LFP vs. NMC battery technologies are two of the most popular choices in energy storage, each gaining significant attention for their unique benefits. These advanced systems have transformed industries ranging from electric vehicles to renewable energy storage. This article delves into the differences between LFP and NMC batteries, highlighting their distinct characteristics, advantages, and limitations.
Part 1. What is an LFP battery?
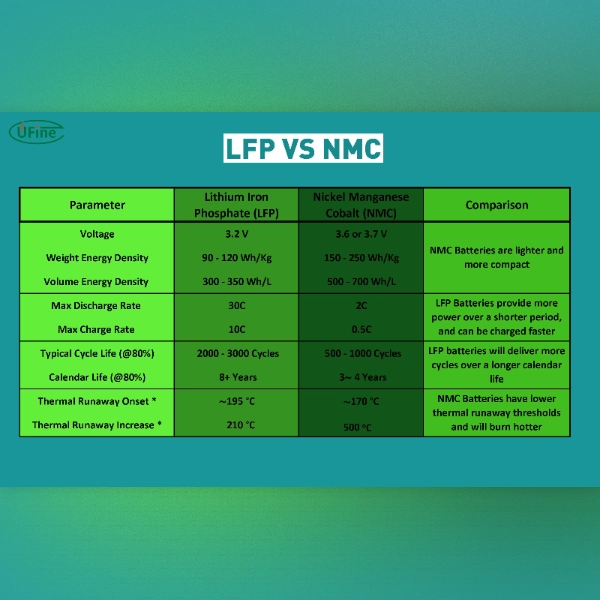
LFP batteries, also known as lithium iron phosphate batteries, are rechargeable lithium-ion batteries that utilize lithium iron phosphate as the cathode material. This chemistry offers several distinct advantages over other lithium-ion battery types, making them ideal for applications such as renewable energy storage systems, electric buses, industrial equipment, and off-grid power solutions where safety, durability, and a long lifespan are essential.
What are the advantages and downsides of LFP?
Advantages:
- Longer lifespan: LFP batteries typically last longer than other lithium-ion batteries, with some models capable of enduring thousands of charge cycles, making them cost-effective over time.
- Enhanced safety: They have a higher thermal stability, reducing the risk of overheating and fire hazards.
- Fast charging capabilities: LFP batteries charge quickly, benefiting various applications, including electric vehicles.
- Wide operating temperature range: LFP batteries perform well in hot and cold environments, making them versatile for different climates.
- Environmental friendliness: LFP batteries are more eco-friendly because they contain no cobalt, a material often associated with environmental and ethical concerns in battery production.
Downsides:
- Lower energy density: Compared to other lithium-ion batteries, LFP batteries have a lower energy density, meaning they store less energy per unit volume or weight.
- Reduced specific power: While they can handle fast charging, LFP batteries may have limitations in delivering high power outputs, impacting performance in particular applications.
- Limited availability: LFP batteries may not be as widely available as other lithium-ion batteries, affecting accessibility and pricing in some markets.
- Larger size and weight: Due to their lower energy density, LFP batteries may require larger dimensions and heavier weights to achieve comparable energy storage capacities, which could be a drawback in space-constrained applications.
- Voltage limitations: LFP batteries have a lower nominal voltage than other lithium-ion chemistries, which may require device design or usage adjustments.
Part 2. What is an NMC battery?
NMC batteries, short for Nickel Manganese Cobalt batteries, are another type of lithium-ion battery widely used in various industries. They utilize a combination of nickel, manganese, and cobalt for their cathode material, offering a different set of advantages and considerations. These batteries are commonly found in electric vehicles, portable electronics like smartphones and laptops, medical devices, and power tools due to their high energy density, compact design, and versatility.
What are the advantages and disadvantages of NMC batteries?
Advantages:
- High energy density: NMC batteries offer a high energy density, meaning they can store much energy in a relatively small space or weight.
- Improved lifespan: NMC batteries have a longer lifespan than other lithium-ion batteries, making them suitable for long-term use in various applications.
- Versatility: Manufacturers can tailor NMC batteries to meet specific energy and power requirements, making them suitable for various applications, from electric vehicles to consumer electronics.
- Fast charging capabilities: NMC batteries charge quickly, allowing for shorter charging times and improved user convenience.
- Enhanced stability: NMC batteries exhibit good thermal stability, reducing the risk of overheating and improving overall safety.
Disadvantages:
- Cost: NMC batteries can be more expensive to manufacture than other lithium-ion chemistries, potentially leading to higher product costs for consumers.
- Limited lifespan at high temperatures: While NMC batteries generally have a good lifespan, exposure to high temperatures can accelerate degradation, reducing overall battery longevity.
- Safety concerns: Although NMC batteries are generally considered safe, there have been thermal runaway and safety issues, primarily when damaged or improperly handled.
- Environmental impact: The production of NMC batteries involves extracting and processing raw materials, which can have ecological implications if not managed responsibly.
- Voltage fade: NMC batteries may experience voltage fade over time, leading to a gradual decrease in capacity and performance, especially after repeated charging cycles.
Part 3. LFP vs. NMC Battery: comparison
Here are some typical comparisons to help you understand the differences between these two battery technologies:
Safety
LFP batteries have a higher safety profile due to their thermal stability and resistance to thermal runaway, making them a more secure choice for applications where safety is paramount.
Cycle Life
LFP batteries exhibit a longer cycle life than NMC batteries, making them suitable for extensive and prolonged applications.
Energy Density
NMC batteries offer a higher energy density, allowing them to store more energy per unit volume or weight, which is advantageous for applications requiring longer-lasting power.
Power Density
LFP batteries have a higher power density, enabling them to deliver a significant amount of power quickly and making them suitable for applications that require rapid energy discharge.
Temperature Tolerance
LFP batteries have a wider temperature range tolerance, allowing them to operate efficiently in harsh environments with extreme temperatures.
Power Capability
NMC batteries excel in power capability, delivering high power output and charging speed performance. They are ideal for applications requiring quick charging or high-power delivery.
Application Suitability
Many prefer LFP batteries in applications where safety and long cycle life are critical, such as energy storage systems and stationary applications. On the other hand, manufacturers commonly use NMC batteries in electric vehicles, portable electronics, and other applications that prioritize energy density and power capability.
Part 4. How to choose between LFP and NMC batteries?
1. Application Type
- LFP batteries: Ideal for energy storage systems, solar power solutions, and industrial equipment where safety, long cycle life, and durability are critical.
- NMC batteries: Better suited for electric vehicles, portable electronics, and devices requiring high energy density and compact designs.
2. Budget
- LFP batteries: Generally more cost-effective over time due to their longer lifespan and reduced maintenance needs.
- NMC batteries: Typically more expensive upfront but can justify the cost for applications that prioritize compact size and high performance.
3. Energy and Power Needs
- LFP batteries: Suitable for applications requiring steady energy output over a long period, such as renewable energy systems or backup power solutions.
- NMC batteries: Preferred for applications demanding high power and energy density, such as electric vehicles and fast-charging devices.
4. Environmental Conditions
- LFP batteries: Perform better in extreme temperatures, making them suitable for outdoor or harsh environments.
- NMC batteries: While reliable, they may degrade faster under high temperatures, requiring careful thermal management in demanding conditions.
5. Safety Requirements
- LFP batteries: A safer option for applications where thermal stability is essential, such as residential energy storage.
- NMC batteries: Safe for most applications, but require more advanced safety management systems, especially in high-stress environments.
6. Sustainability and Environmental Impact
- LFP batteries: More environmentally friendly due to their cobalt-free design and lower ecological footprint during production.
- NMC batteries: Higher environmental concerns due to the use of cobalt and nickel, which require responsible sourcing and recycling measures.
Ultimately, the choice between LFP and NMC batteries will depend on balancing safety, energy needs, cost, and environmental considerations for your specific use case. Consulting a battery expert can further refine your decision to ensure the best fit for your requirements.
Part 5. FAQs
-
Is LFP more expensive than NMC?
LFP batteries are generally less expensive than NMC batteries due to their more straightforward construction and fewer costly materials. -
Is LFP safer than NMC?
Yes, LFP batteries are often considered safer than NMC batteries due to their higher thermal stability, which reduces the risk of overheating and fire hazards. -
Why is NMC over LFP?
Users prefer NMC batteries over LFP batteries for their higher energy density, which allows for more energy storage in a smaller space, making them suitable for applications where space is limited. -
Do LFP batteries last longer?
Yes, LFP batteries generally last longer than NMC batteries. An LFP battery can typically endure around 2000 to 5000 charge cycles, whereas an NMC battery usually lasts around 500 to 1000. -
What is the lifespan of an NMC battery?
The lifespan of an NMC battery is typically around 500 to 1000 charge cycles.
Related Tags:
More Articles

What Is a Disk Battery? A Simple Guide for Non-Tech Users
A disk battery is a small, round cell used in watches, remotes, and other electronic devices. It delivers steady power for compact, low-drain devices.
What Battery Powers a Space Heater?
Discover the type of battery that powers space heaters and learn how to choose the right one for efficient heating in your home or office.
What Is an LR14 Battery? Learn About This C-Size Cell
The LR14 battery, also known as a C battery, delivers steady power. Learn its specs, uses, lifespan, and how it compares to other battery types.
Watch Battery Dimensions Chart: Sizes, Voltages, and Equivalents Explained
Understanding watch battery dimensions helps you choose the right size, voltage, and equivalent model to keep your watch running safely and smoothly.
How Long Can You Rely on Battery-Powered Generators?
Discover battery generator runtime & lifespan factors. Learn how to maximize performance and choose the right power solution.