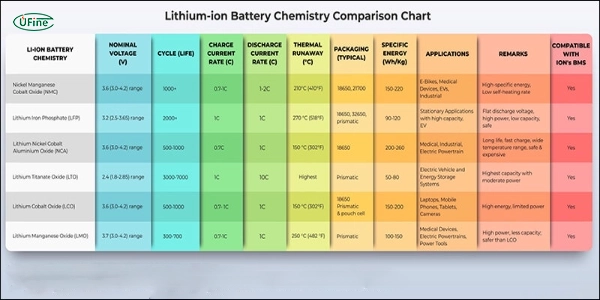
Types of lithium-ion batteries are primarily categorized by their cathode materials, which determine their performance, safety, and applications. This comprehensive guide compares 7 major lithium battery chemistries, including LiFePO4, NMC, LCO, and more, with detailed specifications and real-world use cases.
Part 1. 7 Major lithium battery types comparison
| Type | Energy Density | Cycle Life | Safety | Best Applications | Cost Level |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LCO (LiCoO2) | 150-200 Wh/kg | 500-1000 | Medium | Smartphones, Laptops | $$$ |
| LMO (LiMn2O4) | 100-150 Wh/kg | 300-700 | High | Power Tools, Medical | $$ |
| NMC (LiNiMnCoO2) | 150-220 Wh/kg | 1000-2000 | Medium | EVs, Energy Storage | $$ |
| NCA (LiNiCoAlO2) | 200-260 Wh/kg | 500+ | Low | Electric Vehicles | $$$$ |
| LiFePO4 | 90-120 Wh/kg | 2500+ | Very High | Solar Storage, UPS | $$ |
| LTO (Li4Ti5O12) | 50-80 Wh/kg | 3000-7000 | Extreme | Industrial Equipment | $$$$ |
*Cost levels: $=Lowest, $$$$=Highest
Part 2. Lithium cobalt oxide battery (LiCoO2)
Lithium cobalt acid battery is a type of lithium-ion battery. There are also lithium manganate, lithium ternary, and lithium iron phosphate batteries. The lithium cobalt acid battery is best at charging. It has a stable structure, holds a lot of power, and works really well. But it’s not very safe and costs a lot. It’s mostly used in small and medium-sized devices.
LCO Battery Parameters
- Nominal voltage: 3.6V
- Operating voltage: 3V-4.2V
- Specific energy: 150 Wh/kg to 200 Wh/kg
- Charging rate: 0.7-1C, usually charged to 4.2V within 3 hours
- Discharge rate: 1C, cut-off voltage is 2.5V. Discharge currents above 1C will shorten battery life.
- Cycle life: 500 to 1000 cycles
- Thermal runaway: 150℃
LCO Battery Advantages
- Excellent electrochemical performance
- Excellent processing performance
- The high density of vibration helps to improve the specific volume capacity of the battery
- Product performance is stable, with good consistency
LCO Battery Disadvantages
- Low energy density
- Prone to thermal runaway problems
- High manufacturing cost
LCO Battery use
Lithium cobalt oxide batteries are mainly used as cathode materials for lithium-ion batteries used in manufacturing mobile phones, laptops, and other portable electronic devices.
Part 3. Lithium manganate battery (LiMn2O4)
A lithium manganate battery uses lithium manganate for its positive part. This battery is cheap, safe, and used frequently. The way lithium manganate is made, and its properties depend on the materials and how it’s processed. Different ways of making it can change how well it works in batteries.
LMO battery parameters
- Nominal voltage: 3.7V
- Operating voltage: 3V-4.2V
- Specific energy: 100 Wh/kg to 150 Wh/kg
- Charging rate: 0.7-1C, usually charged to 4.2V within 3 hours
- Discharge rate: 1C, cut-off voltage is 2.5V.
- Cycle life: 300 to 700 cycles
- Thermal runaway: 250℃
LMO battery advantages
- High thermal stability and improved safety
- Low internal battery resistance enables fast charging and high current discharge
- Low-temperature resistance, good magnification performance, easy preparation
LMO battery disadvantages
- Low energy storage capacity
- Short cycle life
- Sensitive to high-temperature
LMO battery use
Lithium manganate is used in power tools, medical devices, and hybrid and pure electric vehicles.
Part 4. Lithium nickel-cobalt-manganate battery (LiNiMnCoO2 or NMC)
Lithium nickel-cobalt manganate is a battery material that uses less expensive nickel and manganese instead of a lot of cobalt. This makes it cheaper. It works almost as well as lithium cobaltate in batteries. It’s becoming a new material for batteries and is slowly replacing lithium cobaltate.
NMC battery parameters
- Nominal voltage: 3.6V
- Operating voltage: 3V-4.2V
- Specific energy: 150 Wh/kg to 220 Wh/kg
- Charging rate: 0.7-1C, usually charged to 4.2V within 3 hours
- Discharge rate: 1C, cut-off voltage is 2.5V; 2C May work on some cells
- Cycle life: 1000 to 2000 times
- Thermal runaway: 210℃
NMC battery advantages
- High energy density, high voltage platform
- Good cycle performance and long service life
- Self-discharge is small and has no memory effect
NMC battery disadvantages
- Sensitive to high-temperature
- Prone to thermal runaway
- The extraction of nickel and manganese may affect the environment
NMC battery use
In the fields of new energy vehicles, electric vehicles, air tools, energy storage, intelligent vacuum cleaners, drones, intelligent wearable devices, and so on.
Part 5. Lithium nickel-cobalt aluminate battery (LiNiCoAlO2 or NCA)
Lithium nickel-cobalt aluminate batteries or Ncas have been used since 1999. It has a high specific energy, quite good specific power, and a long service life similar to NMC. Less flattering are security and cost.
NCA battery parameters
- Nominal voltage: 3.6V
- Operating voltage: 3V-4.2V
- Specific energy: 200 Wh/kg to 260 Wh/kg
- Charge rate: 0.7, usually charged to 4.2V in 3 hours
- Discharge rate: 1C, cut-off voltage is 3V
- Cycle life: 500 times
- Thermal runaway: 150℃
NCA battery advantages
- High energy density, high voltage platform
- Good cycle performance and long service life
- Self-discharge is small and has no memory effect
NCA battery Disadvantages
- High production cost
- Sensitive to high-temperature
- The extraction and processing of nickel, cobalt, and aluminum has environmental impacts
NCA battery use
NCA is generally used for electric vehicles.
Part 6. Lithium iron phosphate Battery (LiFePO4)
Lithium iron phosphate battery is a kind of lithium battery, like the battery used in our mobile phone. The positive electrode material of a lithium iron phosphate battery is mainly phosphorus, acid, iron, and lithium compound.
LiFePO4 battery parameters
- Nominal voltage: 3.2V
- Operating voltage: 2.5V-3.65V
- Specific energy: 90 Wh/kg to 120 Wh/kg
- Charging rate: 0.7-1C, usually charged to 3.65V within 3 hours
- Discharge rate: 1C, cut-off voltage is 2-2.5V; Some cells can be 25C
- Cycle life: 2500 times
- Thermal runaway: 270℃
LiFePO4 battery advantages
- High safety performance
- Long service life
- Good high-temperature performance
- Large capacity
- No memory effect
LiFePO4 battery disadvantages
- The positive electrode of the battery has a small vibration density
- With poor electrical conductivity, the lithium-ion diffusion rate is slow.
- Poor low-temperature performance
- Battery pack life is short
LiFePO4 battery battery use
Because the lithium iron phosphate power battery has the above characteristics, it has many applications. For example: large electric vehicles, power tools, solar and wind power energy storage equipment, UPS and emergency lights, warning lights, and mining lights instead of small medical equipment and portable instruments.
Part 7. Lithium titanate battery (Li4Ti5O12)
Lithium titanate replaces graphite in the anode of a typical lithium-ion battery, and the material forms a spinel structure. The cathode can be lithium manganate or NMC.
LTO battery parameters
- Nominal voltage: 2.4V
- Operating voltage: 2.5V-3.65V
- Specific energy: 50 Wh/kg to 80 Wh/kg
- Charging rate: 0.7-1C, usually charged to 3.65V within 3 hours
- Discharge rate: 10C, cut-off voltage is 1.8V
- Cycle life: 3000-7000 times
- Thermal runaway: 175℃ to 225℃
LTO battery advantages
- Ultra-high security
- Ultra-long life
- Wide range of high and low-temperature operation
- High power
- ow-cost
- Green and environmental protection
LTO battery Disadvantages
- Lithium titanate materials have low energy density
- Strong water absorption
- Battery production has high environmental requirements
LTO battery battery use
The battery is generally used in UPS, electric powertrains, and solar streetlights.
Part 8. How to choose the right lithium battery type?
Follow this decision flowchart to select the optimal battery technology:
Step 1: Define Priority Requirements
- High Energy Density: Choose NMC (220 Wh/kg) or NCA (260 Wh/kg)
- Safety First: Opt for LiFePO4 (270℃ thermal stability) or LTO
- Extreme Longevity: LTO batteries (7,000+ cycles)
- Budget-Conscious: LMO or standard Li-ion
Step 2: Consider Operating Conditions
| Environment | Recommended Type |
|---|---|
| High Temperatures (>45℃) | LiFePO4 or LMO |
| Low Temperatures (<-20℃) | LTO with heating system |
| High Vibration | Prismatic LiFePO4 cells |
Real-World Application Examples
- EV Conversion: NMC pouch cells (Tesla Model 3)
- Home Energy Storage: LiFePO4 wall-mounted systems
- Aviation: Ultra-light LCO batteries
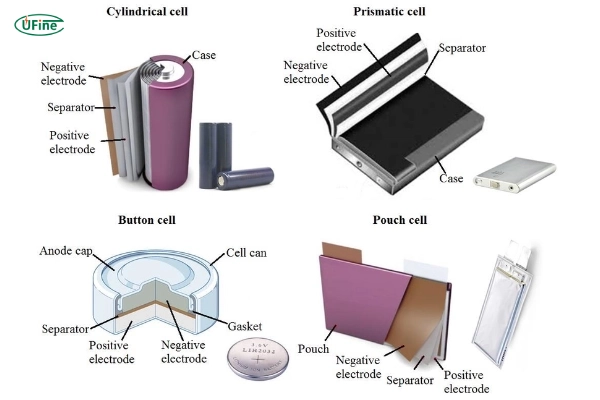
Part 9. Lithium-ion cell morphology classification
In addition to classifying positive and negative battery materials, we can divide them according to the shell material, shape, and cell.
By shell material
- Steel battery: as the name suggests, the shell is steel.
- Aluminum shell battery: the same shell is aluminum material.
- Polymer lithium battery: The shell is a polymer material, mostly silver. A few manufacturers do black, and the industry has become black.
By shape
- Cylindrical batteries, like 18650, 26650, and so on, are used in this general combination a lot. Few combinations, like early laptops, can be used as digital products, generally in the 18650s. Mobile power supply, one to five or six combinations, and Tesla’s more than 7,000 18650 series-parallel combinations.
- Square batteries: Most of these are polymer batteries. Polymer is very malleable and can make many shapes. Its length, width, and height can be adjusted at will, and most digital products are now using this type of battery.
- Special batteries: that is, some strangely shaped batteries, according to the needs of the product. The battery should also be matched in shape, such as the popular smart wearable products, such as smart bracelets, so the battery is also made into a ring.
By cell type
18650 cells
18650 lithium cell is a kind of battery that is 18mm wide, 65mm long, and looks like a cylinder (0 indicates that). This battery is well-developed, works really well, and is used in many things because it’s small. The problem is it’s not as safe as some other batteries and can only be used about 300 times.
Polymer cell
Polymer cells and traditional lithium-ion batteries are different in how they’re made. Lithium batteries are soft and rolled, while polymer batteries have a stiffer shape. Polymer batteries are safer and last a long time (over 500 times), but they cost more, about 100% more than 18650 lithium-ion cells with the same capacity.
Part 9. FAQs about types of lithium battery
Which lithium battery type lasts the longest?
Lithium Titanate (LTO) batteries have the longest lifespan, capable of 7,000+ charge cycles—10 times longer than standard Li-ion batteries.
Are LiFePO4 batteries safer than NMC?
Yes. LiFePO4 batteries have 270℃ thermal runaway protection vs. NMC’s 210℃. They’re preferred for home energy storage systems.
Can I replace lead-acid with lithium batteries?
Absolutely. LiFePO4 can be used as a drop-in replacement with a 3.2V/cell configuration. Ensure your charger supports lithium chemistry.
Why do EV batteries use NMC/NCA instead of LiFePO4?
NMC/NCA provides higher energy density (600km+ range), whereas LiFePO4 is heavier but safer (the BYD Blade battery is an exception).
How to store lithium batteries long-term?
Store at 50% charge in a 15-25℃ dry environment. For LiCoO2 batteries, recharge every 6 months to prevent capacity loss.
Related Tags:
More Articles

What Is a Disk Battery? A Simple Guide for Non-Tech Users
A disk battery is a small, round cell used in watches, remotes, and other electronic devices. It delivers steady power for compact, low-drain devices.
What Battery Powers a Space Heater?
Discover the type of battery that powers space heaters and learn how to choose the right one for efficient heating in your home or office.
What Is an LR14 Battery? Learn About This C-Size Cell
The LR14 battery, also known as a C battery, delivers steady power. Learn its specs, uses, lifespan, and how it compares to other battery types.
Watch Battery Dimensions Chart: Sizes, Voltages, and Equivalents Explained
Understanding watch battery dimensions helps you choose the right size, voltage, and equivalent model to keep your watch running safely and smoothly.
How Long Can You Rely on Battery-Powered Generators?
Discover battery generator runtime & lifespan factors. Learn how to maximize performance and choose the right power solution.