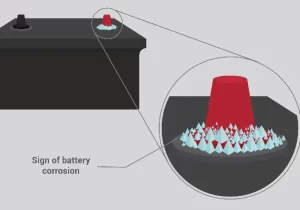
Battery corrosion is a common issue that can hinder the performance and lifespan of batteries. Still, you can ensure optimal battery health and functionality with the proper knowledge and preventive measures. Let’s delve into the causes of battery corrosion, methods to clean corroded battery contacts, their effects, and essential tips to prevent it from occurring in the first place.
Part 1. What causes battery corrosion?
Battery corrosion occurs due to a chemical reaction between the battery’s electrolyte and the metal components, primarily the terminals or contacts. The main culprits behind this corrosive process are:
- Acid Leakage: When a battery undergoes overcharging or experiences physical damage, its sulfuric acid can leak, leading to corrosion.
- External Factors: Exposure to moisture, high humidity, extreme temperatures, and environmental contaminants can accelerate the corrosion process.
- Impurities in the Battery: Manufacturing defects or impurities in the battery can trigger a chemical reaction, resulting in corrosion.
Part 2. How to clean corroded battery terminals?
1. Precautions and Safety Measures
When cleaning corroded battery contacts, it is essential to prioritize safety. Follow these precautions and safety measures before starting the cleaning process:
- Wear Protective Gear: Wear protective gloves and goggles to protect your hands and eyes from any contact with corrosive substances. This will prevent potential injuries and irritation.
- Work in a Well-Ventilated Area: Ensure you work in a well-ventilated space or near an open window. This will help dissipate any fumes released during the cleaning process.
- Disconnect the Battery: Before cleaning, it is crucial to disconnect the battery from any devices or power sources. This step minimizes the risk of electrical hazards, such as short circuits or shocks.
2. Cleaning Materials and Methods
To effectively clean corroded battery contacts, you will need suitable cleaning materials and follow specific methods. Here’s what you need to know:
- Choose the Right Cleaning Materials: Several options exist for cleaning battery corrosion. Baking soda mixed with water, vinegar, or commercial battery cleaners is commonly used. These substances help neutralize the acidic corrosion and facilitate the cleaning process.
- Prepare the Cleaning Solution: If baking soda is used, mix it with equal water to create a paste-like consistency. For vinegar or commercial battery cleaners, follow the instructions on the packaging.
- Apply the Cleaning Solution: Using a cotton swab or a clean cloth, apply the cleaning solution to the corroded battery contacts. Make sure to cover the affected areas thoroughly.
- Gently Scrub the Terminals: To remove the corrosion, gently scrub the battery terminals using a wire brush or a cotton swab soaked in the cleaning solution. Apply light pressure and scrub in circular motions to dislodge the corrosion without damaging the terminals.
- Repeat if Necessary: For severe corrosion, it may be necessary to repeat the cleaning process multiple times to achieve optimal results. Be patient and persistent in your efforts.
3. Rinse and Dry
After cleaning the battery contacts, it is crucial to rinse and dry them properly. Follow these steps:
- Rinse with Clean Water: Rinse the battery terminals once the corrosion is removed. This will help wash away any residue from the cleaning solution and prevent it from causing further damage.
- Thoroughly Dry the Terminals: After rinsing, ensure that the battery terminals are completely dry before reconnecting them. Use a clean, dry cloth or allow them to air dry naturally. Moisture can contribute to future corrosion, so this step is vital in preventing its recurrence.
Following these cleaning methods and taking necessary precautions, you can effectively remove corrosion from battery contacts and restore their functionality. Remember to prioritize safety, choose suitable cleaning materials, and ensure thorough rinsing and drying before reconnecting the battery.
Part 3. What are the effects of battery corrosion?
Detrimental Effects on Battery Performance:
- Reduced Conductivity: Battery corrosion creates a barrier that hinders the flow of electricity, leading to decreased conductivity and compromised power delivery.
- Voltage Drop: Corrosion on battery contacts causes a decrease in voltage when connected to devices, potentially resulting in decreased performance or device malfunction.
- Potential Damage to Electronic Devices: Corrosion can spread to electrical connections within devices, interfering with their proper functioning and causing malfunctions or complete failure.
Examples of Battery Corrosion Situations:
- Automotive Batteries: Corrosion commonly occurs in car batteries due to exposure to moisture, temperature fluctuations, and chemical reactions during charging and discharging processes.
- Household Electronics: Battery corrosion can affect devices such as remote controls, toys, and portable electronics. Humid environments, frequent battery changes, and prolonged inactivity can contribute to corrosion.
- Portable Devices: Battery-powered devices like smartphones, tablets, and laptops are prone to battery corrosion if adequately protected and maintained. Corrosion on battery contacts can hinder functionality and reduce battery life.
Part 4. How to prevent battery corrosion?
Keep Batteries Dry
Moisture is a common cause of battery corrosion. Ensure that batteries and their compartments remain dry. Avoid exposing batteries to water or excessive humidity.
Store Batteries Properly
Store batteries in a cool, dry place when not in use. Avoid storing them in areas with high humidity or extreme temperatures, such as near heating vents or in direct sunlight.
Remove Batteries When Not in Use
If you’re not planning to use a device for an extended period, remove the batteries. This helps prevent continuous exposure to potential moisture or chemical reactions that can lead to corrosion.
Inspect Batteries Regularly
Routinely check your batteries for signs of corrosion. Look for any buildup or discoloration on the battery terminals or contacts. Early detection allows for timely cleaning and prevents corrosion from spreading.
Clean Battery Contacts
Regularly clean battery contacts to remove any existing corrosion or buildup. Use a soft cloth or an eraser to wipe the terminals gently. Ensure the contacts are dry before reinserting the batteries.
Use Quality Batteries
Opt for reputable brands and high-quality batteries. Inferior or expired batteries are more prone to leakage and corrosion. Invest in reliable batteries that have a good reputation for performance and durability.
Install Batteries Correctly
When inserting batteries, ensure they are placed in the device with the correct polarity (+/-) as indicated. A proper installation can lead to battery leakage and corrosion.
Avoid Mixing Different Battery Types
Mixing different types of batteries (e.g., alkaline, lithium, rechargeable) can cause chemical reactions and increase the risk of corrosion. Stick to using a battery in a device.
Replace Damaged Batteries Promptly
If you notice signs of leakage or damage to a battery, replace it immediately. Damaged batteries are more likely to leak and cause corrosion.
Part 5. Conclusion
Battery corrosion is a common problem that can significantly impact the performance and lifespan of batteries. You can effectively clean and prevent battery corrosion by understanding the causes, implementing proper cleaning techniques, and adopting preventive measures. Regular maintenance, adequate storage, and proactive care will go a long way in ensuring optimal battery health and maximizing their longevity.
Related Tags:
More Articles

LiPo Battery Discharge Rate Guide & Calculation Tips
Understand LiPo battery discharge rates, C-ratings, and how to calculate max current. Essential guide for RC, drones, and electronics users.
High‑Capacity 3S LiPo Batteries: 5000 mAh vs. 10000 mAh
Compare 3S LiPo 5000mAh vs 10000mAh batteries by weight, power, and use. Find the best fit for your drone, RC car, or boat setup.
Top 5 Applications for Small 3S LiPo Batteries
Small 3S LiPo batteries power drones, RC gear, wearables, and robotics with high energy and low weight. Making them ideal for compact electronics projects.
Building and Charging Your Own 3S LiPo Pack: A Step‑by‑Step Guide
Learn how to build, balance, and charge a 3S LiPo battery pack safely at home with this complete DIY guide for hobbyists and beginners.
How to Choose the Right LiPo Battery Plug Type?
Discover the best LiPo battery plug types, how to choose them, and expert tips for safe usage, soldering, and maintenance.