Charging parallel batteries is a practice commonly used in various applications, including solar energy systems, electric vehicles (EVs), and even some power tools. However, improper charging can lead to battery damage, reduced efficiency, and safety hazards. In fact, studies have shown that over 30% of battery failures in these systems stem from improper charging techniques. If you’ve ever found yourself wondering about the correct way to charge parallel batteries, you’re not alone. Many users struggle with issues like imbalance and improper voltage, leading to frustration and potential battery issues. This article will guide you through the process of charging parallel batteries correctly, ensuring that you get the most out of your battery system while avoiding common pitfalls.
Part 1. Why is proper parallel battery charging important?
When charging batteries in parallel, it’s crucial to ensure that the batteries are at the same voltage level before connecting them. If the batteries are not evenly matched, it can result in uneven charging, causing some batteries to overcharge while others undercharge. This imbalance can drastically reduce the lifespan of the batteries and might even lead to dangerous situations, like overheating. Therefore, understanding how to charge parallel batteries properly is essential to ensure optimal performance and safety.
Additionally, charging parallel batteries correctly can enhance the overall efficiency of your power system. It ensures that the batteries work in harmony, with each one receiving the appropriate charge without damaging others in the process. In this article, we will explore the correct charging practices, common issues, and essential tips to help you maintain your battery system.
Part 2. Problems when charging batteries in parallel
Charging batteries in parallel is not without its challenges. One of the most common issues is imbalanced charging. When batteries with different charge levels are connected, the higher-charged battery will discharge into the lower-charged one, which can lead to overcharging, undercharging, and, eventually, battery degradation. For instance, if you have two batteries with significantly different voltages connected in parallel, the battery with the lower voltage will try to draw more current, causing stress on the battery and its internal components.
Another problem is uneven battery capacities. Batteries in parallel should ideally have the same voltage, chemistry, and capacity. If one battery has a much higher or lower capacity than the other, it can cause a situation where one battery discharges faster than the other, leading to potential overcharging or deep discharge.
How Can You Prevent These Issues?
The key to avoiding these problems is ensuring balanced charging. By making sure that the batteries are all at the same voltage level before starting the charging process, you can reduce the likelihood of imbalance. If you’re unsure about the charging state of your batteries, use a battery management system (BMS) or a multi-stage charger that balances the charge across all batteries.
Part 3. Balanced charging batteries in parallel
Balanced charging ensures that all batteries in parallel are charged at the same rate, avoiding situations where one battery overcharges while another undercharges. This can be achieved using a Battery Management System (BMS) or a smart charger. These systems monitor each battery’s charge and automatically adjust the charging rate to ensure that each battery receives the appropriate amount of power. This is particularly important in larger battery systems, like those used in solar setups or electric vehicles.
One of the most reliable ways to achieve balanced charging is by using batteries of the same make, model, age, and capacity. This ensures that all batteries have similar characteristics and, therefore, similar charging needs.
What Are the Benefits of Balanced Charging?
Balanced charging offers several advantages:
- Extended battery life: Prevents batteries from overcharging or undercharging, leading to longer overall lifespan.
- Improved system efficiency: Ensures that energy is used effectively, rather than wasted due to imbalanced charging.
- Safety: Reduces the risk of overheating or damage to the batteries, which can occur when charging is not balanced.
At Ufine Battery, we offer customized solutions to suit your specific needs, whether you require lithium-ion batteries, lithium polymer batteries, or LiFePO4 batteries. Contact us now to help ensure that your system operates efficiently with custom-built batteries designed for parallel charging.
Part 4. Unbalanced charging batteries in parallel
In contrast to balanced charging, unbalanced charging can cause significant issues. As previously mentioned, unbalanced charging occurs when batteries of varying voltages, capacities, or chemistries are connected in parallel. When one battery becomes more charged than the others, it forces current into the others, which can damage the internal components and result in reduced battery life or battery failure.
Why Does Unbalanced Charging Happen?
Unbalanced charging can occur due to several factors, such as:
- Different battery ages: Older batteries may have a reduced capacity, making them prone to charging imbalance.
- Different battery chemistries: Mixing batteries with different chemistries, such as lithium-ion and lead-acid, can cause imbalance.
- Temperature variations: Extreme temperatures can affect the performance and charging efficiency of batteries, leading to imbalance.
To avoid these issues, always make sure to use batteries of the same type, age, and capacity. If your batteries are not uniform, consider using a BMS that can help maintain balance during the charging process.
Part 5. Step-by-step guide to charging parallel batteries
Charging parallel batteries requires careful attention to detail to ensure safety, efficiency, and optimal battery life. Follow these steps to correctly charge parallel batteries:
Step 1: Check Battery Voltage
Before connecting any batteries in parallel, the first thing you need to do is check the voltage of each battery using a digital multimeter. All batteries should be at the same voltage level before connecting them. If the voltage difference between the batteries is too large (e.g., more than 0.5V), the batteries could draw excess current from one another, which could damage them.
How to check voltage:
- Set your multimeter to DC voltage mode.
- Place the red probe on the positive terminal and the black probe on the negative terminal of each battery.
- Ensure the voltage reading is close to one another, ideally within a 0.1V range.
Step 2: Balance the Batteries (if needed)
If you find that the batteries are not at the same voltage, you’ll need to balance them before proceeding. This can be done by charging them individually or using a smart charger that features automatic balancing capabilities. A Battery Management System (BMS) also plays a crucial role here by monitoring and balancing the charge across all connected batteries.
Quick Tip:
If your batteries are of different ages or have significant capacity differences, it’s better not to connect them in parallel, as this will cause uneven charging and could result in battery failure over time.
Step 3: Choose the Right Charger
Select a charger designed for parallel battery charging. This is crucial for ensuring that the batteries charge evenly and safely. If you are using a BMS, ensure that the charger is compatible with it. If your batteries are lithium-based (e.g., lithium-ion or LiFePO4), make sure the charger supports that specific chemistry.
What to look for in a charger:
- A charger with multi-stage charging capabilities.
- The correct voltage and current specifications based on the batteries you’re using.
- An automatic shut-off feature once the batteries are fully charged.
Step 4: Use Proper Cables and Connectors
Use high-quality, appropriately rated cables to connect the batteries in parallel. The cables should be capable of handling the total current without overheating or causing damage. Be sure that the connectors are firmly attached to avoid any loose connections, which can result in voltage drop or sparking.
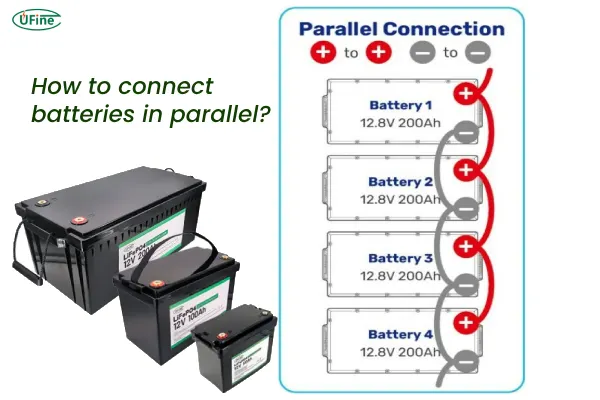
How to connect the batteries:
- Connect the positive terminal of the first battery to the positive terminal of the second battery, and continue this for all batteries in the parallel array.
- Do the same for the negative terminals of each battery.
- Ensure that the connections are tight and secure before proceeding with charging.
Step 5: Set Up the Charging System
Once the batteries are properly connected in parallel, it’s time to set up your charging system. If you’re using a charger with a BMS, connect the charger to the main terminal of the battery bank. If you’re using a simple charger without a BMS, manually monitor the voltage and current during the charging process.
Quick Tip:
For safety, ensure the charging area is well-ventilated and free from flammable materials. Batteries, especially lithium-based ones, can get quite hot during charging.
Step 6: Monitor the Charging Process
As the batteries begin charging, it’s important to monitor the process regularly. Check for any signs of overheating, strange odors, or any other unusual behavior from the batteries. Most chargers will display the charging progress, and a BMS will often provide real-time data on the voltage and status of each individual battery in the bank.
What to check during charging:
- Battery temperature: Excessive heat may indicate a problem.
- Voltage readings: Ensure all batteries are charging evenly.
- Charging time: Follow the manufacturer’s guidelines for how long the charging process should take.
Step 7: Finish Charging and Disconnect
Once all the batteries have reached their fully charged voltage (usually 4.2V for lithium-ion, or 3.65V for LiFePO4), disconnect the charger from the battery bank. If your charger has an automatic shut-off feature, the process will end by itself. However, if you’re using a non-automatic charger, make sure to turn it off manually once the batteries are fully charged to prevent overcharging.
Quick Tip:
Never leave batteries on the charger for extended periods after they are fully charged, as this can lead to overheating or potential damage.
Step 8: Check Battery Status and Disconnect Cables
After charging, check the individual battery voltages again to ensure they are all in sync. If you notice any batteries have a voltage that’s higher or lower than the others, this could indicate a problem with that specific battery. Disconnect all cables and ensure there are no loose connections before storing or using the batteries.
Part 6. Precautions to take when charging parallel batteries
When charging parallel batteries, there are several precautions to keep in mind:
- Always ensure the batteries are of the same voltage and capacity.
- Never mix old and new batteries, as this can cause imbalances.
- Use a charger that is designed specifically for parallel charging.
- Regularly check the batteries for any signs of damage or wear.
- Ensure that the charging environment is cool and dry to prevent overheating.
Part 7. Common faults and solutions
Fault 1: One Battery Drains Faster Than the Others
Solution: This could be a sign that the battery is damaged or has a lower capacity. Replace it with a new battery that matches the others in terms of voltage and capacity.
Fault 2: Overheating During Charging
Solution: Check that the charger is functioning properly and that the cables are of sufficient quality to handle the current. Overheating may also indicate that the batteries are incompatible.
Fault 3: Uneven Voltage Readings
Solution: Recheck the voltage of each battery before charging. If the voltage discrepancy persists, consider replacing the affected battery or checking the charger for faults.
Part 8. FAQs
-
Can I charge lithium-ion and lead-acid batteries in parallel?
It is not recommended to charge lithium-ion and lead-acid batteries in parallel. These two types of batteries have different charge characteristics and could lead to imbalanced charging. Always make sure to charge batteries of the same chemistry together to ensure safety and proper functioning. -
What is the ideal voltage difference between parallel batteries?
Ideally, the voltage difference between parallel batteries should be less than 0.1V. A voltage difference greater than this could cause the batteries to charge unevenly, leading to potential damage or reduced lifespan. -
How do I know if my battery management system (BMS) is working correctly?
A properly functioning BMS will monitor individual battery voltages and balance the charge across all batteries. Most BMS systems will have indicators or alarms that alert you if there’s an issue with one of the batteries (such as over-voltage or under-voltage conditions). Additionally, you can use a multimeter to check if the BMS is ensuring even voltage levels across all batteries. -
What happens if one battery in parallel gets overcharged?
If one battery in a parallel configuration gets overcharged, it can damage the battery’s internal structure, leading to overheating, leakage, or even fire. This is why using a BMS is essential for protecting the system and ensuring balanced charging. -
Can I charge different-sized batteries in parallel?
It is not recommended to charge batteries of different sizes in parallel, as it can lead to voltage imbalance. Ideally, all the batteries should have the same capacity, voltage, and age to ensure that they charge evenly and safely. -
How can I ensure safe parallel charging?
Use a Battery Management System (BMS) and always monitor the charging process to ensure balance and prevent overheating.
Related Tags:
More Articles

LiPo Battery Discharge Rate Guide & Calculation Tips
Understand LiPo battery discharge rates, C-ratings, and how to calculate max current. Essential guide for RC, drones, and electronics users.
High‑Capacity 3S LiPo Batteries: 5000 mAh vs. 10000 mAh
Compare 3S LiPo 5000mAh vs 10000mAh batteries by weight, power, and use. Find the best fit for your drone, RC car, or boat setup.
Top 5 Applications for Small 3S LiPo Batteries
Small 3S LiPo batteries power drones, RC gear, wearables, and robotics with high energy and low weight. Making them ideal for compact electronics projects.
Building and Charging Your Own 3S LiPo Pack: A Step‑by‑Step Guide
Learn how to build, balance, and charge a 3S LiPo battery pack safely at home with this complete DIY guide for hobbyists and beginners.
How to Choose the Right LiPo Battery Plug Type?
Discover the best LiPo battery plug types, how to choose them, and expert tips for safe usage, soldering, and maintenance.