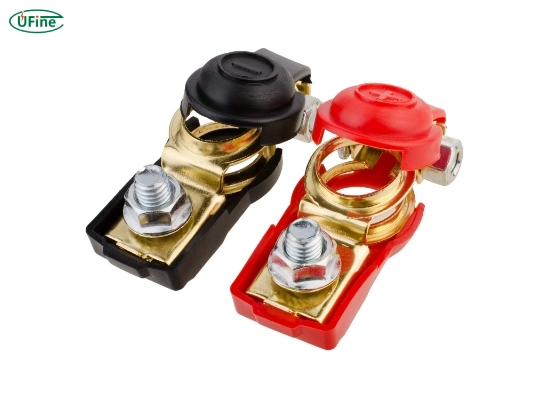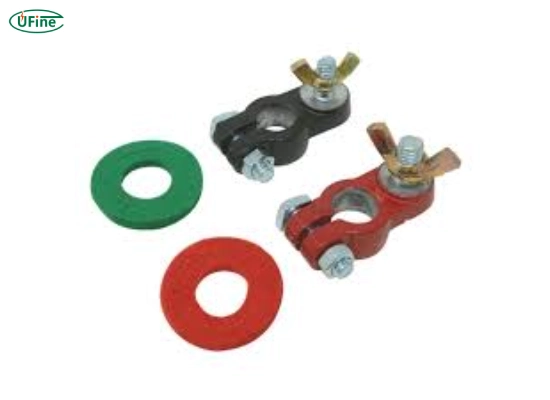
- Part 1. What is a battery terminal?
- Part 2. Types of battery terminals
- Part 3. What is a battery post?
- Part 4. Positive and negative battery terminals diagram
- Part 5. Types of battery posts
- Part 6. The relationship between battery posts and battery terminals
- Part 7. How do you identify positive and negative terminals?
- Part 8. How to clean battery terminals in 5 steps (With Safety Tips)
- Part 9. How to replace battery terminals?
- Part 10. Common issues with battery terminals
- Part 11. How to prevent battery terminal corrosion?
- Part 12. FAQs about battery posts and terminals
Battery posts and terminals are essential components in any battery-powered system, ensuring a reliable connection between the battery and the electrical system of a vehicle or device. This comprehensive guide will delve into everything you need to know about battery posts and terminals, including their types, maintenance, troubleshooting, and more.
Battery Posts & Terminals: A Quick GuideBattery posts and terminals are the connection points between your battery and your vehicle’s electrical system. The battery post is the metal stub on the battery itself, while the battery terminal is the connector attached to your vehicle’s cables. Proper maintenance of these components is crucial for reliable starting and electrical performance.
Part 1. What is a battery terminal?
A battery terminal is an electrical contact used to connect a load or charger to a single or multi-cell battery. These terminals ensure a stable and secure connection, allowing the battery to deliver power efficiently. Every battery has two primary terminals: a positive terminal (typically marked with a red or a plus sign ‘+’) and a negative terminal (marked with a black color or a minus sign ‘-‘).
Part 2. Types of battery terminals
Battery terminals come in various shapes and sizes, each designed for specific applications. Below are the most common types:
Standard Battery TerminalsStandard battery terminals, or SAE posts, are the most common type in automotive batteries. They consist of two lead posts, with the positive terminal being larger than the negative terminal.
Marine Battery TerminalsMarine battery terminals serve boats and other marine applications. They often feature corrosion-resistant coatings and may include both SAE and threaded posts for secure connections.
Hybrid Battery TerminalsHybrid battery terminals combine features from different terminals to offer versatility and compatibility with various battery types and applications.
Side Terminal BatteriesSide terminal batteries have terminals on the side of the battery rather than the top. These terminals are recessed and use bolts to secure the connections, making them less prone to corrosion.
L TerminalsL terminals are L-shaped posts with a hole through the vertical side, commonly used in European cars, motorcycles, and lawnmowers.
Stud TerminalsStud terminals are threaded posts used in heavy-duty applications. They provide a secure connection and are often used in industrial and commercial batteries.
Battery Terminal Types Comparison Table
| Type | Best For | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|---|
| SAE Post (Top Post) | Cars, Trucks, Most Vehicles | Widely compatible, Easy to install | Prone to corrosion |
| Marine (Dual Post) | Boats, RVs, Marine Applications | Corrosion-resistant, Secure connection | Higher cost |
| L-Terminal (L-Post) | Motorcycles, Lawnmowers, Small Equipment | Compact design, Easy to access | Limited current capacity |
| Side Terminal | GM Vehicles, Some Trucks | Low corrosion risk, Space-saving | Harder to access, Special tools needed |
Part 3. What is a battery post?
A battery post is the protruding metal part of a battery to which the battery terminals are connected. These posts are the points of contact for the electrical connections, ensuring the current flow from the battery to the connected device or vehicle.
Part 4. Positive and negative battery terminals diagram
Here’s a diagram of a positive and negative battery terminals diagram to visually explain how these components are arranged on most standard automotive batteries.

- Positive Terminal (+): Usually red, connected to the starter and electrical system.
- Negative Terminal (-): Usually black, connected to the vehicle’s chassis (ground).
Proper identification is crucial for safe battery connection and jump-starting.
Part 5. Types of battery posts
A battery post is the protruding metal part of the battery. In contrast, the battery terminal is the connector that attaches to the post. Understanding the difference between battery post types is essential for choosing the right connection for your vehicle or device.
SAE PostsSAE posts are the most common battery post in most automotive batteries. They fit standard battery terminals and ensure a secure connection.
JIS PostsJIS posts are similar to SAE posts but smaller. They often appear in older Japanese vehicles and fit JIS battery terminals.
Threaded PostsHeavy-duty and marine batteries use threaded posts. Nuts and bolts provide a secure connection.
Tapered PostsTapered posts are conical and designed to fit specific battery terminals that clamp onto the post.
Part 6. The relationship between battery posts and battery terminals
Battery posts and terminals work together to form a complete electrical connection. The battery post serves as the contact point for the battery, while the terminal is the connector that attaches to the post. This connection allows electrical current to flow from the battery to the vehicle or device’s electrical system.
Importance of Battery Posts and Terminals
Battery posts and terminals are critical for the efficient operation of any battery-powered device. They ensure a stable and secure connection, allowing the battery to deliver power to the connected load. Poor or corroded terminals can lead to electrical issues, reduced battery performance, and even complete failure.
Battery Terminal Materials: Lead vs Copper vs Brass
Choosing the right terminal material affects performance:
- Lead Terminals: Cheap but corrode faster (common in cheap car batteries)
- Copper Terminals: Best conductivity, anti-corrosion (ideal for marine/RV)
- Brass Terminals: Balance of cost & durability (common in aftermarket parts)
Part 7. How do you identify positive and negative terminals?
Identifying a battery’s positive and negative terminals is crucial for proper connection and safety. The positive terminal usually shows a red color or a plus sign (‘+’). In contrast, the negative terminal shows a black color or a minus sign (‘-‘). Sometimes, the markings may need to be present or obscured by dirt, so cleaning the terminals and looking for the signs is essential.
Part 8. How to clean battery terminals in 5 steps (With Safety Tips)
Tools You’ll Need:
- Baking soda
- Water
- Wire brush or battery terminal cleaner
- Adjustable wrench
- Protective gloves & goggles
Step-by-Step Cleaning Process:
Step 1: Disconnect the Battery
Always start with the negative terminal (black cable)! Loosen the nut with a wrench and carefully remove the cable. Repeat for the positive terminal (red).
Step 2: Make the Cleaning Solution
Mix 1 tablespoon of baking soda with 1 cup of warm water. This neutralizes battery acid corrosion.
Step 3: Scrub the Terminals
Dip the wire brush into the solution and scrub the terminals and posts until corrosion is removed. For heavy buildup, use a dedicated battery terminal cleaner tool.
Step 4: Rinse and Dry
Wipe the area with a damp cloth to remove residue. Dry thoroughly with a clean towel or compressed air.
Step 5: Reconnect the Battery
Attach the positive terminal first (red cable), tighten securely, then repeat for the negative terminal. Apply anti-corrosion grease to prevent future buildup.
Part 9. How to replace battery terminals?
Replacing battery terminals is necessary when they become too corroded or damaged. Follow these steps to replace battery terminals:
- Disconnect the battery: Remove the negative cable first, then the positive cable.
- Remove the old terminals: Use a wrench to loosen and remove the old terminals.
- Clean the battery posts: Clean the battery posts with a wire brush to remove any corrosion.
- Install the new terminals: Place them on the battery posts and tighten them securely.
- Reconnect the battery: Connect the positive cable first, followed by the negative cable.
Part 10. Common issues with battery terminals
Battery terminals can experience several common problems, including:
- Corrosion: Corrosion can impede the flow of electricity and cause starting issues.
- Loose connections: Loose terminals can lead to poor electrical connections and intermittent power loss.
- Cracked or damaged terminals: Physical damage can prevent a secure connection and lead to electrical problems.
Part 11. How to prevent battery terminal corrosion?
Preventing battery terminal corrosion is essential for maintaining a reliable electrical connection. Here are some tips to prevent corrosion:
- Apply a protective coating: Use a battery terminal protector spray or petroleum jelly to coat the terminals.
- Use anti-corrosion washers: Place anti-corrosion washers on the battery posts before attaching the terminals.
- Regular maintenance: Clean the terminals regularly to prevent the buildup of corrosion.
For heavy corrosion cases, see our guide on removing battery acid corrosion.
Part 12. FAQs about battery posts and terminals
Can You Mix SAE and JIS Battery Terminals?
No. SAE posts (19.5mm diameter) are larger than JIS posts (17.3mm). Forcing incompatible terminals causes loose connections, voltage drops, and fire risks. Always use matching terminal types.
Why Do Battery Terminals Corrode So Fast in Hot Weather?
Heat accelerates chemical reactions between lead posts and sulfuric acid vapors, increasing corrosion. To slow corrosion:
- Use AGM or gel batteries (low gas emission)
- Apply silicone-based terminal protector spray
- Install battery heat shields in engine bays
How Tight Should Battery Terminal Clamps Be?
Tighten until the clamp cannot rotate on the post. Over-tightening cracks lead posts. Use a torque wrench: 5-7 Nm for standard cars, 8-10 Nm for trucks/RVs.
Are Copper Battery Terminals Worth the Cost?
Yes, especially for high-demand applications. Copper offers better conductivity than lead (25% more efficient), reduces voltage drop in car audio and RV systems, and is ideal for marine use with anti-oxidation coating.
Can Corroded Battery Terminals Drain Your Battery?
Yes. Corrosion increases resistance, making the alternator work harder, which can lead to parasitic drain even when the vehicle is off.
What is the Difference Between a Battery Post and a Battery Terminal?
The battery post is the metal protrusion on the battery itself (positive and negative), while the battery terminal is the connector that clamps onto the post to link the battery to the electrical system.
How Do I Know If My Battery Terminals Need Replacement?
If you notice severe corrosion, cracking, or difficulty tightening the terminal, it’s time for replacement. Intermittent electrical issues are also signs of worn-out terminals.
What Are the Best Battery Terminals for High-Performance Applications?
Copper terminals are recommended for high-performance systems (like car audio and RV) due to their superior conductivity and corrosion resistance.
Related Articles
Related Tags:
More Articles
Capacitor vs Battery: What is the Difference?
Capacitor vs battery explained in detail. Learn the difference between capacitor and battery in energy storage, charging speed, lifespan, and real applications.
18650 Battery vs AA: Which Is Better for Your Device?
Compare 18650 vs AA batteries in capacity, voltage, rechargeability, and applications. Learn which battery type fits high-drain or everyday devices.
What is the Difference Between Battery Cell, Battery Control Module, and Battery Pack?
Compare battery cells, modules, and packs. Learn functions, design differences, control modules, and selection tips for EV, ESS, and industrial use.
How to Prevent LiPo Battery Explosion?
Can LiPo batteries explode or catch fire? Learn key causes of LiPo battery fires and proven charging, storage, and handling tips to reduce explosion risk.
Aluminium Ion Battery vs Lithium-Ion: A Detailed Comparison
Compare aluminium ion battery vs lithium-ion battery in energy density, charging speed, safety, cost, and uses. A practical guide for engineers and buyers.




