- Part 1. Understanding battery voltage ratings
- Part 2. Good battery voltage by battery type
- Part 3. Good voltage for common applications
- Part 4. How to measure battery voltage correctly
- Part 5. Signs of a battery with poor voltage
- Part 6. What causes voltage to drop?
- Part 7. How to maintain good battery voltage
- Part 8. Troubleshooting low or fluctuating voltage
- Part 9. Battery voltage vs. state of charge (SOC)
- Part 10. Safety considerations with battery voltage
- Part 11. Ufine Battery — your partner for reliable power
Part 1. Understanding battery voltage ratings
Battery voltage ratings are one of the first specifications to look at when determining whether a battery is healthy and operating correctly. Every battery has several important voltage points:
Nominal Voltage – The general or “average” voltage the battery provides during discharge. For example, most lithium-ion batteries have a nominal voltage of 3.6–3.7V per cell, while a lead-acid battery has 2V per cell.
Fully Charged Voltage – The maximum safe voltage a battery reaches when fully charged. Exceeding this can cause overcharging and damage.
- Lithium-ion cell: 4.2V
- LiFePO4 cell: 3.6–3.65V
- 12V lead-acid battery: 12.6–12.8V
Minimum Safe Voltage – The lowest recommended voltage before the battery suffers from over-discharge.
- Lithium-ion cell: ~3.0V
- LiFePO4 cell: ~2.5V
- 12V lead-acid battery: ~11.8V at rest
Voltage Range Under Load – Real-world voltages vary during use. A “good” battery should maintain close to nominal voltage when powering a device.
Understanding these ratings helps you determine whether the battery is functioning at a healthy level or needs maintenance.
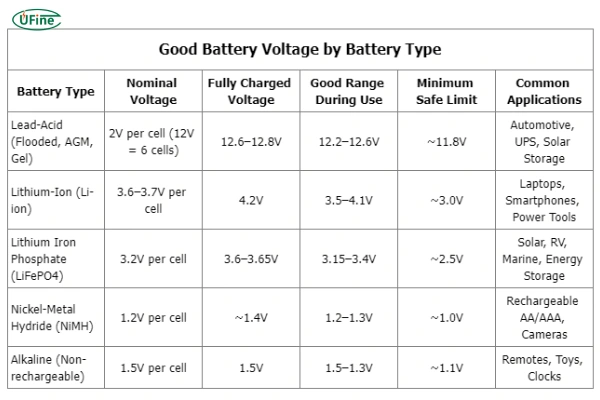
Part 2. Good battery voltage by battery type
Different chemistries have different voltage characteristics. Knowing the correct voltage range for your battery type ensures accurate diagnosis.
Lead-Acid Batteries (Flooded, AGM, Gel)
- Nominal voltage: 2V per cell (12V battery = 6 cells)
- Good voltage at rest (full charge): 12.6–12.8V
- 50% charge: ~12.2V
- Discharged: 11.8V or lower
- Common in automotive, UPS, and solar storage systems.
Lithium-Ion (Li-ion) Batteries
- Nominal voltage: 3.6–3.7V per cell
- Full charge: 4.2V
- Good range during use: 3.5–4.1V
- Minimum safe limit: 3.0V (lower can damage cells)
- Found in laptops, smartphones, power tools.
Lithium Iron Phosphate (LiFePO4)
- Nominal voltage: 3.2V per cell
- Full charge: 3.6–3.65V
- Good range during use: 3.15–3.4V
- Minimum safe limit: ~2.5V
- Common in solar storage, RVs, and marine batteries due to long lifespan and safety.
Nickel-Metal Hydride (NiMH)
- Nominal voltage: 1.2V per cell
- Full charge: ~1.4V
- Minimum safe limit: ~1.0V
- Used in rechargeable AA/AAA batteries, cameras, and handheld electronics.
Common Household Batteries (Alkaline)
- Nominal voltage: 1.5V per cell
- Good range: 1.5–1.3V
- Low voltage: Below 1.1V
- Non-rechargeable, found in remotes, toys, clocks.
Part 3. Good voltage for common applications
Different applications demand different voltage ranges for optimal performance.
Automotive Batteries (12V Lead-Acid)
- Good at rest: 12.6–12.8V
- Cranking engine: should stay above 10V
- Charging system: 13.7–14.7V
Solar Power Storage (LiFePO4)
- Good daily range: 13.2–13.6V (for a 12.8V pack)
- Fully charged: ~14.4V
- RV and Marine Batteries
- Lead-acid: Same as automotive
LiFePO4: Full ~14.4V, good operating ~13.2V
- Consumer Electronics (Li-ion)
- Operates well between 3.6–4.1V per cell
- Falls below 3.3V means it’s time to recharge.
Part 4. How to measure battery voltage correctly
Tools Needed
- Digital Multimeter – Preferred for accuracy.
- Analog Voltmeter – Less precise but usable.
- Battery Monitoring Systems (BMS) – For continuous tracking.
Steps
- Set the meter to DC voltage.
- Connect the red probe to the positive terminal and the black probe to the negative.
- Read voltage at rest (no load) for baseline.
- Optionally, measure under load to see real-world performance.
Safety Tips
- Avoid short-circuiting the terminals.
- Use insulated probes.
- For large battery banks, wear protective gloves and eye protection.
Part 5. Signs of a battery with poor voltage
- Slow or weak device performance
- Dim lights in vehicles or solar setups
- Frequent recharging needed
- Inconsistent readings when measured multiple times
- Voltage drops quickly under even small loads
Poor voltage can be a sign of sulfation in lead-acid batteries, worn electrodes in lithium-ion cells, or increased internal resistance.
Part 6. What causes voltage to drop?
Several factors can lead to a drop in voltage:
- Age & Wear – Battery capacity naturally declines over cycles.
- Over-Discharging – Damages chemistry and increases internal resistance.
- Temperature – Cold temperatures reduce voltage temporarily.
- Poor Maintenance – Leaving batteries uncharged for long periods causes deterioration.
- Faulty Cells – One bad cell in a multi-cell pack can pull down overall voltage.
Part 7. How to maintain good battery voltage
Proper Charging Habits
- Avoid overcharging; use smart chargers.
- Charge before voltage drops too low.
Correct Storage
- Store at 40–60% charge for long-term storage.
- Keep in cool, dry conditions.
Avoid Deep Discharge
- Especially important for lithium-ion and lead-acid batteries.
Use Battery Management Systems (BMS)
- Protects from over-voltage, under-voltage, and imbalance.
Part 8. Troubleshooting low or fluctuating voltage
- Test Under Load – If voltage drops sharply, the battery may be weak.
- Check Charging Equipment – Alternator, solar controller, or charger may be faulty.
- Inspect for Loose Connections – Resistance at terminals can cause voltage loss.
- Look for Damaged Cells – In multi-cell batteries, test each cell individually.
- Replace When Necessary – When a battery can no longer maintain good voltage under normal load.
Part 9. Battery voltage vs. state of charge (SOC)
Voltage often correlates with the battery’s state of charge, but it’s not always linear. Below is a quick reference:
| Battery Type | 100% SOC | 75% SOC | 50% SOC | 25% SOC | 0% SOC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 12V Lead-Acid | 12.6–12.8V | 12.4V | 12.2V | 12.0V | 11.8V |
| Lithium-Ion (3.7V) | 4.2V | 3.95V | 3.75V | 3.45V | 3.0V |
| LiFePO4 (3.2V) | 3.6–3.65V | 3.4V | 3.3V | 3.2V | 2.5V |
Note: Voltages are typical values at rest and may vary with temperature, load, and battery age.
Note: Load and temperature can affect these readings.
Part 10. Safety considerations with battery voltage
- Overcharging – Can cause swelling, leakage, or fire in lithium batteries.
- Under-voltage – Can permanently damage cells.
- Fire Hazards – Use correct chargers and avoid damaged batteries.
- Proper Disposal – Recycle old batteries to prevent environmental harm.
Part 11. Ufine Battery — your partner for reliable power
If you’re looking for a battery that maintains good voltage consistently, Ufine Battery can provide custom solutions for your exact needs.
Ufine Battery is a Chinese custom lithium battery manufacturer, supplying:
- Lithium polymer batteries
- LiFePO4 batteries
- 18650 and other cylindrical batteries
- Ultra-thin, high-rate, high/low-temperature batteries
We customize sizes, voltages, capacities, and discharge rates to meet your application’s requirements. Whether for solar energy storage, electric vehicles, or industrial equipment, we ensure every battery delivers reliable voltage performance.
Contact Ufine Battery today to discuss your custom project and get a quote.
Related Tags:
More Articles

How Much Does a Car Battery Weigh?
Discover the average car battery weight, key differences between lead-acid and lithium types, and how battery weight affects performance and efficiency.
What Is the Life of the Level Lock Battery?
Learn how long your Level Lock battery lasts, how to replace it, and tips to extend battery life for reliable smart lock performance all year.
Smart Charger — What Is It and How Does It Work?
Discover how smart chargers work, extend battery life, and safely charge lithium, NiMH, and lead-acid batteries for long-lasting performance.
Do Batteries Go Out of Date? Explained Clearly
Find out if batteries expire, how to check their shelf life, and what affects their performance over time. Learn proper storage tips to extend battery life.
Maximize the Life of Your Rechargeable D-Cell Battery
Learn how long rechargeable D-cells last, what affects their lifespan, and how to choose durable, high-capacity batteries for long-term use.