- Part 1. Why lithium batteries require different mounting methods
- Part 2. Why vibration control is critical for lithium batteries
- Part 3. What happens if you use the wrong strap down on a lithium battery?
- Part 4. Do lithium batteries need special strap downs?
- Part 5. When a strap down must be used (Lithium-Specific Situations)
- Part 6. When special strap downs are not required
- Part 7. Recommended strap-down features for lithium batteries
- Part 8. Strap down vs. hold-down bracket for lithium batteries
- Part 9. Best practices for securing lithium batteries
- Part 10. Conclusion
Lithium batteries—especially LiFePO₄, NMC, and LCO packs—have become the preferred choice for RV systems, marine trolling motors, solar storage banks, motorcycles, robotics, and portable equipment. They deliver longer cycle life, higher energy density, and stable voltage output. But as more users replace lead-acid batteries with lightweight lithium alternatives, one question becomes increasingly important:
Do lithium batteries require special battery strap downs?
The short answer: Yes.
Lithium batteries have different internal structures, casing characteristics, vibration behavior, and compression tolerances compared to traditional lead-acid batteries. While some mounting accessories overlap, securing a lithium battery safely often requires a more suitable strap-down method.
This guide explores why lithium batteries need dedicated securing solutions, how vibration affects lithium chemistry, the risks of using improper mounting hardware, and the best practices for choosing safe strap-down systems.
Part 1. Why lithium batteries require different mounting methods
Lithium batteries are fundamentally different from lead-acid batteries in both design and mechanical structure.
1 Internal Construction Differences
A typical lead-acid battery uses thick ABS casings and multiple internal lead plates submerged in electrolyte. This design is inherently rigid and resistant to moderate compression.
Lithium batteries, however, use one of three internal structures:
- Prismatic cells — aluminum or steel shells with stacked layers
- Pouch cells — flexible layered cells sealed in polymer film
- Cylindrical cells — steel-can 18650/21700 formats
Lithium packs also integrate components such as:
- BMS (battery management system)
- MOSFETs
- Temperature sensors
- Copper or nickel busbars
- Insulation pads and separators
While durable, these components are more sensitive to external pressure and vibration.
Result:
Lithium batteries cannot tolerate the same compressive force or rigid clamping that lead-acid batteries can.
2 Casing Strength and Compression Sensitivity
Lithium battery enclosures are typically:
- Thinner
- Lighter
- More compact
- Built from ABS, aluminum, or soft polymer laminates
Although strong, they are designed for weight reduction, not heavy external compression.
Compressive pressure can cause:
- Slight case deformation
- Stress on internal cells
- Misalignment of cell stacks
- Damage to BMS components
- Movement of busbars
- Potential internal short hazards
This is why lithium batteries benefit from flexible, non-compressive securing solutions.
Part 2. Why vibration control is critical for lithium batteries
Lithium batteries are more sensitive to vibration compared to lead-acid units, especially pouch and prismatic designs. In many applications—ATVs, UTVs, boats, motorcycles, drones, and off-road vehicles—vibration becomes one of the main contributors to battery failure.
1 How Vibration Affects Lithium Chemistry
Constant vibration can:
- Loosen busbar connections
- Increase terminal wear
- Stress solder joints
- Damage BMS circuits
- Cause micro-cracks in prismatic cell shells
- Trigger insulation wear
- Reduce cycle life
Even if these effects do not create immediate failures, vibration accelerates degradation.
2 Why Strap Downs Matter for Vibration Damping
Proper strap downs serve two key roles:
- They secure the battery firmly in place
- Preventing sliding, bouncing, or collision with other components.
- They absorb vibration
- When made from flexible materials such as nylon, polyester, or marine-grade fiber.
Rigid brackets, by comparison, transfer vibration directly into the battery casing.
Part 3. What happens if you use the wrong strap down on a lithium battery?
A strap-down system that works for lead-acid batteries may be unsuitable or even harmful when used with lithium batteries. The wrong mounting method can create serious long-term problems.
1 Risk of Case Deformation
Over-tightened brackets or metal clamps may deform the battery shell. Lithium cases are typically not designed for point-pressure compression.
2 Internal Component Damage
Internal welds, busbars, and BMS modules may detach or loosen due to pressure and vibration transfer.
3 BMS Malfunction or Failure
A stressed BMS can experience thermal drift, PCB cracking, or wiring damage, affecting:
- charge protection
- cell balancing
- overcurrent response
- temperature cutoff
4 Terminal Bending or Stress Cracking
Lithium terminals are typically smaller and lighter than lead-acid posts, making them easier to stress or crack under repeated vibration.
5 Voided Warranty
Many lithium manufacturers specify mounting limitations. Using rigid or incompatible brackets can void warranty terms relating to:
- physical damage
- case deformation
- terminal breakage
- electrical component damage
Bottom line:
Using the wrong strap-down method can shorten lithium battery lifespan and compromise safety.
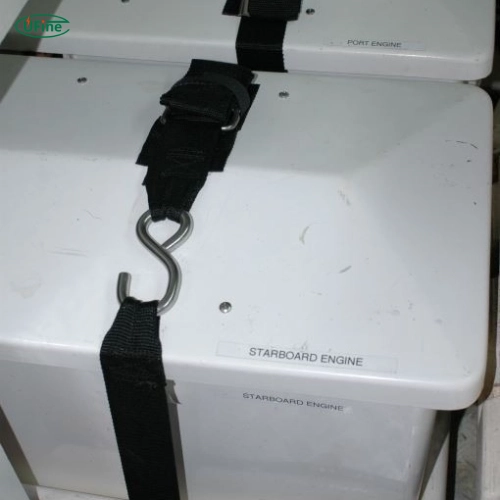
Part 4. Do lithium batteries need special strap downs?
Yes—in most cases, lithium batteries perform best with flexible, vibration-absorbing strap downs rather than rigid, compressive brackets.
Recommended Strap-Down Types for Lithium Batteries
- Nylon Webbing Straps
- High tensile strength, lightweight, adjustable.
- Polyester Marine-Grade Straps
- UV-resistant and ideal for marine environments.
- Hook-and-Loop (Velcro) Straps
- Easy to adjust and prevent over-compression.
- Ratchet Straps with Soft Pads
- Excellent for securing mid-weight packs without rigid pressure points.
- Two-Point or Four-Point Tie-Down Straps
- Provide balanced tension distribution.
- Vibration-Isolating Straps
- Can include rubber, silicone, or neoprene pads.
Part 5. When a strap down must be used (Lithium-Specific Situations)
Lithium batteries require special strap downs in scenarios involving:
1 High Vibration Environments
- Marine (trolling motors, fishing boats)
- Off-road vehicles
- Motorcycles
- Snowmobiles
- ATVs / UTVs
- Construction equipment
Flexible straps are essential to minimize shock transfer.
2 Lightweight Installations
Lithium batteries weigh up to 60–70% less than lead-acid batteries.
This makes them more likely to bounce or shift if not secured properly.
A hold-down bracket designed for a 15–25 kg lead-acid battery may be too loose for a 5–10 kg LiFePO₄ battery.
3 Mobile Power Stations and Outdoor Equipment
Portable lithium systems benefit from straps that are:
- adjustable
- removable
- compatible with various mounting conditions
Rigid brackets restrict mobility and flexibility.
4 Enclosed or Battery-Box Installations
When lithium batteries are installed inside:
- plastic battery boxes
- portable cases
- custom enclosures
- marine compartments
Straps must prevent movement without applying damaging point pressure.
Part 6. When special strap downs are not required
There are cases where a standard bracket or strap-down method is acceptable:
1 Stationary Energy Storage (ESS)
- Lithium solar wall batteries
- Rack-mounted LiFePO₄ packs
- Cabinet-style energy storage
These systems are physically heavy or enclosed in metal housings, and vibration is minimal.
2 OEM Automotive Lithium Packs
EV batteries or hybrid batteries use custom rigid housings engineered for impact resistance.
They should NEVER be modified with aftermarket strap-downs.
In these cases, specialized strap downs are not necessary.
Part 7. Recommended strap-down features for lithium batteries
When selecting a strap-down system, the following characteristics provide the best performance and safety for lithium packs.
1 Flexible Yet High-Strength Material
Look for materials such as:
- Nylon
- Polyester
- Marine-grade polypropylene
- Elastic fiber blends
They provide a balance between strength and flexibility.
2 Wide Contact Surface Area
A wider strap reduces point pressure and distributes load evenly.
This prevents:
- casing dents
- BMS pressure
- deformation of prismatic cells
3 Non-Metallic or Padded Contact Points
Metal straps can scratch, dent, or short the battery.
Choose:
- padded contact surfaces
- rubber strips
- silicone buffers
4 Anti-Slip Design
The strap should include anti-slip stitching or textures to prevent lateral movement.
5 UV and Corrosion Resistance (For Marine Use)
For boats or salt-water environments, choose:
- UV-resistant straps
- stainless corrosion-resistant hardware
- marine-grade fibers
6 Adjustable Tension Levels
Lithium batteries should never be overtightened.
Look for:
- ratchet or cam-lock adjusters
- soft tension systems
Part 8. Strap down vs. hold-down bracket for lithium batteries
Which is better?
| Feature | Strap Down | Hold-Down Bracket |
|---|---|---|
| Compression Level | Low, even | High, concentrated |
| Vibration Absorption | Excellent | Poor |
| Installation | Easy | Requires tools |
| Lithium Safety | Safe | ⚠️ Risky if overtightened |
| Weight | Very light | Medium to heavy |
| Mobility | High | Low |
| Adjustability | High | Low |
| Use Case | Lithium-friendly | Lead-acid focused |
Conclusion:
Strap downs are the safest and most reliable option for lithium batteries in mobile or vibration-heavy environments.
Part 9. Best practices for securing lithium batteries
To ensure long-term safety and performance, follow these professional guidelines:
1 Avoid Excessive Compression
Lithium packs must be secured firmly but not crushed.
Ensure the battery does not deform when tightening the strap.
2 Add Cushioning for High-Vibration Environments
Use:
- foam padding
- neoprene strips
- silicone vibration-absorbing mats
These reduce shock loads transferred to internal cells.
3 Maintain Proper Terminal Orientation
Make sure the strap does not stress or bend terminals; a perpendicular orientation is ideal.
4 Inspect Straps Regularly
Look for:
- fraying
- UV damage
- buckle wear
- tension loss
Replace worn straps immediately.
5 Do Not Use Metal-to-Metal Contact
Avoid brackets or straps that contact the battery case directly with bare metal.
6 Ensure Clearance Around the BMS and Wiring
Straps should not sit directly over wiring harnesses or BMS housing areas.
Part 10. Conclusion
Lithium batteries are not drop-in replacements for lead-acid batteries when it comes to securing them. Their lightweight structure, vibration sensitivity, and internal BMS components make them more susceptible to damage if the wrong mounting method is used.
- Lithium batteries require flexible, vibration-absorbing strap downs.
- Rigid metal brackets can cause deformation and internal stress.
- Proper strap selection improves safety, lifespan, and performance.
- Strap-down methods designed specifically for lithium batteries deliver the best results in RV, marine, off-grid, power sports, and portable power applications.
Related Tags:
More Articles

Can You Really Buy Cheap Batteries Safely?
Learn the truth about cheap batteries, hidden risks, and how to find affordable yet safe lithium batteries from Ufine Battery experts.
Battery Strap Down Safety Tips: Preventing Vibration Damage and Terminal Stress
Follow these expert battery strap down safety tips to prevent vibration damage, terminal stress, and ensure LiFePO4 battery longevity.
How to Choose a Good 18650 Battery with Reliable Quality?
Battery quality defines performance and safety. Ufine Battery shares how to source good 18650 batteries and avoid unstable suppliers.
Can I Use a Universal Battery Strap Down on LiFePO4 Batteries? (Compatibility Guide)
Learn whether universal battery strap downs are compatible with LiFePO4 batteries, and how to install them safely for vibration control.
Battery Strap Down vs Battery Hold-Down Bracket: What’s the Difference?
Compare battery strap downs and hold-down brackets. Learn key differences, installation tips, and which is safer for lithium batteries.