Part 1. What is a prismatic(LiFePO4) battery?
A prismatic battery is a rechargeable battery with a rectangular or square shape. Unlike cylindrical batteries, which are round, prismatic batteries are designed to maximize the use of space within a device.
Prismatic battery cells satisfy the demand for thinner, flat geometries. Prismatic cells use space optimally by layering versus the traditional jelly roll style.
This shape allows for more efficient packing and better usage of the available volume. These batteries are commonly seen in applications where space optimization and energy density are critical, such as electric vehicles, consumer electronics, and large-scale energy storage systems.
- High working voltage (3.7V)
- High energy density
- Long life cycle (more than 500 cycles)
- Agile shape & dimension
- No memory effect
- Low self discharge
- Environmental friendly
Key Features
- Safety: LiFePO4 batteries are known for their thermal stability and low risk of thermal runaway compared to other lithium-ion batteries.
- Cycle Life: They have a long cycle life, often exceeding 2,000 cycles, making them suitable for applications requiring durability.
- Energy Density: While they have lower energy density compared to other lithium-ion chemistries (like LiCoO2), they offer a good balance of performance, cost, and safety.
Part 2. How does prismatic LiFePO4 battery work?
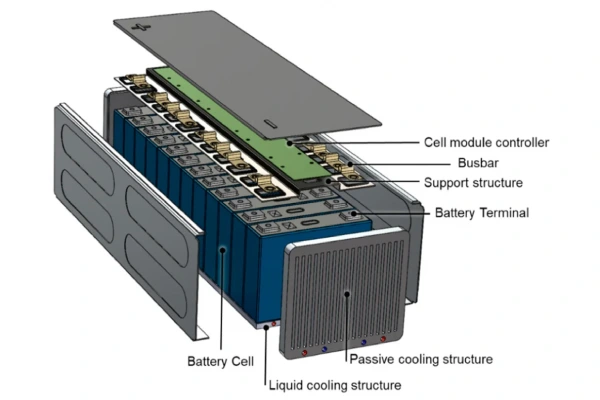
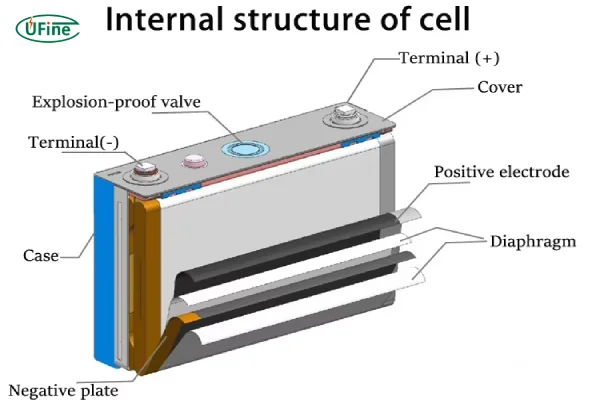
1.Prismatic battery structure
Understanding the structure of a prismatic battery can help you appreciate its efficiency and functionality.
Here are the main components:
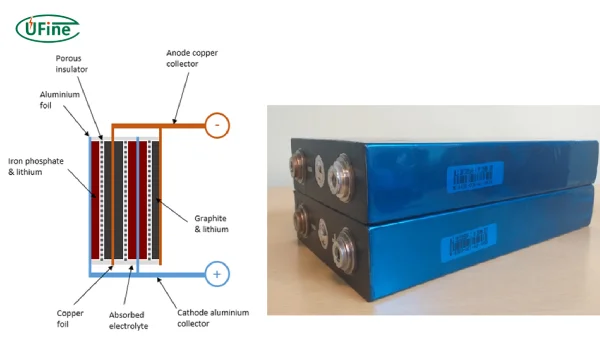
- Anode: The negative electrode, usually made from graphite. It stores lithium ions during charging.
- Cathode: The positive electrode, often made from lithium cobalt oxide or other lithium compounds. It releases lithium ions during discharging.
- Electrolyte: A liquid or gel substance that facilitates the movement of lithium ions between the anode and cathode. This electrolyte is crucial for the battery’s operation.
- Separator: A thin, porous membrane that keeps the anode and cathode apart while allowing ions to pass through. It prevents short circuits within the battery.
- Casing: The outer shell, typically made from aluminum or steel, which provides protection and structural integrity. It ensures the components remain in place and safe from external damage.
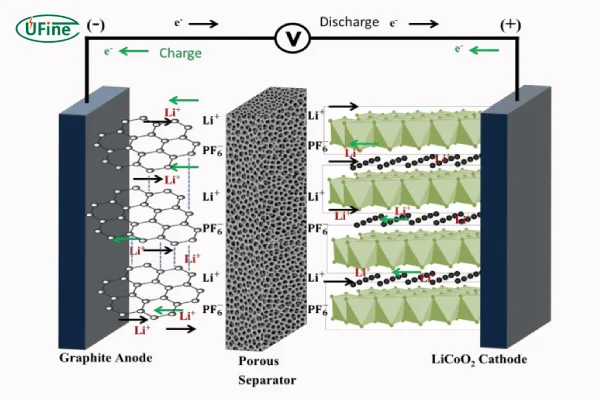
2. Working Principle
Charging:
- When the battery is charged, lithium ions move from the cathode (LiFePO4) through the electrolyte and separator to the anode (graphite).
- Electrons flow from the cathode to the anode through an external circuit, creating electrical energy.
Discharging:
- During discharge, the process reverses: lithium ions move back from the anode to the cathode through the electrolyte.
- Electrons flow from the anode to the cathode through the external circuit, providing power to the connected device.
Part 3. Prismatic battery types
Prismatic batteries can be classified based on the chemical materials used in their construction.
Here are some common types:
- Lithium Iron Phosphate (LiFePO4): Known for its stability and long cycle life, it is ideal for high-power applications.
- Lithium Cobalt Oxide (LiCoO2): Offers high energy density, commonly used in consumer electronics like laptops and smartphones.
- Lithium Manganese Oxide (LiMn2O4): Provides a good balance between cost, safety, and performance, suitable for power tools and electric bikes.
- Nickel Manganese Cobalt Oxide (NMC): Known for excellent performance and energy density, it is widely used in electric vehicles and energy storage systems.
- Nickel Cobalt Aluminum Oxide (NCA): Offers high energy density and a long lifespan and is often used in high-end electric vehicles.
Part 4. Where is the prismatic (LFP) battery used?
1. Electric Vehicles (EVs)
- Widely used in electric cars, buses, and trucks for their safety and longevity.
- Suitable for applications where weight and space are critical.
2. Energy Storage Systems
- Employed in residential and commercial energy storage solutions, particularly for solar energy storage.
- Used in grid-scale energy storage to balance supply and demand.
3. Power Tools
Commonly found in cordless power tools due to their robustness and ability to handle high discharge rates.
4. Electric Bicycles and Scooters
Popular in e-bikes and e-scooters for their lightweight and compact design.
5. Backup Power Systems
Utilized in uninterruptible power supplies (UPS) and backup power systems for critical applications.
6. Telecommunications
Used in telecommunications equipment for backup power to ensure reliability during outages.
7. Medical Equipment
Found in portable medical devices that require reliable and safe power sources.
8. Robotics and Drones
Used in robotic systems and drones for their high energy density and safety characteristics.
Part 5. Prismatic battery advantages and disadvantages
Advantages
- High Energy Density: Prismatic batteries can store a significant amount of energy in a compact space, making them ideal for applications where space is a premium.
- Space Efficiency: Their rectangular shape allows for better utilization of available space within devices, leading to more compact designs.
- Safety: Due to their robust casing and well-structured internal components, prismatic batteries are generally safer and less prone to issues like leakage or thermal runaway.
- Long Cycle Life: Prismatic batteries are designed to endure many charge-discharge cycles, making them a durable choice for long-term use.
- Thermal Management: The flat surfaces of prismatic batteries make it easier to implement cooling systems, which is crucial for maintaining performance and safety in high-power applications.
Disadvantages
- Cost: Prismatic batteries are often more expensive to manufacture compared to other types, such as cylindrical batteries.
- Weight: They tend to be heavier, which can be a disadvantage in applications where weight is a critical factor.
- Manufacturing Complexity: Producing prismatic batteries can be more challenging, requiring precise engineering and quality control to ensure consistent performance.
- Limited Flexibility: Their rigid shape offers less flexibility in terms of design modifications compared to pouch batteries, which can be more easily tailored to fit different device shapes.
Part 6. Prismatic battery vs. pouch Battery vs. cylindrical battery
To understand where prismatic batteries stand in comparison to other battery types, let’s take a closer look at their differences:
| Criteria | Prismatic LFP Battery | Pouch Battery | Cylindrical Battery |
|---|---|---|---|
| Form Factor | Flat, rectangular design | Flexible, flat, and lightweight | Cylindrical, rigid structure |
| Energy Density | Moderate (90-160 Wh/kg) | Higher (150-250 Wh/kg) | Moderate to high (150-250 Wh/kg) |
| Thermal Management | Good thermal stability | Requires careful thermal management | Good thermal management |
| Manufacturing Cost | Generally higher | Lower manufacturing cost | Lower manufacturing cost |
| Cycle Life | Excellent (up to 3,000 cycles) | Moderate (up to 1,500 cycles) | Good (up to 1,000 cycles) |
| Safety | Very safe, low risk of thermal runaway | Moderate risk if punctured | Moderate risk of thermal runaway |
| Applications | Used in EVs, energy storage | Common in smartphones, tablets | Widely used in laptops, power tools |
Form Factor:
Prismatic batteries are flat and rectangular, making them suitable for space-constrained applications. Pouch batteries are flexible and lightweight, allowing for custom shapes. Cylindrical batteries have a standard round shape and are robust.
Energy Density:
Pouch and cylindrical batteries generally offer higher energy densities compared to prismatic LFP batteries, making them more suitable for applications where weight and space are critical.
Thermal Management:
Prismatic LFP batteries excel in thermal stability, reducing the risk of overheating. Pouch batteries need careful thermal management, while cylindrical batteries offer moderate thermal handling capabilities.
Manufacturing Cost:
Prismatic batteries tend to have higher manufacturing costs due to their complex design. Pouch batteries are cheaper to produce, while cylindrical batteries benefit from economies of scale.
Cycle Life:
Prismatic LFP batteries have an excellent cycle life, making them ideal for applications requiring long-term usage. Pouch batteries have a shorter cycle life, while cylindrical batteries offer moderate longevity.
Safety:
Prismatic LFP batteries are very safe, with a low risk of thermal runaway. Pouch batteries may pose a higher risk if damaged, while cylindrical batteries are generally robust but can still face safety issues under extreme conditions.
Applications:
Prismatic LFP batteries are commonly used in electric vehicles and energy storage systems. Pouch batteries are found in portable electronics, and cylindrical batteries are prevalent in various consumer electronics and power tools.
Part 7. Prismatic battery and LiFePO4 battery
Are All Prismatic Batteries LiFePO4?
Not all prismatic batteries use Lithium Iron Phosphate (LiFePO4) chemistry. Prismatic batteries can employ various chemistries such as NMC (Nickel Manganese Cobalt Oxide), NCA (Nickel Cobalt Aluminum Oxide), and others, each tailored to specific performance requirements and applications.
Are All LiFePO4 Batteries Prismatic?
LiFePO4 batteries come in different shapes and sizes, including cylindrical and pouch formats. The choice of shape depends on the application and the design requirements of the device they will be used in.
Part 8. Conclusion
Prismatic batteries play a crucial role in modern technology, offering high energy density, space efficiency, and safety. Their unique rectangular shape makes them ideal for various applications, from electric vehicles to consumer electronics and large-scale energy storage systems. Understanding their structure, types, and advantages helps appreciate why they are preferred in many high-performance applications.
Whether you’re considering them for a new tech gadget or a large-scale energy solution, prismatic batteries offer a robust and efficient power source that continues to evolve with advancements in battery technology.
Related Tags:
More Articles

LiPo Battery Discharge Rate Guide & Calculation Tips
Understand LiPo battery discharge rates, C-ratings, and how to calculate max current. Essential guide for RC, drones, and electronics users.
High‑Capacity 3S LiPo Batteries: 5000 mAh vs. 10000 mAh
Compare 3S LiPo 5000mAh vs 10000mAh batteries by weight, power, and use. Find the best fit for your drone, RC car, or boat setup.
Top 5 Applications for Small 3S LiPo Batteries
Small 3S LiPo batteries power drones, RC gear, wearables, and robotics with high energy and low weight. Making them ideal for compact electronics projects.
Building and Charging Your Own 3S LiPo Pack: A Step‑by‑Step Guide
Learn how to build, balance, and charge a 3S LiPo battery pack safely at home with this complete DIY guide for hobbyists and beginners.
How to Choose the Right LiPo Battery Plug Type?
Discover the best LiPo battery plug types, how to choose them, and expert tips for safe usage, soldering, and maintenance.