- Part 1. What is battery certification?
- Part 2. Top 10 battery certifications required for global markets (2026 Guide)
- Part 3. Costs associated with battery certification
- Part 4. Timeframes for battery certification
- Part 5. Understanding battery standards
- Part 6. The certification process
- Part 7. Challenges in battery certification
- Part 8. 5 Critical battery certification mistakes to avoid
- Part 9. FAQs about battery certification
Battery certification plays a crucial role in ensuring the safety and performance of battery products across various industries. In this guide, we’ll break down the essential certifications you need to know, including the types of certifications, the costs involved, expected timeframes, and the standards that govern them. Whether you’re a manufacturer or a consumer, this guide will help you easily navigate the certification process.
Key Takeaways: Battery Certification Essentials
- ✅ 6 Must-Have Certifications: UL, IEC, CE, UN38.3, KC, PSE
- 💵 Average Cost Range: $2,000 – $20,000 per certification
- ⏳ Typical Timeline: 4-12 weeks depending on battery type
- 🌍 Critical for: US, EU, Japan, South Korea markets
- ⚠️ Key Challenge: 30% projects fail initial UN38.3 testing
Part 1. What is battery certification?
Battery certification involves testing and verifying batteries to meet specific safety, performance, and environmental standards. These certifications ensure that batteries are safe and comply with regulatory requirements. They help manufacturers demonstrate that their products are reliable and secure for consumers, enhancing marketability and consumer trust.
Why is Battery Certification Important?
- Safety Assurance: Certification helps to ensure that batteries do not pose safety risks, such as overheating or exploding.
- Regulatory Compliance: Many regions have legal requirements for battery certification, particularly lithium-ion batteries.
- Market Access: Certain certifications are required to sell batteries in specific markets, especially in the European Union and North America.
- Consumer Confidence: Certifications assure consumers of the product’s quality and safety.
Part 2. Top 10 battery certifications required for global markets (2026 Guide)
Batteries may require several key certifications depending on their chemistry, intended use, and market. Here are some of the most common types:
UL Certification
Underwriters Laboratories (UL) is a global safety certification organization that tests and certifies batteries for safety and performance. Essential UL standards include:
- UL 1642: Tests lithium cells for safety.
- UL 2054: Covers battery packs for portable applications.
- UL 1973: Pertains to stationary batteries used in energy storage systems.
IEC Certification
The International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) develops international standards for electrical and electronic devices, including batteries. Necessary IEC standards include:
- IEC 62133: Safety requirements for portable sealed secondary cells.
- IEC 62619: Safety requirements for lithium-ion batteries used in electric vehicles.
CE Marking
The CE Mark indicates conformity with health, safety, and environmental protection standards for products sold within the European Economic Area (EEA). This marking is essential for batteries sold in Europe.
UN38.3 Certification
This certification applies specifically to lithium batteries, which are needed for transportation. It ensures that shippers can safely transport the batteries without risking public safety.
ISO Certifications
The International Organization for Standardization (ISO) provides several standards that can apply to battery manufacturers, including:
- ISO 9001: Quality management systems.
- ISO 14001: Environmental management systems.
KC Certification
The KC mark is a certification required in South Korea. It ensures that products meet safety and quality standards, which is crucial for battery market access in South Korea.
CB Scheme
The CB Scheme facilitates international trade by providing a single certification recognized in multiple countries. It covers battery safety standards, making it easier for manufacturers to access global markets.
PSE Certification
In Japan, the PSE (Product Safety Electrical Appliance & Material) certification is mandatory for electrical products, including batteries. This certification ensures that products meet safety standards set by the Japanese government.
RoHS Compliance
The Restriction of Hazardous Substances (RoHS) directive restricts using specific hazardous materials in electrical and electronic products. Compliance with RoHS is essential for manufacturers aiming to sell batteries in the European Union.
MSDS (Material Safety Data Sheet)
While not a certification, the MSDS provides essential safety information about the materials used in batteries. Manufacturers must provide this documentation to ensure the safe handling and use of their products.
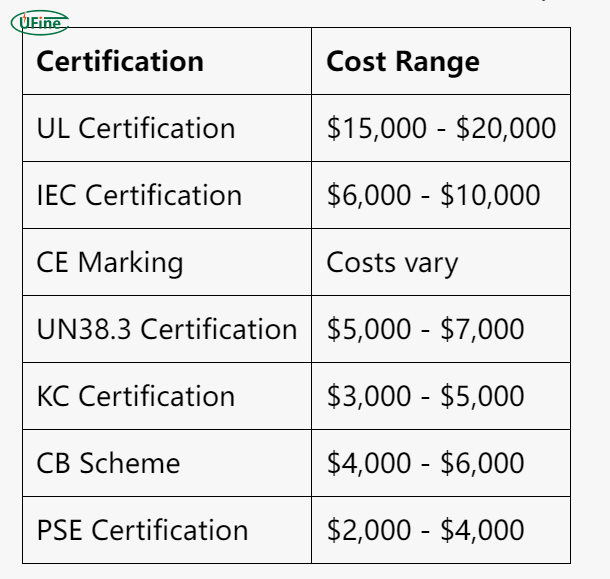
Part 3. Costs associated with battery certification
Battery Certification Cost & Time Comparison
| Certification | Avg Cost | Timeframe | Key Markets |
|---|---|---|---|
| UL 1642 | $15k-$20k | 10-12w | North America |
| IEC 62133 | $6k-$10k | 6-8w | EU/Global |
| UN38.3 | $5k-$7k | 4-6w | Transportation |
The costs of obtaining battery certifications can vary widely based on several factors, including the type of battery, the complexity of the tests, and the certification body. Here’s a general overview of costs associated with standard certifications:
- UL Certification: $15,000 – $20,000
- IEC Certification: $6,000 – $10,000
- CE Marking: Costs vary; often involves self-declaration but may require testing.
- UN38.3 certification: $5,000 – $7,000
- KC Certification: $3,000 – $5,000
- CB Scheme: $4,000 – $6,000
- PSE Certification: $2,000 – $4,000
These costs can fluctuate based on the specific requirements of the battery design and the testing agency’s fees.
Part 4. Timeframes for battery certification
The time it takes to obtain battery certification can also vary significantly. Here’s an estimated timeframe for some standard certifications:
- UL Certification: 10 – 12 weeks
- IEC Certification: 6 – 8 weeks
- CE Marking: Varies; can be quicker if self-declared.
- UN38.3 Certification: 4 – 6 weeks
- KC Certification: 4 – 8 weeks
- CB Scheme: 6 – 10 weeks
- PSE Certification: 4 – 6 weeks
These timeframes depend on the battery design’s complexity and the testing agency’s efficiency.
Part 5. Understanding battery standards
Battery standards are essential guidelines that ensure safety and performance. Various organizations develop them, and they are crucial for manufacturers to understand. Here are some key standards:
Safety Standards
- UL 1642: Focuses on the safety of lithium batteries, ensuring they do not pose a risk of fire or explosion.
- IEC 62133: Provides safety requirements for portable batteries, addressing risks associated with misuse.
Performance Standards
- UL 2054: Evaluates the performance of battery packs in real-world applications.
- IEC 61960: Covers performance specifications for lithium batteries in consumer electronics.
Environmental Standards
- ISO 14001 Ensures manufacturers minimize their environmental impact throughout the battery’s lifecycle.
Part 6. The certification process
The certification process typically involves several key steps:
- Preliminary Assessment: Manufacturers assess which certifications are necessary for their products based on market requirements.
- Testing: Batteries undergo rigorous testing by certified laboratories to ensure compliance with relevant standards.
- Documentation: Manufacturers must compile detailed documentation demonstrating safety and performance standards compliance.
- Certification Issuance: Upon successful testing and documentation review, the certification body issues the necessary certifications.
- Ongoing Compliance: Manufacturers must maintain compliance and may undergo periodic audits to ensure continued adherence to standards.
Part 7. Challenges in battery certification
Obtaining battery certification can be fraught with challenges, including:
- Complex Regulations: Navigating the various regulations across different markets can be daunting.
- Cost Implications: The high costs associated with testing and certification can be a barrier for smaller manufacturers.
- Time Delays: Lengthy testing and approval processes can delay product launches.
Need Help? Get Free Consultation on Battery Certification
Part 8. 5 Critical battery certification mistakes to avoid
1. Using Non-Certified Cell Suppliers
30% of certification failures originate from uncertified raw cells. Always demand valid UL/IEC certificates and batch test reports from suppliers.
2. Ignoring 2024 EU Battery Directive Updates
New carbon footprint labeling mandates effective February 2024. Non-compliance risks €50,000 fines and product recalls across EU markets.
3. Underestimating UN38.3 Altitude Testing
15,000m altitude simulation causes 40% failure rate. Implement pressure relief valves and maintain ≤20% state of charge during testing.
4. Incomplete Technical Documentation
25% applications get rejected due to missing:
- Battery MSDS (Material Safety Data Sheet)
- Cell specification documents
- Protection circuit design diagrams
- ISO 9001 quality system certificates
5. Neglecting Transportation Certifications
Certified batteries still require:
- IATA/IMDG approvals for air/sea transport
- 1.2m drop test reports (FedEx/DHL requirement)
- External short-circuit protection proof
Part 9. FAQs about battery certification
How to get battery certification?
Follow these 5 steps:
- Identify target markets
- Select accredited lab
- Prepare test samples
- Submit technical documents
- Pass compliance audit.
Most lithium batteries require 3-6 months for full certification.
What is the cheapest battery certification?
UN38.3 transportation certification typically has the lowest cost ($2,500-$5,000), while multi-country certifications like CB Scheme can save 40% compared to applying separately.
Does CE certification cover all EU countries?
Yes, CE marking is mandatory for batteries sold in all 27 EU member states. However, Germany requires additional GS certification for consumer products.
How long is battery certification valid?
Most certifications like UL and IEC are valid for 3-5 years. UN38.3 requires retesting if battery design changes. Annual factory audits are mandatory for ISO certifications.
Can I self-certify CE marking?
For batteries with capacity below 100Wh, manufacturers can self-declare CE compliance. Batteries over 100Wh must be tested by Notified Bodies like TÜV or SGS.
Related Tags:
More Articles

12V STD vs 12V AGM: Meaning, Differences, and Which Is Better
Understand what STD and AGM batteries mean, their key differences, and which 12V battery fits your needs best in 2026.
Battery Reconditioning Explained: A Comprehensive Guide
Learn what battery reconditioning is, how it works, how long it takes, and when reconditioning chargers are used for lead-acid and lithium-ion batteries.
Recommended 10 Best Batteries For Smoke Detectors
Compare the best batteries for smoke detectors in 2026. See which 9V lithium and alkaline batteries last longest and perform best in smoke alarms.
Triple A Battery Voltage: Everything You Need to Know
How many volts is a AAA battery? See a clear AAA battery voltage chart, compare alkaline, lithium and NiMH cells, and learn how voltage affects device use.
What Size Battery for Digital Thermometer: The Complete Guide
What size battery does a digital thermometer use? See common sizes like AAA, AA, CR2032, and LR41, plus tips to choose the right battery and extend lifespan.