- Part 1. Industry challenges in glucose meter power design
- Part 2. Solution overview: Ufine’s glucose meter battery framework
- Part 3. Key technical advantages
- Battery Runtime Calculator
- Part 4. Recommended battery solutions by application scenario
- Part 5. Certifications & regulatory compliance
- Part 6. R&D support for glucose meter projects
Glucose meter batteries face unique challenges such as voltage sensitivity affecting measurement accuracy, long standby periods with intermittent peak loads, and strict medical compliance requirements.
Beyond supplying lithium batteries, Ufine understands the glucose meter application itself and delivers system-level battery solutions that address real-world usage, reliability, and production scalability across different glucose meter designs.
Part 1. Industry challenges in glucose meter power design

Blood glucose meters operate in a highly regulated and accuracy-critical environment. Based on industry standards, medical device guidelines, and real product usage patterns, glucose meter power systems typically face the following challenges:
1 Voltage Sensitivity and Measurement Accuracy
According to medical electronics design guidelines, glucose meters rely on stable reference voltages for analog front-end circuits and ADC conversion.
Low or unstable battery voltage may affect blood sugar readings, especially during end-of-life battery stages or cold-temperature operation.
2 Intermittent Usage with Long Standby
Industry surveys show that home-use glucometers may remain in standby mode for over 90% of their lifecycle, yet must instantly deliver peak current during measurement, display activation, and data processing.
3 Space-Constrained Industrial Design
Modern glucose meters prioritize portability and ergonomics. This limits battery volume while increasing expectations for device lifespan and user experience.
4 Regulatory and Safety Constraints
Medical device batteries must meet transportation, safety, and market-access regulations across regions such as the U.S., EU, Japan, and other regulated markets.
These challenges require application-driven battery design, not generic off-the-shelf solutions.
Part 2. Solution overview: Ufine’s glucose meter battery framework
Ufine supports glucose meter manufacturers with a systematic solution framework, developed through multiple portable medical device projects.
Solution Coverage
| Glucose Meter Architecture | Battery Solution Strategy | Typical Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| Ultra-slim portable meters | Custom lithium polymer battery | Stable voltage + thin profile |
| Smart glucose meters with display / memory | Rechargeable Li-polymer or small cylindrical Li-ion | Supports higher peak current |
| Diagnostic accessories or docking units | 18650 or other cylindrical lithium batteries | Scalable capacity and durability |
Read our in-depth guide to choosing the right battery for your glucose meter.
The Ultimate Guide to Glucose Meter Battery
Watch Ufine create custom lithium battery samples from design to testing.
Part 3. Key technical advantages
1 Challenge: Low Battery Affecting Blood Sugar Readings
Can low battery affect blood sugar readings?
Yes. Voltage drop near battery end-of-life can impact sensor signal stability and conversion accuracy.
Our Technology:
- Flat discharge curve lithium chemistry
- Defined cutoff voltage aligned with device operating thresholds
- Protection circuits designed to avoid unstable voltage zones
2 Challenge: Short Battery Life Despite Low Power Consumption
How long do glucometer batteries last?
In rechargeable designs, typical lifespan ranges from 6–24 months, depending on usage and power management.
Our Technology:
- Capacity matching based on real usage cycles, not nominal ratings
- Low self-discharge lithium polymer designs for long standby
- Support for firmware-level power optimization collaboration
Use our online battery runtime calculator to see how long your device can run.
3 Challenge: Limited Internal Space
Compact glucose meters restrict battery size and geometry.
Our Technology:
- Custom lithium polymer battery shapes and thickness control
- Energy density optimization for small enclosures
- Mechanical design coordination with device housing
For a similar challenge in medical device power design, check out our laser therapy device battery case study.
Longer Battery Life for Laser Therapy Devices: Ufine’s Innovation
Part 4. Recommended battery solutions by application scenario
1 Portable Home Glucose Meters
Solution: Custom lithium polymer battery
- Optimized thickness for handheld devices
- Stable voltage across long standby periods
Ufine Battery can customize thickness, capacity, voltage range, and form factor to match compact glucose meter designs — supporting prototype validation and scalable production.
Request Your Custom Design2 Smart or Connected Glucose Meters
Solution: Rechargeable Li-polymer or small cylindrical lithium-ion battery
- Supports display, memory, and communication modules
- Designed for frequent charging cycles
Ufine Battery provides rechargeable lithium battery options optimized for displays, memory, and connectivity modules — from early-stage development to mass manufacturing.
Start Your Project Consultation3 Diagnostic Accessories and Peripheral Devices
Solution: 18650 or other cylindrical lithium batteries
- Higher capacity and durability
- Suitable for docking stations or accessory modules
Ufine Battery offers 18650 and other cylindrical lithium battery solutions with configurable capacity and protection design — suitable for medical diagnostic accessories and peripheral devices.
Explore Your Application OptionsPart 5. Certifications & regulatory compliance
Ufine supports battery compliance for glucose meter projects targeting regulated markets. Common regulatory and certification references include:
- UN38.3 – Lithium battery transportation testing (UNECE)
- IEC 62133 – Safety requirements for secondary lithium cells
- FDA Medical Device Framework – U.S. market reference
- EU MDR (Medical Device Regulation) – European Union
- PSE (Japan) – Electrical appliance safety law
Part 6. R&D support for glucose meter projects
Ufine provides end-to-end battery R&D support for glucose meter development:
- Early-stage battery feasibility evaluation
- Small-batch prototyping and sample delivery
- Multi-round sample optimization based on testing feedback
- Support for pilot production and mass manufacturing
- Stable supply planning for long product lifecycles
We regularly support projects from concept validation to volume production, enabling manufacturers to reduce risk and development time.
Explore More Medical Device Battery Solutions
If your project involves multiple medical monitoring devices, you may also be interested in our battery solutions for Blood Pressure Monitors and ECG Devices, engineered for reliability, long cycle life, and medical-grade safety.
High Energy Density
It stores large amounts of energy in a smaller and lighter package
Longer Cycle Life
Withstands extensive charge and discharge cycles
Low Self-Discharge
Maintains power longer when not in use
Safety
Minimizes the risk of accidents and ensures safe operation
More Information About Glucose Meter Battery
-
What factors determine the optimal battery type for a specific glucose meter?
-
What protection features should be included in a glucose meter battery pack?
-
How does temperature affect battery performance in portable glucose meters?
-
Can Ufine support small-batch or prototype glucose meter battery projects?
-
How to extend the usable life of a glucose meter battery?
Latest Blogs
About Lithium Battery Industry News
Capacitor vs Battery: What is the Difference?
Capacitor vs battery explained in detail. Learn the difference between capacitor and battery in energy storage, charging speed, lifespan, and real applications.
2026/02/28 Ufine

18650 Battery vs AA: Which Is Better for Your Device?
Compare 18650 vs AA batteries in capacity, voltage, rechargeability, and applications. Learn which battery type fits high-drain or everyday devices.
2026/02/28 Ufine
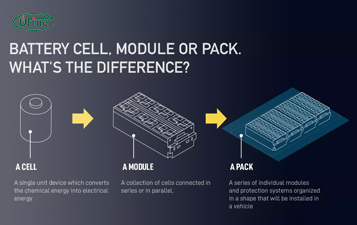
What is the Difference Between Battery Cell, Battery Control Module, and Battery Pack?
Compare battery cells, modules, and packs. Learn functions, design differences, control modules, and selection tips for EV, ESS, and industrial use.
2026/02/28 Ufine

How to Prevent LiPo Battery Explosion?
Can LiPo batteries explode or catch fire? Learn key causes of LiPo battery fires and proven charging, storage, and handling tips to reduce explosion risk.
2026/02/28 Ufine

Aluminium Ion Battery vs Lithium-Ion: A Detailed Comparison
Compare aluminium ion battery vs lithium-ion battery in energy density, charging speed, safety, cost, and uses. A practical guide for engineers and buyers.
2026/02/28 Ufine

C vs D vs AA Battery: Size, Voltage, Capacity & Key Differences Explained
Compare AA, C, and D batteries by size, voltage, capacity, and lifespan. Learn the real difference between C and D batteries and which one you should use.
2026/02/28 Ufine






