- Part 1. Voltage vs current: Core comparison
- Part 2. What is battery voltage?
- Part 3. What is battery current?
- Part 4. Difference between voltage and current
- Part 5. Practical applications comparison
- Part 6. Relationship between voltage and current
- Part 7. FAQs about voltage vs current
- Part 8. Conclusion
Part 1. Voltage vs current: Core comparison
| Voltage | Current | |
|---|---|---|
| Symbol | V | I |
| Unit | Volts (V) | Amperes (A) |
| Measurement | Voltmeter | Ammeter |
| Nature | Potential Energy | Charge Flow |
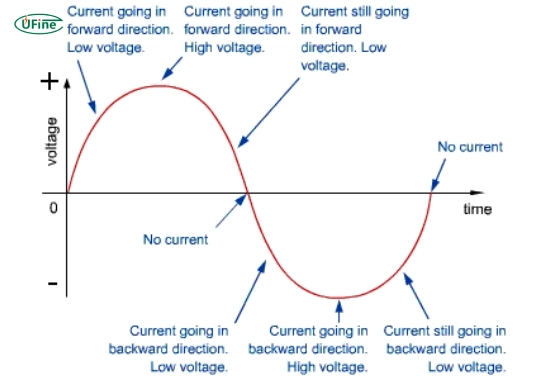
voltage vs current flow diagram
Two fundamental concepts are crucial in electrical circuits and devices: voltage vs current. Understanding their differences and how they relate to each other is essential for anyone delving into the world of electronics. This comprehensive guide will explore the disparities between voltage and current, their definitions, and their significance in various applications.
Part 2. What is battery voltage?
Voltage, often called electric potential difference, measures the electric potential energy per unit charge within a circuit. In simpler terms, it represents the force that drives electrical current through a conductor. Battery voltage refers to the electromotive force (EMF) generated by a battery, which provides the necessary energy to power electrical devices.
When we talk about battery voltage, we are essentially discussing the potential energy difference between the positive and negative terminals of the battery. This potential difference creates an electric field that propels the flow of electrons, thereby enabling the transfer of electrical energy from the battery to connected devices.
Part 3. What is battery current?
On the other hand, current is the flow of electric charge through a conductor or circuit. It is measured in units called amperes (A) and is represented by the symbol ” I .”The voltage drives current in a circuit, directly proportional to the voltage applied and inversely proportional to the resistance encountered.
In the context of batteries, current refers to the flow of electrons from the battery’s negative terminal to its positive terminal. The electrons, propelled by the voltage difference, travel through the circuit, powering electrical components along the way.
Part 4. Difference between voltage and current
While voltage and current are closely related, they represent distinct aspects of electrical systems. Understanding their differences is crucial for comprehending the behavior and functioning of circuits. Here are the critical disparities between voltage and current:
1. Definition:
Voltage is the difference in electric potential or the force that drives current flow. It is measured in volts (V). On the other hand, current is the actual flow of electric charge and is measured in amperes (A).
2. Nature:
Voltage is a scalar quantity with magnitude but no specific direction. Current, however, is a vector quantity, as it has both magnitude and direction.
3. Representation:
Voltage is typically represented by the symbol “V,” while current is denoted by “I.”
4. Role:
Voltage serves as the driving force for current flow. It provides the necessary energy to move electrons through a circuit. Current, on the other hand, represents the actual flow of electrons.
5. Measurement:
Voltage is measured using a voltmeter, while current is calculated using an ammeter.
6. Dependency:
Voltage and current are interdependent but distinct. Voltage creates an electric field that propels the current flow. In contrast, current depends on the voltage applied and the resistance encountered in the circuit.
Real-World Analogy: Water Pipe System
To better understand voltage vs current:
- ⚡ Voltage = Water Pressure (force pushing water)
- 💧 Current = Flow Rate (gallons per minute)
- 🔧 Resistance = Pipe Narrowness
This analogy explains why high voltage with low current (like static shock) is less dangerous than low voltage with high current (car battery).
Part 5. Practical applications comparison
Where Voltage Matters Most:
- ⚡ Power Grids (High Voltage Transmission)
- 🔋 Battery Specifications (12V car battery)
- 💡 LED Lighting (Forward Voltage Requirements)
Where Current is Critical:
- 🔌 Circuit Breaker Ratings
- 🔋 Charging Speed (Fast Chargers)
- ⚡ Electric Vehicle Motors
Part 6. Relationship between voltage and current
Let’s explore how voltage and current are connected and how changes in one affect the other:
Direct Proportionality:
- Voltage and current are directly proportional. This means that as voltage increases, current increases, and vice versa, assuming other factors remain constant.
- For example, suppose the voltage across a circuit is doubled. The current flowing through the circuit will double, provided the resistance remains the same.
Ohm’s Law:
- Ohm’s Law describes the relationship between voltage, current, and resistance in a circuit. It states that the current flowing through a circuit is directly proportional to the voltage applied and inversely proportional to the resistance encountered.
- Mathematically, Ohm’s Law can be expressed as I = V / R.
- Here, I represents the current in amperes (A), V represents the voltage in volts (V), and R represents the resistance in ohms (Ω).
Resistance Influence:
- Changes in resistance can impact the relationship between voltage and current.
- If resistance increases while voltage remains constant, the current will decrease. This is because higher resistance restricts the flow of electrons, resulting in a decrease in current.
- Conversely, the current will increase if resistance decreases while voltage remains constant. With lower resistance, there is less hindrance to the movement of electrons, leading to an increase in current.
Power Calculation:
- Voltage and current are crucial for calculating power in an electrical circuit.
- Power, measured in watts (W), is the product of voltage and current: P = V * I.
- This relationship highlights that both voltage and current play a significant role in determining the amount of power consumed or delivered by a circuit.
Series and Parallel Circuits:
- In series circuits, voltage is divided among the components, while the current remains the same throughout the circuit. The sum of the voltages across individual components equals the total voltage applied.
- In parallel circuits, the voltage remains constant across each branch while the total current is divided among the components. The sum of the currents in each branch equals the total current flowing into the circuit.
Part 7. FAQs about voltage vs current
Can voltage exist without current?
No, voltage requires a closed circuit to produce current. In an open circuit (e.g., an unconnected battery), voltage can exist without current flow. This is commonly observed when a switch is turned off.
Does higher voltage mean higher current?
Under the same resistance, voltage and current are directly proportional (Ohm’s Law). For example, in a circuit with 10Ω resistance, increasing voltage from 12V to 24V will raise the current from 1.2A to 2.4A. However, in high-impedance circuits (e.g., insulators), even high voltage may result in negligible current.
What is the difference between current and electricity?
Current is the carrier of electrical energy, specifically the directional flow of charge (unit: ampere). Electricity is a broader concept encompassing all electromagnetic phenomena, including voltage, current, and resistance. Analogously, current is like water flow, while electricity represents the entire hydraulic system.
What happens if the voltage is too high?
Excessive voltage poses three main risks: 1) Component breakdown (e.g., capacitor explosion), 2) Insulation failure (potentially causing short circuits), and 3) Device overheating (Joule’s Law: Q=I²Rt). For instance, connecting a 5V device to a 12V power supply may instantly damage the circuit board.
Is energy a current or voltage?
Electrical energy is the product of voltage and current (P=VI). Specifically, voltage represents energy per unit charge (joules/coulomb), current is the rate of charge flow (coulombs/second), and their product yields power (joules/second = watts). This explains why high-voltage transmission uses high voltage and low current to minimize energy loss.
Which is more dangerous: high voltage or high current?
Human injury primarily depends on current magnitude. As little as 0.005A (5mA) can cause an electric shock sensation, while 0.1A (100mA) can be fatal. However, according to Ohm’s Law (I=V/R), with human body resistance around 100kΩ, 50V can only produce 0.0005A current. Therefore, safety standards classify voltages above 50V as hazardous.
Part 8. Conclusion
In conclusion, voltage and current are integral components of electrical systems. Voltage represents the electric potential difference that drives current flow, while current signifies the actual flow of electric charge. Understanding the disparities between voltage and current and their interdependence is essential for comprehending the behavior of electrical circuits and devices.
Related Tags:
More Articles

Battery Boosters: How They Work and Choosing the Best
What is a battery booster? Learn how battery boosters work, key types, applications, and how to choose the right booster battery for vehicles and equipment.
Top Rated 18650 Batteries In 2026: Expert Recommendations
Compare top rated 18650 batteries in 2026 by capacity, discharge rate, and use. Expert recommendations on choosing reliable 18650 cells and battery packs.
Ternary Battery or LFP Battery: How to Choose for EV?
Compare ternary lithium battery vs LiFePO4 for EVs. Learn differences in range, safety, cost, cycle life, and which battery suits your driving needs.
8 Lithium Battery Parameters You Should Understand Before Use
A clear guide to lithium battery parameters, including capacity, voltage, C-rate, energy density, cycle life, internal resistance, and temperature range.
Top 10 Lithium Motorcycle Batteries for Optimal Performance
Compare the best lithium motorcycle batteries for 2026, including LiFePO4 vs lead-acid, lifespan, CCA ratings, cold-start performance, and expert buying tips.