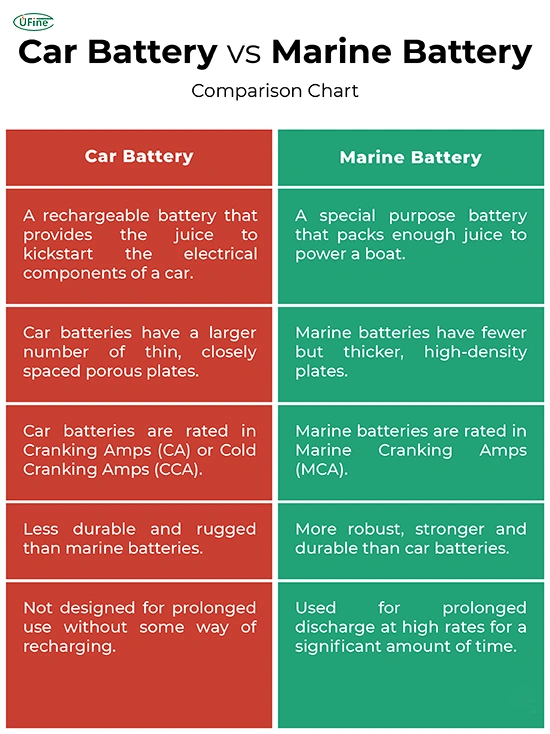
Marine and car batteries are two commonly used types of batteries that serve different purposes. Both batteries provide electrical energy, but they differ significantly in their design and functionality. In this article, we will explore the characteristics and distinctions of marine and car batteries to help you understand their unique functionalities and make informed decisions.
Part 1. Marine battery
We specifically design marine batteries to meet the unique demands of marine applications. Unlike car batteries, which primarily supply power to start an engine, manufacturers build marine batteries to provide a steady energy flow over extended periods. They are commonly used to power trolling motors, navigational equipment, marine lighting, and other electrical components on boats and watercraft.
Marine batteries are typically deep-cycle, designed to discharge a significant portion of their capacity without damage. This feature allows them to provide a consistent and reliable power source for extended periods, even when subjected to heavy loads. Additionally, marine batteries are constructed with thicker plates and robust internal components to withstand the harsh marine environment, including moisture, vibrations, and corrosion.
Part 2. Car battery
On the other hand, manufacturers primarily design car batteries for starting engines. They are also known as automotive batteries or starting batteries. Car batteries deliver a high burst of power to ignite the engine. Once the engine runs, the alternator supplies electricity to the vehicle’s electrical systems and recharges the battery. Generally, car batteries are not intended for deep discharge, as it can significantly reduce their lifespan.
Car batteries are typically less expensive than marine batteries and have thinner plates. They are optimized to deliver a quick burst of energy, known as cranking amps (CA) or cold cranking amps (CCA). These are crucial for starting a vehicle’s engine, especially in cold weather. Manufacturers do not build car batteries to endure frequent deep discharges, which can lead to a loss of capacity and a shortened lifespan.
Part 3. Difference between marine battery and car battery
Design and Construction
Marine batteries have thicker plates and more robust internal components to withstand the harsh marine environment. In contrast, car batteries have thinner plates designed for engine starting.
Battery Capacity
Marine batteries typically have higher amp-hour (Ah) ratings than car batteries. This design allows them to deliver power consistently over extended periods while manufacturers optimize car batteries for quick bursts of energy during engine start-ups.
Cycling Ability
Manufacturers design marine batteries for deep cycling, allowing them to be discharged and recharged multiple times without significant damage. On the other hand, manufacturers do not intend car batteries for deep cycling. They can experience a reduced lifespan if frequently discharged deeply.
Reserve Capacity
Marine batteries often have a higher reserve capacity, which indicates the time a battery can deliver a specific amount of current before falling below a usable voltage threshold. Car batteries typically have lower reserve capacities since they primarily serve short bursts of power.
Vibration Resistance
Manufacturers engineer marine batteries to withstand the vibrations and shocks commonly experienced in aquatic environments, ensuring their reliability and longevity. Car batteries are less resistant to vibrations and may suffer damage if subjected to excessive shaking.
Corrosion Resistance
Manufacturers design marine batteries with enhanced corrosion resistance to combat the corrosive effects of saltwater and other aquatic elements. While generally protected against corrosion, car batteries may not have the same resistance level as marine batteries.
Polarity
The polarity of marine battery terminals is often reversed compared to car battery terminals. Positive and negative terminals have different positions, requiring specific attention when connecting electrical components.
Price
Car batteries are typically less expensive than marine batteries due to their different design and intended usage. Marine batteries have a higher price point with their specialized features and durability.
Part 4. What’s the difference between a car battery and a deep-cycle battery?
- Manufacturers design car batteries to provide energy to start a vehicle’s engine. In contrast, manufacturers make deep-cycle batteries to provide steady power over a more extended period.
- Car batteries have thinner plates and are optimized to deliver a high current quickly. In contrast, deep-cycle batteries have thicker plates to withstand repeated charging and discharging cycles.
- Deep cycle batteries can be discharged to a lower percentage of their capacity without causing damage, whereas discharging a car battery too intensely can lead to permanent damage.
- People typically use car batteries for short, high-energy bursts, like starting an engine. In contrast, they use deep cycle batteries for applications requiring sustained power output, like powering electric trolling motors or RV appliances.
The main difference lies in their design and purpose: car batteries prioritize quick bursts of energy, while deep cycle batteries focus on providing steady power over an extended period.
Part 5. What is the difference between car and marine battery terminals?
- Car battery terminals are usually smaller and rounder, designed to fit the standard battery terminals found in most vehicles.
- On the other hand, marine battery terminals are often larger and more rectangular to accommodate the heavier gauge cables used in marine applications.
- Car battery terminals typically have a single positive terminal (marked with a “+” sign) and a single negative terminal (marked with a “-” sign). In contrast, marine batteries may have multiple terminals for connecting various accessories.
- Marine battery terminals are often coated with corrosion-resistant materials like lead alloy or tin to withstand exposure to saltwater and moisture, which are common in aquatic environments.
- Marine battery terminals may also feature additional connections for accessories like trolling motors, fish finders, or navigation lights. In contrast, car battery terminals are usually more straightforward in design, focusing solely on starting the vehicle.
In summary, while both car and marine battery terminals serve the same primary function of connecting cables to the battery, marine terminals are designed to withstand harsher environments. They may offer additional connections for marine-specific accessories.
Part 6. FAQs
-
Can you use a marine battery in a car?
Yes, you can use a marine battery in a car. However, due to differences in design and intended usage, it may not perform optimally when starting the engine. -
Can you use a deep-cycle battery in a car?
You can use a deep cycle battery in a car, but experts don’t recommend it for everyday driving. Manufacturers design it for sustained power, not quick bursts like starting a car engine. -
Can you use a car battery in a boat?
While it’s possible to use a car battery in a boat for some applications, marine batteries are generally better suited for marine environments due to their construction and ability to withstand factors like vibration, moisture, and corrosion. -
Is a marine battery better than a car battery?
Manufacturers design marine batteries for aquatic environments and sustained power output while they optimize car batteries for starting engines. -
Can you use marine batteries in a golf cart?
You can use marine batteries in a golf cart, especially if you need longer run times between charges. However, ensure the battery’s voltage and capacity match the requirements of your golf cart. -
Can you use a marine battery in a truck?
It’s possible to use a marine battery in a truck. Still, it may not provide optimal performance for starting the engine compared to a battery designed for automotive use. Manufacturers build marine batteries to withstand marine environments so that they may have different starting power than truck batteries.
Related Tags:
More Articles

Comprehensive Guide to Choosing the Right Cart Battery
Choosing the right cart battery ensures optimal performance and longevity. This guide covers cart battery types and helps you make an informed choice.
The Ultimate Guide to 18650 Button Top Battery
18650 button top batteries are popular for their high energy density and reliability. This guide covers their key features, usage, and maintenance tips.
The Power of Slim: Unveiling the Potential of Flat Lithium Ion Battery
Flat lithium-ion batteries power devices from phones to vehicles. This article explores their design, benefits, types, applications, charging, and safety.
The Comprehensive Guide to Battery Balancing and Battery Balancer
Battery balancing and balancers optimize performance, longevity, and safety. This guide covers techniques and tips for choosing the right balancer.
10 Key Facts About Drone Battery for 2024
Uncover crucial insights with "10 Key Facts About Drone Battery for 2024." Learn the latest trends and essential details on drone batteries.