- Key Takeaways
- Part 1. What is a power battery?
- Part 2. What is an energy battery?
- Part 3. Power battery vs energy battery: key differences
- Part 4. What is a lithium energy battery?
- Part 5. Why lithium energy batteries are critical for renewable energy
- Part 6. Applications of lithium energy batteries
- Part 7. Engineering selection: power battery or energy battery?
- FAQs: Power Battery vs Energy Battery
Power batteries and energy batteries are designed for different electrical demands. A power battery delivers high current over short periods, while an energy battery stores and releases electricity steadily over longer durations.
Although both may use lithium-ion chemistry, their internal design, discharge behavior, and ideal applications are fundamentally different. Selecting the wrong battery type can reduce lifespan, efficiency, and system reliability.
Key Takeaways
- Power batteries prioritize high discharge rates and rapid energy delivery, while energy batteries focus on long-duration energy storage.
- Energy density and power density are different metrics and must be matched to the application’s load profile.
- Lithium energy batteries are the dominant solution for renewable energy storage due to efficiency, scalability, and cycle life.
- Using a power battery in an energy-storage scenario (or vice versa) leads to faster degradation and higher system costs.
- Battery selection should be driven by duty cycle, discharge rate (C-rate), lifespan requirements, and thermal constraints.
Part 1. What is a power battery?
A power battery is a rechargeable battery designed to deliver high power output over short periods. Its primary role is to support applications that require rapid acceleration, high current discharge, or sudden power surges.
Power batteries are optimized for power density rather than total stored energy.
1 Core characteristics of power batteries
- High discharge rates (high C-rate)
- Fast charge and discharge capability
- Lower overall energy density
- Designed for frequent high-load cycles
2 Common power battery chemistries
- Lithium-ion batteries: Used in electric vehicles, power tools, and aerospace systems.
- Nickel-metal hydride (NiMH): Found in hybrid vehicles and industrial equipment.
- Lead-acid (SLI type): Used for engine starting and emergency power due to reliability and cost.
Part 2. What is an energy battery?
An energy battery (also called a high-energy battery) is designed to store and deliver electricity steadily over long periods. These batteries prioritize energy density and cycle efficiency rather than peak output.
Energy batteries are the foundation of renewable energy storage, backup power systems, and portable electronics.
1 Core characteristics of energy batteries
- High energy density
- Stable, long-duration discharge
- Long cycle life
- Optimized for deep charge/discharge cycles
2 Common energy battery types
- Lithium-ion batteries: Residential and commercial energy storage, EVs.
- Lead-acid batteries: Backup power and off-grid systems.
- Flow batteries: Utility-scale and long-duration grid storage.
- Sodium-sulfur batteries: Industrial and grid-level applications.
Part 3. Power battery vs energy battery: key differences
| Aspect | Power Battery | Energy Battery |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Goal | Rapid energy delivery | Long-term energy storage |
| Discharge Rate | High (short bursts) | Low to moderate (continuous) |
| Energy Density | Lower | Higher |
| Lifespan | Shorter under heavy load | Longer with controlled cycling |
| Typical Applications | EV acceleration, power tools | Solar storage, backup power |
Part 4. What is a lithium energy battery?
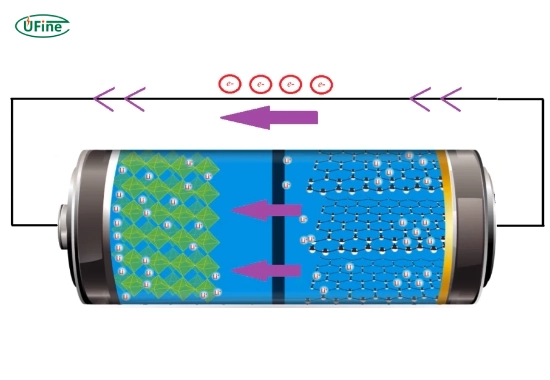
A lithium energy battery is a lithium-ion battery optimized for high energy density and long-duration discharge. During charging and discharging, lithium ions move between the cathode and anode through an electrolyte, enabling efficient energy storage.
Compared with lead-acid and nickel-based batteries, lithium energy batteries offer superior efficiency, lifespan, and scalability.
Part 5. Why lithium energy batteries are critical for renewable energy
Renewable energy sources like solar and wind are intermittent. Lithium energy batteries solve this problem by storing excess energy during peak generation and releasing it during low-generation periods.
According to the International Energy Agency (IEA), large-scale energy storage systems play a critical role in stabilizing power grids and enabling higher penetration of renewable energy sources such as solar and wind.
Part 6. Applications of lithium energy batteries
- Residential energy storage: Home solar systems and peak shaving.
- Utility-scale storage: Grid stabilization and frequency regulation.
- Off-grid systems: Remote and industrial power solutions.
- Electric vehicles: Long-range energy supply.
- Smart grids: Intelligent load balancing.
Part 7. Engineering selection: power battery or energy battery?
Choosing between a power battery and an energy battery depends on:
- Peak current demand
- Duty cycle duration
- Thermal constraints
- Expected lifespan
- System cost optimization
For mixed-use systems, hybrid battery architectures are often employed.
FAQs: Power Battery vs Energy Battery
What is the difference between a power battery and an energy battery?
A power battery is optimized for high current and short discharge, while an energy battery is designed for long-duration energy storage and stable output.
Is a lithium-ion battery a power battery or an energy battery?
Lithium-ion batteries can be designed as either power batteries or energy batteries depending on cell structure, C-rate design, and application requirements.
When should an energy battery be used instead of a power battery?
Energy batteries are preferred for renewable energy storage, backup power systems, and applications requiring long discharge duration rather than peak power.
What applications require power batteries?
Power batteries are required for electric vehicles, power tools, hybrid systems, and other applications with high peak current demand.
How do manufacturers choose between power and energy battery designs?
Manufacturers evaluate discharge rate, duty cycle, thermal limits, and lifespan targets to determine whether a power or energy battery design is appropriate.
Related Tags:
More Articles

Solar Battery: A Comprehensive Guide
Learn what a solar battery is, how it works, main types, typical costs, and how to choose the right battery for solar panels in real applications.
Top 10 Lithium Iron Phosphate Manufacturers in the World
2026 guide to the top 10 LiFePO4 battery manufacturers. Compare who makes LFP batteries, certifications, applications, and reliable suppliers.
Get practical insights on selecting, using, and troubleshooting 24V power supplies. Avoid common mistakes and optimize your setup today.
A Simple Guide to 3.7V 2000mAh Li Ion Batteries
Is a 3.7V 2000mAh battery enough for your device? Learn runtime, replacement rules, connector types, and how to avoid common battery mistakes.
How Much Does a Golf Cart Battery Weigh?
Learn how golf cart batteries affect total golf cart weight and size, with average weight ranges and standard dimensions for electric golf carts.