- Part 1. Learn lithium D cells
- Part 2. The Chemistry behind lithium D cells
- Part 3. Key features and technical specifications
- Part 4. Advantages of lithium D cells over alkaline batteries
- Part 5. Common applications of lithium D cells
- Part 6. Rechargeable vs. primary lithium D cells
- Part 7. Safety considerations and proper handling
- Part 8. Comparison with other lithium battery types
- Part 9. Top brands and product recommendations
- Part 10. Looking for custom lithium D cells?
- Part 11. FAQs
Part 1. Learn lithium D cells
Lithium D cells are high-performance cylindrical batteries designed for demanding power applications. They are built in the standard D size (33.2 mm in diameter and 61.5 mm in length), similar to the more familiar alkaline or NiMH D batteries. However, while the physical dimensions remain the same, the internal chemistry of lithium D cells sets them apart in terms of energy density, shelf life, and operational performance.
Unlike alkaline and NiMH batteries, lithium D cells are available in both primary (non-rechargeable) and secondary (rechargeable) versions. Their superior capabilities make them ideal for devices that require long-lasting, stable power—such as emergency equipment, industrial tools, and medical devices.
Compared to traditional D cells:
- Alkaline D Cells: Lower energy density, short lifespan, less suitable for high-drain applications.
- NiMH D Cells: Rechargeable but suffer from self-discharge and shorter shelf life.
- Lithium D Cells: Higher capacity, longer life, better high and low temperature performance, and lighter weight.
NiMH vs. Li-ion: 15 Essential Facts Compared
Part 2. The Chemistry behind lithium D cells
Lithium D cells use advanced chemical systems that provide much higher energy output than conventional batteries. The most commonly used chemistries include:
- LiFeS₂ (Lithium Iron Disulfide): Widely used in primary (non-rechargeable) lithium batteries, offering high energy density and excellent performance at extreme temperatures.
- Li-MnO₂ (Lithium Manganese Dioxide): Stable, long-lasting, and capable of delivering high current for industrial and commercial use.
These chemistries differ significantly from the zinc-carbon and alkaline systems in older D cells. For instance, lithium batteries provide a much flatter discharge curve. While alkaline batteries gradually lose voltage as they discharge, lithium cells maintain a consistent voltage output until nearly depleted.
In terms of voltage, lithium D cells are available in different ratings:
- 1.5V Lithium D Cells: Designed as a direct replacement for standard 1.5V D batteries. Ideal for consumer electronics, flashlights, and toys.
- 3.0V or 3.6V Lithium D Cells: Used primarily in industrial, military, and specialized high-power devices. These provide significantly more energy and are often found in primary lithium or Li-ion rechargeable formats.
This variation in voltage is critical when selecting the right lithium D cell for your application.
Part 3. Key features and technical specifications
Lithium D cells are built to outperform traditional D batteries. Here are the key specifications that define their performance:
- Size: Standard D size (33.2 mm diameter × 61.5 mm length).
- Nominal Voltage:
1.5V (for compatibility with traditional devices).
3.0V or 3.6V (for high-energy or industrial use).
- Capacity:
1.5V lithium D cells: ~18,000 to 21,000 mAh.
3.6V lithium D cells: Can reach 25,000 mAh or more.
- Operating Temperature Range: Typically -40°C to +60°C.
- Shelf Life: Up to 10-20 years, depending on the chemistry and storage conditions.
- Weight: Lighter than alkaline counterparts due to lithium’s lower atomic mass.
These features make lithium D cells incredibly reliable in demanding environments.
Part 4. Advantages of lithium D cells over alkaline batteries
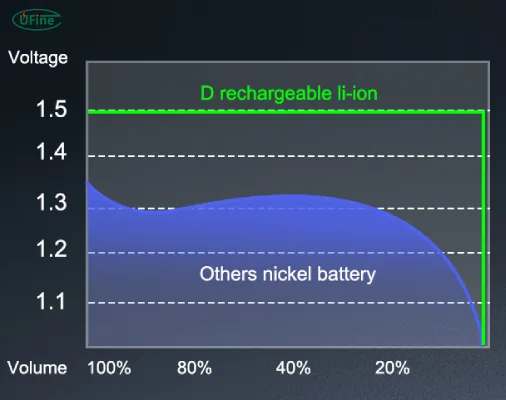
The performance benefits of lithium D cells are clear when compared to traditional alkaline batteries:
- Longer Lifespan: Lithium D cells often last 2 to 5 times longer than alkaline in similar conditions.
- Higher Energy Density: More power in the same size means longer runtime for your devices.
- Wide Operating Temperature: Perfect for both cold outdoor use and high-temperature environments.
- Lightweight Design: Easier to carry, especially for portable and wearable devices.
- Leak-Proof Construction: Reduces the risk of corrosion and damage to electronic devices.
These advantages explain why lithium D cells are becoming the preferred choice for professionals in critical fields.
Part 5. Common applications of lithium D cells
Lithium D cells are used in a wide range of devices and systems, particularly those requiring high power and reliability:
- High-Drain Devices: Flashlights, motor-driven tools, and electronic locks.
- Medical Equipment: Infusion pumps, portable monitors, and diagnostic devices.
- Industrial Applications: Sensors, remote monitoring units, and robotics.
- Military Equipment: Communications gear, GPS trackers, and surveillance tools.
- Emergency and Off-Grid Power: Solar backup systems, emergency beacons, and survival gear.
In short, lithium D cells are indispensable in mission-critical environments.
Part 6. Rechargeable vs. primary lithium D cells
There are two primary categories of lithium D cells:
Primary Lithium D Cells
- Non-rechargeable
- Longer shelf life (up to 20 years)
- Stable performance in cold and hot environments
- Ideal for emergency kits and low-use devices
Rechargeable Lithium D Cells
- Typically use Li-ion or LiFePO4 chemistry
- Rechargeable for 500–1000 cycles
- Environmentally friendly and cost-effective over time
- Best for frequently used tools and portable electronics
When deciding between them, consider the usage pattern of your device. Rechargeables save money long term, while primary cells are best for long-storage or rarely-used gear.
Part 7. Safety considerations and proper handling
While lithium batteries are generally safe, proper care is important to prevent accidents:
- Avoid Overheating: Do not expose to fire, direct sunlight, or high heat.
- No Short Circuits: Store batteries in original packaging or use plastic holders.
- Safe Disposal: Recycle according to local battery disposal guidelines. Never throw in trash.
- Use Certified Batteries: Look for UL, IEC, or RoHS certified cells.
- Do Not Recharge Primary Cells: Only recharge batteries specifically labeled as rechargeable.
Part 8. Comparison with other lithium battery types
Lithium D cells are part of a broader lithium battery ecosystem. Here’s how they stack up:
- 18650 Batteries:
Common in laptops and flashlights.
Higher energy density in a smaller format.
Requires custom holders or battery packs.
- CR123A Batteries:
Compact 3V cells used in cameras and small devices.
Not suitable for D-cell battery compartments.
- Lithium AA/AAA Batteries:
Lower capacity, used for small gadgets.
Incompatible with devices requiring high continuous current.
Why Choose a D Cell? When you need a balance of size, power, and reliability, lithium D cells deliver unmatched performance.
Part 9. Top brands and product recommendations
Several leading manufacturers offer high-quality lithium D cells:
- Energizer Ultimate Lithium D: Reliable and widely available.
- Duracell High Power Lithium D: Trusted brand with consistent output.
- Panasonic Industrial Lithium D Cells: Ideal for OEM and industrial use.
Price vs. Performance Though lithium D batteries are more expensive upfront, they offer a better cost-to-use ratio due to longer life and fewer replacements.
Part 10. Looking for custom lithium D cells?
If you need custom lithium D cells for your device or project, we recommend contacting Ufine Battery.
Ufine Battery is a professional Chinese manufacturer of custom lithium batteries. We supply:
- Lithium polymer batteries
- LiFePO4 batteries
- 18650 cylindrical cells
- Ultra-thin, high-rate, and high-temperature lithium batteries
We support customized solutions in different sizes, voltages, capacities, and rates for your specific application.
✉️ Contact Ufine Battery today to discuss your custom battery needs and get professional support.
Part 11. FAQs
Can I use a 3.6V lithium D cell instead of a 1.5V battery?
No, not unless your device supports higher voltage. Using a 3.6V battery in a 1.5V-rated device can damage it.
What is the difference between 1.5V and 3.6V lithium D cells?
1.5V lithium D cells are for standard electronics. 3.6V versions are for high-performance applications.
Are lithium D batteries safe?
Yes, when used correctly. Always follow manufacturer guidelines and use certified cells.
How do I know if my lithium D cell is rechargeable?
Check the label. Rechargeable batteries are marked with “Li-ion” or “LiFePO4.”
Related Tags:
More Articles

NiMH vs Lithium 7.2V Battery and Charger: Which Is Better?
Compare 7.2V NiMH vs Lithium batteries and chargers in 2025. Learn runtime, weight, charging, lifespan, and cost to choose the best for your device.
How to Choose the Right 7.2V Battery and Charger for Your Device?
Learn how to choose the right 7.2V battery and charger for optimal performance, safety, and longevity across RC, tools, medical, and industrial devices.
Big Square Battery Safety Standards You Must Know
Learn key safety standards for big square batteries to avoid fire risks, shipping delays, and compliance issues in EV, industrial, and energy storage projects.
Big Square Battery Applications in Solar & Industrial Equipment
Big square batteries deliver high capacity, stable output, and long life for solar, industrial, and backup power. Explore key uses and advantages.
Big Square Battery vs Cylindrical Battery: Complete 2025 Guide for EVs, ESS & Industrial Devices
Choosing the right battery is key for designers and engineers. Compare big square vs cylindrical batteries to find the best fit for your application.




