- Part 1. What is a battery post adapter?
- Part 2. Why LiFePO₄ batteries use M6/M8 terminals instead of SAE posts?
- Part 3. Types of battery post adapters for LiFePO₄ batteries
- Part 4. Compatibility considerations: How to choose the correct adapter
- Part 5. Safety guidelines before installing an adapter on LiFePO₄ terminals
- Part 6. Common problems when using adapters on LiFePO₄ batteries
- Part 7. When you actually need a battery post adapter for LiFePO₄ batteries
- Part 8. Best practices for long-term reliability
- Part 9. FAQ: Battery post adapter for LiFePO₄ batteries
LiFePO₄ batteries are becoming the preferred choice for RV owners, solar users, marine systems, golf carts, and portable power storage. Their long cycle life, stable chemistry, and lightweight design make them ideal for both off-grid and everyday energy applications. However, LiFePO₄ batteries do not always come with the same terminals found on traditional lead-acid batteries—most use threaded M6 or M8 terminals, not SAE posts.
This creates a challenge for users who need to connect car-style clamps, marine posts, or legacy inverter cables. The solution? A battery post adapter.
But using the wrong adapter—or installing it incorrectly—can damage the battery, increase resistance, or void the warranty. This article explains everything you need to know before using a battery post adapter with a LiFePO₄ battery, including types, compatibility, safety practices, torque guidance, and real-world use cases.
Part 1. What is a battery post adapter?
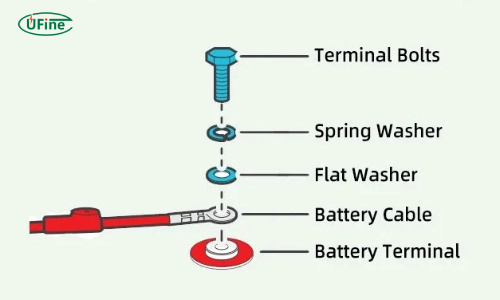
A battery post adapter is a connector that converts one type of battery terminal into another. For LiFePO₄ batteries, most adapters convert:
- M6 → SAE post
- M8 → SAE post
- M6/M8 → stud terminals
- Threaded insert → clamp-compatible post
- Flat lug terminals → ring terminal mounts
LiFePO₄ batteries commonly use threaded metal inserts instead of traditional lead posts because they offer:
- Better vibration resistance
- Higher mechanical strength
- Easier cable management
- More stable current transfer
However, many vehicles and systems still rely on old-style post clamps, so a battery post adapter acts as the “bridge” allowing compatibility.
Part 2. Why LiFePO₄ batteries use M6/M8 terminals instead of SAE posts?
Traditional lead-acid batteries use molded SAE posts because they are easy to clamp and provide a large contact surface.
LiFePO₄ packs, on the other hand, are built differently.
Advantages of threaded M6/M8 terminals- They withstand higher tightening torque
- Less chance of terminal deformation
- They do not crack under load (lead posts are soft)
- Better suited for high-current LiFePO₄ BMS output
- Smaller form factor allows compact battery casing
Most aftermarket accessories—including car clamps, trolling motor cables, RV wires, and jump-start connectors—are designed for SAE posts, not threaded terminals.
Without an adapter, users struggle to attach cables securely. In some cases, the connection becomes unsafe due to:
- Too-small contact area
- Loose ring terminals
- Wrong bolt length
- Unstable pressure from clamps
- Battery terminals being overtightened
A battery post adapter solves these issues—if selected correctly.
Part 3. Types of battery post adapters for LiFePO₄ batteries
Not all adapters are equal. Choosing the correct type matters for safety and performance.
1. M8 → SAE post adapters (most common)Used for:
- 12V 50Ah–200Ah LiFePO₄ batteries
- RV, camping, marine, trolling motor systems
- Solar storage power stations
Used for:
- Small LiFePO₄ packs (6Ah–20Ah)
- Portable power devices
- Motorcycles and small scooters
Best for:
- High-current inverter cables
- DC distribution blocks
- Solar charge controllers
- Used where space is limited (battery boxes, RV compartments).
Used for:
- Multi-battery systems
- Parallel bank setups
- Solar + marine installations
- Preferred when cable routing needs to change direction or height.
Artikel Terkait: Battery Post Adapter Sizing Chart
Part 4. Compatibility considerations: How to choose the correct adapter
To safely use a battery post adapter with a LiFePO₄ battery, consider the following:
1. Terminal size (M6 vs M8)Always check your battery’s user manual or label.
Most LiFePO₄ batteries use:
- M6 terminals → 10Ah–20Ah models
- M8 terminals → 30Ah–200Ah models
Using the wrong bolt size may strip the threads.
2. Bolt length and thread depth
A common mistake is using a bolt that is too long, which bottoms out inside the battery terminal and cracks the insert.
General rule:
- Use bolts supplied by the battery manufacturer
- Recommended thread engagement: 70–90% of hole depth
Best materials:
- Copper
- Tin-plated copper
- Brass
- Aluminum → high resistance
- Steel → rust + low conductivity
High-current applications require:
- Larger contact surface
- High-conductivity metals
- Stable mechanical fastening
For example:
- 2000W inverter → M8 or busbar adapter
- Trolling motor → M8 preferred
- Tiny LiFePO₄ → M6 sufficient
If you’re connecting:
- Automotive clamps → choose SAE adapters
- Ring terminals → use stud adapters
- Inverter lugs → choose copper busbars
Marine or outdoor use requires:
- Anti-corrosion plating
- Waterproof seals
- Vibration-resistant hardware
Part 5. Safety guidelines before installing an adapter on LiFePO₄ terminals
Improper installation is one of the main reasons lithium battery terminals fail. Follow these safety rules before installing any adapter.
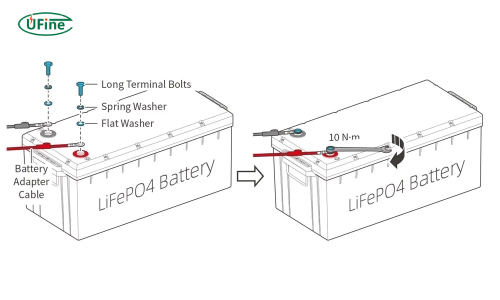
1. Never overtighten the boltLiFePO₄ threaded inserts—usually stainless steel or brass—can crack if excessive torque is applied.
General torque guidelines:
- M6 terminal → 3–5 N·m
- M8 terminal → 6–9 N·m
Manufacturers often include:
- Proper bolt length
- Correct thread pitch
- Corrosion-resistant material
Avoid hardware store bolts unless identical specifications are confirmed.
3. Ensure flat, clean contact surfacesDirty or uneven surfaces cause:
- Heat buildup
- Voltage drop
- Sparks
Multiple stacked lugs reduce contact pressure on the terminal.
If stacking is unavoidable:
- Use a busbar
- Use longer bolts recommended by the manufacturer
- High-gauge wires can pull sideways on adapters, leading to terminal loosening.
- Use cable ties or brackets to relieve stress.
- Old-style lead clamps can apply uneven pressure, damaging SAE adapters on lithium batteries.
Part 6. Common problems when using adapters on LiFePO₄ batteries
- ❌ Increased electrical resistance
- Poor-fitting adapters lead to heat, voltage drop, or inefficiency.
- ❌ Terminal rotation or thread stripping
- Often caused by overtightening or incorrect bolt length.
- ❌ Galvanic corrosion
- Occurs when dissimilar metals contact each other.
- Solution: use tin-plated copper adapters.
- ❌ Adapter loosening due to vibration
- Common in:
- Boats
- ATVs
- RVs
- Use lock washers or thread-lock compounds approved for electrical systems.
- ❌ Warranty issues
- Some battery manufacturers specify acceptable adapters; others do not.
- Always verify before modification.
Part 7. When you actually need a battery post adapter for LiFePO₄ batteries
You should use an adapter when:
- Your system uses automotive clamps
- Traditional clamps require SAE posts.
- You replaced a lead-acid battery with LiFePO₄
- Most lead-acid models use SAE posts; lithium uses M8.
- You are connecting an inverter with large lugs
- Adapters help create a secure connection.
- You need to raise terminal height
- Battery boxes sometimes require elevated posts for access.
- You are converting to a custom cable layout
- Adapters allow more flexibility in routing.
You do not need an adapter when:
- Your system uses ring terminals
- You have dedicated M6/M8 lugs
- You are wiring a low-current device
- Your manufacturer prohibits post adapters
Part 8. Best practices for long-term reliability
- Use dielectric grease
- Prevents corrosion and improves contact stability.
- Re-check torque every 6–12 months
- Especially important for high-current installations.
- Use high-purity copper or tin-plated adapters
- Reduces resistance and overheating.
- Avoid quick-release automotive clamps
- They can deform adapter posts.
- Constantly check for heat
- Warm terminals indicate a bad connection.
Part 9. FAQ: Battery post adapter for LiFePO₄ batteries
Can using a battery post adapter damage a LiFePO₄ battery?
Yes—if overtightened, incorrectly sized, or made from poor materials. Proper torque and compatible adapters prevent damage.
Do LiFePO₄ batteries support automotive-style SAE clamps?
Not directly. Most require an M6/M8 → SAE adapter to use automotive clamps safely.
What material is best for LiFePO₄ battery post adapters?
Tin-plated copper and brass are ideal due to high conductivity and corrosion resistance.
Should I use thread-lock compound when installing adapters?
Yes, but only non-conductive, vibration-safe thread-lock approved for electrical connections.
Can I use one adapter for both positive and negative terminals?
Yes—as long as the adapter size (M6 or M8) matches each terminal. Polarity does not affect adapter design.
Related Tags:
More Articles

Battery Post Adapter Sizing Chart (SAE, JIS, M6, M8): What Fits Your Application?
Find the right battery post adapter with our sizing chart for SAE, JIS, M6, and M8 terminals. Ensure compatibility with your lithium battery setup.
Battery Post Adapter Guide: Types, Compatibility, and When You Actually Need One
Learn about battery post adapters, their types, and compatibility with M6, M8, and SAE terminals for lithium batteries, including how to choose the right fit.
How to Choose & Maintain the Perfect Moped Battery
Discover the right moped battery, replacement tips, and maintenance strategies for peak performance.
Comprehensive Understanding of 7.4 V Battery [Updated in 2025]
Discover the world of 7.4V batteries - from understanding the differences to learning how to charge and use them effectively. Dive into this comprehensive guide now!
Hydride Battery Explained: Benefits, Uses & Charging Tips
Understand hydride battery operation, lifespan, and maintenance. Find out how NiMH batteries power modern devices and hybrid cars.