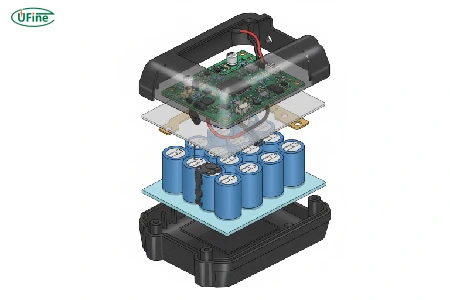
Whether you’re designing for industrial production lines or rugged field service, the wrong battery choice leads to inconsistent torque, overheating, shortened runtime, and safety risks under load. We don’t just manufacture battery cells — we understand cordless tool power systems and what applications truly demand. Our solutions solve the core electrical, mechanical, and reliability challenges behind cordless screwdriver battery design.
Part 1. Industry challenges — what really matters
Professional cordless screwdriver applications reveal three recurrent pain points:
1 Power Delivery Under Load
High current draw during continuous fastening demands batteries that hold voltage under load without sagging, otherwise motor performance and torque consistency suffer — a top failure mode reported in tool reliability analyses.
2 Runtime & Duty Cycle Predictability
In industrial assembly, runtime isn’t casual — it’s a KPI. A battery that lasts 15 minutes less per shift directly increases downtime and labor cost.
3 Thermal & Safety Constraints
Tools used in hot environments, repeated rapid discharge, and vibration can trigger thermal runaway if the battery lacks robust protection systems.
4 Compatibility & Footprint Constraints
Tool manufacturers face fragmentation in voltage (12V / 18V / 20V / 24V), form factor, and communication protocols — a practical compatibility challenge that causes up to 65 % of aftermarket battery fitment issues observed in field tests.
5 Regulatory Barrier to Global Distribution
Lithium batteries for tools must comply with international safety and transport standards, or they cannot be legally shipped or sold worldwide — including UN 38.3 for transport and IEC 62133 for portable battery safety.
These are not abstract quality metrics — they are decision criteria used by tool designers, OEM engineers, and compliance officers.
Part 2. Screwdriver battery solution overview
We approach screwdriver battery challenges as engineering problems, not product listings.
| Screwdriver Type | Recommended Battery | Key Advantages | Application Scenario |
|---|---|---|---|
| Precision / Light Duty | 10–12 V Li-ion | Compact, lightweight, sufficient torque | Home DIY, electronics assembly |
| Standard / Professional | 18 V Li-ion | Balanced runtime and power | Furniture assembly, general construction |
| Heavy Duty / Industrial | 20–24 V Li-ion / LiFePO₄ | High torque, long cycle life, temperature resistant | Industrial assembly lines, power tool rental |
Solution Architecture Layers:
Cell Chemistry & Form Factor Selection- Li‑ion cylindrical for balance of energy density and discharge performance.
- Prismatic for higher capacity in limited space.
- Real‑time monitoring of cell voltage, temperature, and current to prevent over‑discharge, over‑charge, and thermal stress.
- Tool use environments demand robust packs with structural reinforcement.
- Heat spreaders, venting, and thermal cut‑offs for sustained high‑power use.
- Physical keying and pinout standards to ensure correct voltage, communication, and safety handshake between battery and tool controller.
This systematic approach has been validated across design partnerships with multiple OEMs in industrial, construction, and consumer tool segments.
Use Case: See how our batteries extend tool lifespan and reliability in real-world applications — explore this detailed case study.
Part 3. Key technical advantages
1 Torque Sag Under High Load
Challenge: Battery voltage droops under high current, reducing motor torque.
Our Technology: Low internal resistance cell selection + BMS fast response current path.
Outcome: Maintains ≥95 % rated voltage under 10C discharge rates for consistent torque.
2 Short Runtime Under Continuity Use
Challenge: Frequent shallow cycles shorten effective runtime.
Our Technology: Adaptive capacity management that schedules cell balancing only under low‑load conditions.
Outcome: Extends usable runtime without degrading cycle life.
3 Overheat & Thermal Runaway Risk
Challenge: Heat from fast discharge & environmental exposure raises safety risk.
Our Technology: Multi‑level thermal cut‑off + PCB‑level temperature feedback loop.
Outcome: Meets global safety benchmarks including IEC 62133 for portable lithium batteries.
4 Global Compliance Complexity
Challenge: Different markets enforce different safety standards.
Our Technology: Integrated test planning for UN 38.3 (transport), IEC 62133, plus optional regional marks (CE/UL/CCC).
Outcome: One battery design can carry multiple approvals, simplifying international distribution.
For more on portable battery safety standards, see this resource on IEC 62133 safety testing. IEC 62133 Safety Testing Explained
Watch how Ufine Battery packs undergo rigorous safety testing to ensure reliable operation under all conditions.
Part 4. Application‑driven battery recommendations
| Product Series | Voltage | Capacity | Form Factor | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 18650 Li-ion Pack | 12–24 V | 2–6 Ah | Cylindrical | Standard replacement or OEM integration |
| LiFePO₄ Pack | 20 V | 4–6 Ah | Prismatic | Industrial, high-temperature tolerant |
| Custom LiPo | 10–20 V | Flexible | Flat / Compact | Precision or portable screwdrivers |
Here we match common use applications for screwdrivers with tailored battery solutions — not just model lists.
1 Precision & Electronics Assembly
- Typical needs: compact form factor, controlled discharge, low heat.
- Battery Approach: 12–14 V cylindrical Li‑ion, 2.0–4.0 Ah with BMS optimized for light duty cycles
- Benefit: consistent speed control, long calendar life.
2 Professional Construction & Furniture Assembly
- Typical needs: moderate torque, several hours continuous use.
- Battery Approach: 18–20 V high‑rate Li‑ion, 4.0–6.0 Ah with thermal protection
- Benefit: sustained torque with thermal margin for heavy shifts.
3 Heavy‑Duty Industrial Fastening
- Typical needs: peak current draw, rugged environments, duty cycles >8 h.
- Battery Approach: 20–24 V high capacity packs with reinforced housings and deep BMS insight
- Benefit: predictable performance under heavy loads.
Each solution set comes with design documentation, integration guidelines, and test profiles so engineers can assess performance quickly.
Part 5. Certifications & regulatory compliance
Battery packs for cordless tools must satisfy a range of legal and safety requirements before commercial use:
1 Mandatory Safety & Transport Standards
- UN 38.3 — Required for any internationally shipped lithium battery. Tests include altitude simulation, thermal shock, vibration, and impact.
- IEC 62133‑2 — International safety benchmark for portable lithium batteries covering abuse tests (short circuit, overcharge, thermal stability).
2 Regional Certification Requirements
- CE (Europe) — Product safety, EMC, and battery directive compliance.
- UL (North America) — Widely followed safety standards like UL 1642/UL 2054 for battery systems.
- CCC (China) — Mandatory certification under battery safety laws.
Note: Compliance isn’t optional — many countries legally forbid sale or transport of uncertified batteries. Proper certification also simplifies supply chain and aftermarket support.
Part 6. R&D support for screwdriver battery projects
We’re not here just to sell cells — we partner through the entire product lifecycle:
✅ Early‑Stage Feasibility
- Power budget analysis
- Voltage & load profiling
✅ Prototype & Sample Iterations
- Quick turn sample builds
- BMS tuning cycles
- Thermal & vibration test suites
✅ Certification Help
- Documentation packages for UN 38.3, IEC 62133, CE/UL/CCC submissions
✅ Low to High Volume Bridge Production
- Small batch pilot runs
- Design for manufacturability (DFM) guidance
Whether you need a specialized form factor, high-current output, or unique battery curvature, Ufine Battery can deliver solutions for every stage of development.
Contact Our Experts NowHigh Energy Density
It stores large amounts of energy in a smaller and lighter package
Longer Cycle Life
Withstands extensive charge and discharge cycles
Low Self-Discharge
Maintains power longer when not in use
Safety
Minimizes the risk of accidents and ensures safe operation
More Information About Screwdriver Battery
-
What voltage should I choose for my cordless screwdriver?
-
Are international safety standards required if I only sell locally?
-
Why doesn’t every battery fit every screwdriver?
-
How do I predict real runtime from battery specs?
Latest Blogs
About Lithium Battery Industry News

Lithium-Ion vs Lead-Acid AMR & AGV Batteries Compared
Discover the pros and cons of lithium-ion and lead-acid AMR & AGV batteries. Learn about cost, lifespan, safety, and which is right for your fleet.
2026/01/14 Ufine

Robot Vacuum Battery Replacement: Easy Step-by-Step Guide
Learn how to replace a robot vacuum battery safely and easily. Step-by-step instructions, battery types, costs, and common mistakes to avoid.
2026/01/14 Ufine

Discover how to choose the right battery for your robot. Compare Li-ion, LiFePO₄, NiMH, and more for performance, safety, and cost.
2026/01/14 Ufine

Inside Humanoid Robot Battery Pack Design
A deep dive into humanoid robot battery pack design, covering battery life, voltage, capacity, safety, and real-world engineering trade-offs.
2026/01/14 Ufine

Humanoid Robot Battery Life: How Long Do They Really Last?
Most humanoid robots run 1.5–4 hours per charge. Learn real-world battery life, battery types, capacity limits, and future improvements.
2026/01/13 Ufine

Battery Load Test: A Comprehensive Guide
Step-by-step battery load test guide for car, solar & industrial use. Learn how to load test a battery, interpret voltage charts, and avoid common mistakes.
2025/12/18 Ufine