- Part 1. 18650 Battery specifications & applications
- Part 2. Lithium-ion (Li-ion) 18650 battery
- Part 3. LiFePO4 18650 battery
- Part 4. 18650 LiPo battery
- Part 5. Nickel-metal hydride 18650 battery
- Part 6. 18650 Protected battery
- Part 7. Unprotected 18650 battery
- Part 8. High drain 18650 battery
- Part 9. Low drain 18650 battery
- Part 10. How to choose the right 18650 battery?
- Part 11. FAQs about 18650 batteries
18650 batteries stand as the backbone of various industries, powering an extensive array of devices that span from consumer electronics to aerospace technology.
These compact yet powerful batteries have revolutionized portable electronics, electric vehicles, medical equipment, and more, due to their high energy density and rechargeable nature.
This article provides an in-depth overview of the various types of 18650 batteries available on the market, highlighting their distinct characteristics, applications, and suitability across diverse industries.
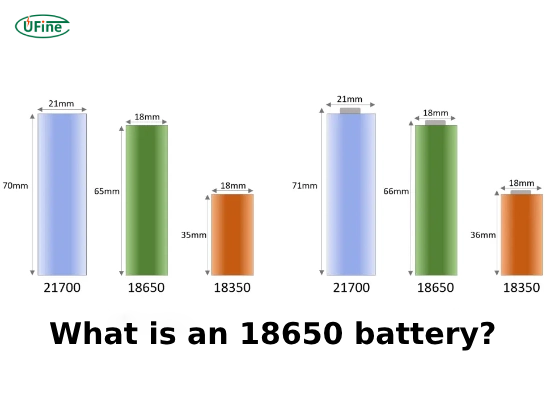
What is an 18650 battery? An 18650 battery is a rechargeable lithium cell that measures 18mm in diameter and 65mm in length, with a typical voltage of 3.6–3.7V and capacity between 2000mAh–3500mAh. It is one of the most common lithium-ion batteries, widely used in laptops, flashlights, vape mods, and electric vehicles.
Types of 18650 batteries include:
- Li-ion 18650 (high energy density, used in laptops & flashlights)
- LiFePO4 18650 (safer & long lifespan, used in solar storage & medical devices)
- LiPo 18650 (lightweight & flexible, used in drones & RC models)
- NiMH 18650 (eco-friendly, used in emergency lighting)
- Protected & Unprotected (with/without safety PCB)
- High-Drain vs Low-Drain (for vapes or long-runtime devices)
Part 1. 18650 Battery specifications & applications
The 18650 battery measures 18mm × 65mm, offering a balance of compact size and powerful output. With a nominal voltage of 3.6–3.7V and capacities from 2000mAh to 3500mAh, it supports a wide range of energy-demanding devices. High-drain variants can deliver strong bursts of current for vape mods and power tools, while high-capacity models provide long runtime for flashlights, laptops, and backup power banks. In industrial use, multiple 18650 cells are combined into electric vehicle battery packs and solar storage systems. For maximum safety, users should follow proper handling guidelines to prevent overheating or short circuits.
18650 Battery Size Chart & Types Comparison
This 18650 battery size chart compares different chemistries, voltage, capacity, and best uses, helping you choose the right type.
| Type | Voltage | Capacity | Best For | Safety |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Li-ion | 3.6-3.7V | 2000-3500mAh | Laptops, Flashlights | Medium |
| LiFePO4 | 3.2V | 1000-2000mAh | Medical Devices | High |
| LiPo | 3.7V | 1500-3000mAh | RC Drones | Low |
| NiMH | 1.2V | 2000-3000mAh | Emergency Lights | High |
| High Drain | 3.6-3.7V | 1500-2500mAh | Vape Mods | Medium |
| Low Drain | 3.6-3.7V | 3000-3500mAh | Clocks | High |
| Protected | 3.6-3.7V | 2000-3500mAh | Multi-cell Packs | High |
| Unprotected | 3.6-3.7V | 2000-3500mAh | Single-cell Devices | Medium |
Pro Tip: For vaping devices, select high-drain 18650 batteries with a discharge rate of≥20A, such as the Sony VTC5A.
Part 2. Lithium-ion (Li-ion) 18650 battery
A Lithium-Ion (Li-ion) 18650 battery, known for its rechargeable nature, relies on lithium ions moving between electrodes during charge and discharge cycles. This battery chemistry typically employs a lithium cobalt oxide (LiCoO2) cathode and a graphite anode separated by an electrolyte.
Advantages
- High energy density: Li-ion 18650 batteries offer exceptional energy density, delivering significant power in a compact form, ideal for portable electronics and high-demand applications.
- Extended lifespan: These batteries exhibit a longer lifespan compared to many other types, enduring multiple charge-discharge cycles while maintaining performance.
- Low self-discharge rate: With a relatively low self-discharge rate, Li-ion 18650 batteries retain their charge for extended periods when not in use, ensuring they are ready for deployment.
Disadvantages
- Safety concerns: Although generally safe, Li-ion batteries can be susceptible to thermal runaway if damaged, which can lead to overheating and potential hazards.
- Initial cost: The initial investment for Li-ion 18650 batteries might be higher compared to certain alternatives, impacting upfront costs for some applications.
- Environmental impact: The improper disposal of Li-ion batteries poses environmental challenges due to the materials they contain, emphasizing the importance of responsible recycling practices.
Part 3. LiFePO4 18650 battery
A LiFePO4 18650 battery is a specific type of rechargeable battery, distinguished by its use of iron phosphate as the cathode material, which sets it apart from traditional lithium-ion batteries. It utilizes lithium ions moving between the cathode (LiFePO4) and anode during charging and discharging cycles, storing and releasing energy efficiently.
Advantages
- Enhanced safety: LiFePO4 18650 batteries are renowned for their superior thermal and chemical stability, which reduces the risk of thermal runaway and enhances overall safety compared to other lithium-ion batteries.
- Longer lifespan: These batteries boast an extended lifespan, with a high number of charge-discharge cycles, maintaining their performance over a longer period.
- Stability: The use of iron phosphate in the cathode provides excellent stability, even at higher temperatures, ensuring consistent performance and reliability.
Disadvantages
- Lower energy density: Compared to some other lithium-ion chemistries, LiFePO4 batteries tend to have a slightly lower energy density, which might affect their suitability for applications requiring higher power-to-weight ratios.
- Limited voltage: LiFePO4 batteries have a lower voltage range compared to some other lithium-ion variants, which might necessitate more cells in series for certain applications.
- Slightly slower charging: While durable and long-lasting, LiFePO4 18650 batteries may have a slower charging rate compared to other lithium-ion batteries, which can impact their charging efficiency.
Part 4. 18650 LiPo battery
The Lithium Polymer (LiPo) 18650 battery represents a specific type of rechargeable battery characterized by its composition, which utilizes a polymer electrolyte instead of the traditional liquid electrolyte found in standard lithium-ion batteries. This battery variant utilizes a solid or gel-like substance as its electrolyte, enabling a more flexible and compact design compared to traditional cylindrical lithium-ion batteries.
Advantages
- Flexibility in design: LiPo 18650 batteries offer a more flexible form factor due to the use of a polymer electrolyte, allowing for different shapes and sizes to suit various device designs.
- High energy density: These batteries boast a high energy density, delivering substantial power relative to their size and weight, making them ideal for compact devices that require high power output.
- Lightweight construction: The use of a polymer electrolyte enables a lighter battery design, which is advantageous for applications that prioritize weight reduction without compromising power.
Disadvantages
- Safety concerns: LiPo batteries are more prone to swelling or puffing, particularly when exposed to overcharging, over-discharging, or physical damage, which can lead to safety hazards.
- Durability: While offering high energy density, LiPo 18650 batteries might have a shorter lifespan compared to some other lithium-ion variants, particularly if not properly maintained or operated within recommended parameters.
- Complex charging requirements: LiPo batteries often require specialized chargers and careful monitoring during charging to prevent overcharging or damage, adding complexity to their usage and maintenance.
Part 5. Nickel-metal hydride 18650 battery
The Nickel-Metal Hydride (NiMH) 18650 battery is a type of rechargeable battery that utilizes a nickel oxyhydroxide positive electrode, a hydrogen-absorbing negative electrode (metal hydride), and an alkaline electrolyte. These batteries are known for their ability to store energy through the reversible electrochemical reactions between nickel oxyhydroxide and hydrogen ions.
Advantages
- Higher energy density: NiMH 18650 batteries offer a higher energy density compared to traditional nickel-cadmium batteries, providing more power in a similar form factor.
- Reduced environmental impact: These batteries are more environmentally friendly than their predecessors, the nickel-cadmium batteries, as they contain no toxic metals like cadmium and present fewer disposal concerns.
- Cost-effectiveness: NiMH batteries can be more cost-effective over their lifespan due to their rechargeability, reducing the need for frequent battery replacements.
Disadvantages
- Self-discharge rate: NiMH 18650 batteries have a higher self-discharge rate compared to other lithium-ion counterparts, losing charge over time even when not in use.
- Lower voltage output: These batteries typically have a lower voltage output compared to lithium-ion batteries, affecting their suitability for high-power applications.
- Memory effect: Although less prone to the memory effect compared to older nickel-cadmium batteries, NiMH batteries can still experience reduced capacity if not properly cycled.
Part 6. 18650 Protected battery
An 18650-protected battery refers to a specific type of rechargeable battery that incorporates added safety features into its design. These safety measures often include a protective circuit board (PCB) that helps regulate and manage the battery’s operation. The PCB safeguards against overcharging, overdischarging, and short circuits, thereby enhancing the battery’s safety during use.
Advantages
- Enhanced safety: The protective circuitry in 18650 protected batteries mitigates the risks of overcharging, over-discharging, and short circuits, reducing the likelihood of accidents or damage caused by improper usage.
- Longevity: These safety measures can extend the battery’s lifespan by preventing excessive strain or damage caused by unsafe operating conditions, resulting in improved overall durability.
- Wide applicability: Protected 18650 batteries are used extensively in various devices, particularly those requiring an added layer of safety, such as flashlights, electronic devices, and portable power banks.
Disadvantages
- Increased size: The incorporation of protective circuitry might slightly increase the size of the 18650 battery, potentially affecting its fit in certain devices designed for standard-sized 18650 batteries.
- Limited availability: Some specialty or high-performance 18650 batteries might not be readily available with built-in protection, limiting choices for users seeking specific features or capacities.
- Price variation: Although not directly discussing costs, it is worth noting that the presence of protective circuitry may impact the pricing of these batteries compared to unprotected counterparts.
Part 7. Unprotected 18650 battery
An unprotected 18650 battery refers to a type of rechargeable battery that lacks additional safety features, such as a protective circuit board (PCB). Unlike protected variants, these batteries lack built-in safeguards against overcharging, over-discharging, and short circuits.
Advantages
- Compact size: Unprotected 18650 batteries typically maintain a standard size without additional protective circuitry, making them suitable for devices with specific size constraints.
- Wider availability: Due to their simpler design, unprotected 18650 batteries might offer a broader range of options in terms of capacity, discharge rates, and chemistry types, catering to various needs.
- Potential performance: In some scenarios, unprotected batteries might offer slightly higher performance characteristics, such as higher discharge rates, which can be advantageous for specific applications.
Disadvantages
- Safety risks: Without protective circuitry, unprotected 18650 batteries are more susceptible to potential hazards, including overcharging, over-discharging, and short circuits, which pose significant safety risks during use.
- Limited safety measures: The absence of built-in safeguards increases the risk of damage to the battery or connected devices in case of misuse, improper charging, or extreme conditions.
- Lifecycle concerns: Unprotected batteries might experience a shorter lifespan if subjected to frequent stress from improper usage, potentially leading to quicker degradation over time.
Part 8. High drain 18650 battery
A high-drain 18650 battery is a specialized rechargeable power source designed to deliver high current outputs rapidly. Unlike standard batteries, these high-drain variants are engineered to meet the demanding power requirements of devices that necessitate quick and intense energy discharges.
Advantages
- Rapid Power Output: High-Drain 18650 batteries excel at providing quick and substantial bursts of energy, making them ideal for devices with high-performance demands such as high-powered flashlights, vaping devices, and certain electronics.
- Suitability for High-Performance Devices: Devices like high-end vaping mods, power tools, and high-performance flashlights benefit from the elevated power output of high-drain batteries, ensuring optimal functionality.
- Performance Consistency: These batteries maintain stable performance even under high-stress conditions, allowing for sustained high-current applications without significant degradation.
Disadvantages
- Reduced Overall Capacity: Drain batteries may have a lower overall energy capacity compared to standard batteries, which means they may require more frequent recharging in applications with sustained high-current draws.
- Shorter Lifespan: The intense demands of high-current applications can contribute to a shorter overall lifespan of high-drain 18650 batteries, requiring careful management to maximize their longevity.
- Limited Applicability: Not all devices require or can take advantage of the high-current capabilities of these batteries, making them less suitable for applications with lower power demands.
Part 9. Low drain 18650 battery
A low-drain 18650 battery represents a type of rechargeable battery designed to discharge energy at a slower and steadier rate compared to high-drain counterparts. These batteries are tailored for devices with lower power requirements and are often characterized by their ability to deliver consistent, long-lasting power.
Advantages
- Extended lifespan: Low-drain 18650 batteries typically endure more charge-discharge cycles due to their lower discharge rates, resulting in an extended overall lifespan compared to high-drain variants.
- Suitability for low-power devices: Devices such as remote controls, clocks, and specific electronics benefit from the steady and reliable power supply of low-drain batteries, ensuring consistent performance over extended periods.
- Stable performance: These batteries offer stable and predictable performance, making them suitable for devices that require a continuous, albeit lower, power output without the need for rapid energy discharges.
Disadvantages
- Lower power output: Low-drain batteries may not suffice for devices with high power demands, as they are designed for steady but lower-energy applications, lacking the rapid discharge capability of high-drain variants.
- Limited applicability: Devices requiring quick and intense energy bursts might not benefit from low-drain batteries, which are optimized for steady, lower-power applications.
- Potential over-discharge risks: If used in devices that draw more power than the battery can supply, low-drain batteries might face risks of over-discharge, potentially leading to reduced performance or damage.
Part 10. How to choose the right 18650 battery?
Follow these steps to select the best 18650 battery for your needs:
- Check Device Requirements
Match voltage (3.2V LiFePO4 vs 3.7V Li-ion) and discharge rate (e.g., 10A for flashlights, 30A for vaping). - Prioritize Safety
Use protected batteries in multi-cell devices, such as laptop battery packs. - Capacity vs Power
High-drain (20A+) for power tools, 3500mAh for long runtime in LED flashlights.
Part 11. FAQs about 18650 batteries
Are all 18650 batteries the same?
No. 18650 batteries differ by chemistry (Li-ion, LiFePO4, LiPo, NiMH), capacity (2000–3500mAh), and discharge rate (high-drain vs low-drain). Always match your device’s requirements.
What are the different types of 18650 lithium batteries?
The main 18650 types are: Li-ion, LiFePO4, LiPo, NiMH, plus protected/unprotected and high-drain/low-drain versions.
What is an 18650 battery used for?
They are widely used in flashlights, vapes, laptops, power tools, EV packs, and solar storage.
What is the difference between 18650 and 18650B?
“18650B” usually refers to a higher-capacity variant (e.g., Panasonic NCR18650B, 3400mAh), compared to standard 18650 cells.
What is the difference between flat-top and button-top 18650 batteries?
Flat-top has a flat positive terminal, while button-top has a raised terminal. Choose based on device compatibility.
What is the difference between 18650 3.6V and 3.7V?
They are the same cell type. Manufacturers list 3.6V or 3.7V as the nominal voltage, with a max charge voltage of 4.2V.
Which 18650 battery is best for vaping?
High-drain cells like Sony VTC5A (25A, 2600mAh) or Molicel P26A (30A, 2600mAh) are the safest and most reliable for vape mods.
Can I charge an 18650 battery with a phone charger?
No. Always use a dedicated 18650 charger with overcharge protection, such as Nitecore or XTAR models.
Related Tags:
More Articles

Bad Battery Cell Symptoms: How to Tell If a Battery Cell Is Dead
Learn how bad battery cells behave, how to test them, and when replacement is the safest option.
18650 Maximum Capacity in 2026: What’s Real and What’s Hype?
Discover the real 18650 battery capacity limits in 2026, top high-capacity cells, and how to avoid fake claims.
Lithium Battery Sizes Guide: 18650, 21700, LiPo & Coin
Learn about lithium battery sizes, form factors, and uses. Compare dimensions and capacities for cylindrical, pouch, prismatic, and more.
What’s the Difference Between Lithium Metal AA Battery and Lithium Ion Battery?
Learn the difference between lithium metal AA batteries and other types. Find out if AA batteries are lithium and which type performs best for your devices.
9v Lithium or Alkaline Battery: Which One’s More Reliable?
9v lithium vs alkaline battery: Which one packs more power? Learn the key differences and choose the right battery for your needs now.