–25°C (68°F–77°F) to prevent thermal degradation.
- Keep software updated – Updates often improve power management and optimize energy use.
- Limit power-hungry apps – High-drain apps accelerate battery depletion and increase cycle count.
- Avoid overnight charging – Continuous charging can stress the battery; use timers or smart plugs instead.
- Use quality chargers – Original or certified chargers provide stable voltage and current for safe charging.
- Turn off or reduce background features while charging – Disable Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, or background apps to reduce heat and load.
- Store at ~50% charge in a cool, dry place – Ideal for long-term storage to maintain battery health.
Part 5. How does charging to 80% instead of 100% affect battery lifespan?
Charging your device to 80% instead of 100% can significantly impact its lifespan. Charging batteries to total capacity puts more stress on them due to higher voltage levels. This stress can lead to faster chemical reactions inside the battery, ultimately reducing its lifespan.
Benefits of Charging to 80%
- Reduced Stress: Lowering the charge level reduces stress on the battery’s internal components.
- Fewer Cycles: By avoiding total charges, you decrease the number of complete charge cycles over time.
- Longer Lifespan: Many studies suggest that consistently charging to around 80% can double or even triple the lifespan of lithium-ion batteries compared to those charged fully every time.
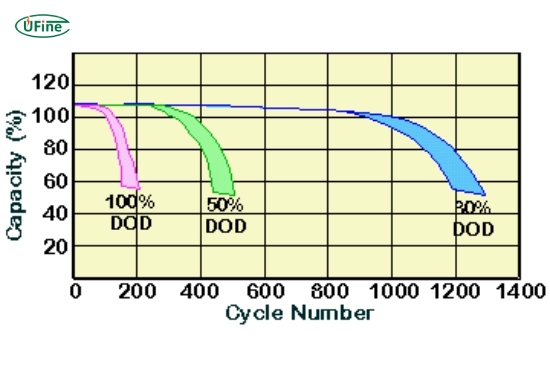
Part 6. Understanding depth of discharge (DoD)
The term Depth of Discharge (DoD) refers to how much energy a battery uses before it is recharged again. A lower DoD means fewer cycles and a longer lifespan for the battery.
Key Insights on DoD
- Shallow Discharges: Performing shallow discharges (e.g., using only 20-30% of the total capacity) can significantly increase cycle life.
- Cycle Life vs. Usable Capacity: While shallow discharges extend cycle life, they may not utilize the battery’s full capacity in terms of energy output.
Part 7. The role of battery management systems (BMS)
A Battery Management System (BMS) plays a crucial role in monitoring and managing battery performance:
- Charge Control: BMS regulates the charging process to prevent overcharging or excessive discharging of batteries.
- Temperature Management: It helps maintain optimal operating temperatures, protecting against overheating.
- State Monitoring: BMS tracks batteries’ health and performance metrics, providing valuable data for maintenance decisions.
Part 8. Charging habits that help extend battery life
Adopting better charging habits can also help minimize cycles:
1. Avoid Overnight Charging
While many people charge their devices overnight, this practice can lead to overcharging unless appropriately managed. Instead, try charging when you can monitor it closely or use timers.
2. Use Quality Chargers
Using original or high-quality chargers ensures your device receives stable power without fluctuations that could harm the battery. Cheap chargers may not provide consistent voltage levels and could damage your battery over time.
3. Turn Off While Charging
Turn off your device while charging it; this reduces power consumption and heat generation during the charging process. Turning off unnecessary features like Bluetooth or Wi-Fi can also help conserve energy.
Part 9. Storing batteries properly
If you need to store devices for an extended period:
- Charge Level: Store batteries at around 40-50% charge.
- Environment: Keep them in a cool, dry place away from direct sunlight or heat sources.
Proper storage helps maintain battery health over long periods without use.
Part 10. FAQs about reducing battery cycles and extending battery life
What is a battery cycle?
A battery cycle means one full discharge and recharge (from 0% to 100%). Each complete cycle gradually wears down the battery’s capacity.
How many charge cycles does a lithium-ion battery last?
Most lithium-ion batteries deliver about 300–500 full charge cycles before their capacity falls noticeably, though partial charging habits can extend this lifespan.
Is overnight charging bad for phones and laptops?
Keeping devices at 100% charge for long periods adds stress to the battery. Using smart charging features, timers, or unplugging after full charge helps reduce wear.
How does temperature affect battery life?
Heat is the biggest battery killer. Operating batteries in moderate temperatures (20°C–25°C / 68°F–77°F) helps slow degradation and extend overall lifespan.
How to reduce battery cycle count on iPhone?
Enable Optimized Battery Charging to limit charging to 80%, avoid draining to 0%, and keep the battery between 20%–80%. Turning off background refresh also reduces power drain and cycle count.
Related Tags:
More Articles

What are Watts and Watt Hours in Battery?
Understand watt vs watt-hour in batteries, how to calculate battery watt hours, and what Wh means for car batteries, devices, and energy storage.
A Complete Guide to the Best Batteries for Flashlights
Compare the best batteries for flashlights, including AA, AAA, 18650, 21700, CR123A. See which battery offers the best brightness, runtime, and reliability.
How Long Do Rechargeable AA Batteries Last?
How long do rechargeable AA batteries last? Compare NiMH and lithium AA lifespan, recharge cycles, key factors, and performance vs alkaline batteries.
How Much Current Can a 9V Battery Really Supply?
Discover how many amps a 9V battery can supply, its actual current output, discharge rate, and capacity for alkaline, lithium, and rechargeable 9V batteries.
12V STD vs 12V AGM: Meaning, Differences, and Which Is Better
Understand what STD and AGM batteries mean, their key differences, and which 12V battery fits your needs best in 2026.