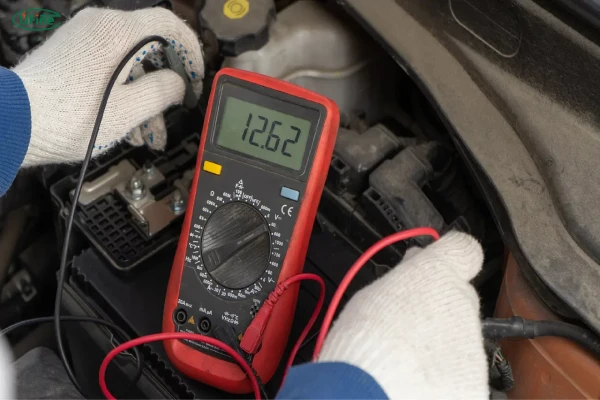
According to industry reports, nearly 70% of vehicle breakdowns are related to battery issues. A failing car battery can leave you stranded at the worst possible time—whether you’re heading to work or embarking on a long road trip. This highlights the importance of auto battery voltage, which is a key indicator of battery health and overall vehicle performance.
Many drivers only think about their battery when their car fails to start, but by regularly checking and maintaining the battery voltage, you can extend battery life, prevent unexpected failures, and ensure optimal vehicle performance. This guide will cover:
- What auto battery voltage is and how it works
- Factors that influence voltage levels
- How to test your car battery’s voltage
- How to prevent voltage drops and extend battery lifespan
- Signs of a failing battery and the best battery brands
Part 1. What is auto battery voltage?
Definition and Basic Functionality
Auto battery voltage refers to the electrical potential difference within a vehicle’s battery, typically measured in volts (V). It represents the energy available to power the car’s electrical components, including the ignition system, lights, radio, and onboard computers.
Most vehicles today use a 12-volt lead-acid battery, though 24V and 48V systems are also common in commercial and hybrid vehicles. However, the actual battery voltage varies depending on whether the car is running, charging, or turned off.
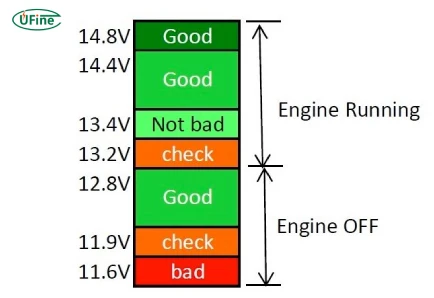
Car Battery Voltage Chart
A healthy car battery should maintain the following voltage levels under different conditions:
| Battery Condition | Voltage (V) |
|---|---|
| Fully Charged (Resting) | 12.6 – 12.8V |
| Partially Charged (50%) | 12.2 – 12.4V |
| Low Charge (25%) | 12.0 – 12.2V |
| Dead Battery | Below 11.8V |
| Charging (Engine Running) | 13.7 – 14.7V |
Part 2. What are the different auto battery voltages?
Different types of vehicles require different battery voltages:
- 12V Batteries – Standard in passenger cars and motorcycles.
- 24V Batteries – Used in heavy-duty trucks, buses, and industrial vehicles.
- 48V Batteries – Found in electric and hybrid vehicles for improved fuel efficiency.
Higher voltage systems (such as 400V or more) are common in fully electric vehicles (EVs) to power high-performance motors.
Part 3. What affects auto battery voltage?
Several factors can influence the voltage of your car battery, potentially leading to power loss and failure:
1. Temperature Extremes
- Cold Weather: Batteries lose efficiency as temperatures drop, leading to slower chemical reactions and reduced voltage. In subzero conditions, a battery can lose up to 50% of its capacity.
- Hot Weather: Excessive heat accelerates battery degradation, causing overcharging and internal damage.
Battery Charging and Discharging at Extreme Temperatures
2. Charging System Efficiency
A failing alternator or voltage regulator can cause an unstable voltage supply, preventing the battery from charging properly.
3. Battery Age and Wear
Batteries degrade over time. After 3-5 years, they may no longer hold a full charge, leading to voltage drops.
4. Parasitic Drains
Even when your car is off, certain electronic systems (such as security systems, onboard computers, and clocks) draw small amounts of power. If excessive, this can cause battery drainage.
5. Corroded or Loose Battery Terminals
Poor connections can increase resistance, leading to voltage drops and starting issues.
6. Frequent Short Trips
If you frequently take short trips, the alternator may not have enough time to fully recharge the battery, leading to gradual voltage depletion.
Part 4. How many volts is a fully charged car battery?
A fully charged 12V battery should read 12.6V to 12.8V when the vehicle is off. If the voltage drops below 12.4V, the battery is partially discharged and may require recharging.
Part 5. Car battery voltage when driving
When the engine is running, the alternator supplies power to charge the battery, maintaining a voltage between 13.7V and 14.7V. If the voltage exceeds 15V, it may indicate an overcharging issue.
Part 6. Car battery voltage when off
When the car is off, a normal battery voltage should range between 12.4V and 12.8V. A reading below 12V suggests that the battery is weak and may struggle to start the engine.
Part 7. What causes auto battery voltage to drop?
A significant drop in voltage can be caused by:
- Leaving lights or electronics on overnight.
- A failing alternator that cannot recharge the battery.
- Battery sulfation, reducing its ability to hold a charge.
- Extreme weather conditions affecting battery chemistry.
- Poor battery maintenance or infrequent use.
Part 8. How to prevent auto battery voltage loss
To extend battery life and maintain proper voltage, consider the following:
- Regularly check battery voltage using a multimeter.
- Turn off unnecessary electronics when the engine is off.
- Keep battery terminals clean to ensure a strong connection.
- Use a battery maintainer for long-term parked vehicles.
- Drive longer distances occasionally to fully recharge the battery.
Part 9. How to test auto battery voltage?
You can test battery voltage using a digital multimeter:
- Set the multimeter to DC volts (20V range).
- Connect the red probe to the positive (+) terminal.
- Connect the black probe to the negative (-) terminal.
- Read the displayed voltage:
- 12.6V – 12.8V → Healthy battery.
- 12.4V – 12.6V → Partially discharged.
- Below 12.0V → Needs charging or replacement.
Part 10. Signs that your car battery voltage is too low
- Slow engine crank.
- Dim or flickering headlights.
- Clicking noise when turning the key.
- Dashboard warning lights.
- Electrical malfunctions.
Part 11. How to tell if your car battery is dead or dying
A failing battery may show these signs:
- Car won’t start despite multiple attempts.
- Requires frequent jump-starts.
- Swollen or leaking battery case.
- Strange electrical behavior, such as radio resets.
Part 12. Best vehicle battery brands
If you’re considering a replacement, these brands offer reliable car batteries:
- Optima Batteries – Known for deep-cycle and high-performance batteries.
- DieHard – Offers long-lasting and durable batteries.
- ACDelco – A popular choice for GM vehicles.
- Odyssey Batteries – High-performance AGM batteries.
Part 13. FAQs
1. What Happens If a Car Battery Voltage is Too High?
Excessive voltage can cause battery swelling, overheating, and electrolyte loss, reducing battery lifespan. High voltage can also damage sensitive electronic components in modern vehicles, such as ECUs, sensors, and infotainment systems.
2. Can a Weak Battery Affect Engine Performance?
Yes, a weak battery with low voltage may cause irregular engine performance, including rough idling, misfires, and reduced fuel efficiency. Since modern cars rely heavily on electrical systems, low voltage can lead to poor sensor readings and inefficient fuel combustion.
3. Does Auto Battery Voltage Drop Over Time Even If the Car is Not Used?
Yes, all car batteries experience self-discharge over time. On average, a healthy lead-acid battery loses about 3-5% of its charge per month. Factors like extreme temperatures and parasitic drains (security systems, clocks, and onboard computers) can accelerate voltage loss.
4. Can Jump-Starting a Car Damage the Battery?
Jump-starting is safe when done correctly, but improper connections or using the wrong voltage can damage the battery and electrical system. Frequent jump-starting also stresses the battery, reducing its lifespan.
5. Does Revving the Engine Increase Battery Voltage?
Yes, revving the engine increases alternator output, temporarily boosting battery voltage. However, this is only a short-term solution. If the battery isn’t holding a charge, it may need replacement.
6. Can I Use a Lithium Battery Instead of a Lead-Acid Battery in My Car?
Yes, lithium car batteries offer higher energy efficiency, lighter weight, and longer lifespan compared to lead-acid batteries. However, they require a battery management system (BMS) to regulate voltage and prevent overcharging. Ufine Battery specializes in custom LiFePO4 and lithium-ion battery solutions for automotive applications.
Related Tags:
More Articles

Stick Up Cam Battery Life: What to Expect and How to Improve It
How long does Stick Up Cam battery last? Learn about battery types, charge time, tips to extend battery life, and how to replace it—simple and easy to follow.
Best Security Camera Batteries: Complete Buying Guide
Find the best security camera battery for your needs. Learn about types, lifespan, charging tips, and how to avoid common battery problems.
ICR18650 Battery Explained: Chemistry, Use Cases, and Limitations
The ICR18650 battery is widely used in electronics. Learn its chemistry, uses, pros, and cons to see if it's right for your device or project.
A Detailed Exploration of Wireless Keyboard Battery
Learn how to choose, maintain, and troubleshoot wireless keyboard batteries. Discover why lithium batteries are the best choice for long-lasting performance.
Best Rechargeable Batteries for Solar Lights: Lithium vs NiMH vs NiCd Compared
Compare lithium-ion, NiMH, and NiCd batteries to find the best rechargeable option for solar lights based on performance, cost, and lifespan.




