Understanding lithium ion cell sizes is critical for optimizing battery performance. This guide dives deep into standard lithium ion cell sizes (including a detailed comparison chart), their applications, and expert tips for choosing the right battery. Discover why the 18650 dominates laptops while Tesla EVs rely on 21700 cells.
Part 1. What are lithium-ion cells?
Lithium-ion cells are rechargeable batteries that utilize lithium ions as the primary component in their electrochemical reactions. They are renowned for their high energy density, low self-discharge rate, and ability to be recharged multiple times without significant degradation. These cells are available in various shapes and sizes. Their versatility makes them suitable for numerous applications, from consumer electronics to electric vehicles.
Key Characteristics of Lithium-Ion Cells
- High Energy Density: Lithium-ion cells can store much energy relative to size and weight.
- Low Self-Discharge Rate: They maintain their charge for extended periods, making them ideal for devices that people use infrequently.
- Long Cycle Life: With proper care, lithium-ion batteries can last several years, providing reliable power.
- Environmental Impact: Lithium-ion cells are generally more environmentally friendly than lead-acid batteries, mainly when appropriately recycled.
Part 2. Standard lithium-ion cell sizes
Understanding standard lithium-ion cell sizes is essential for selecting the correct battery for specific applications. Here are some standard sizes and their dimensions:
Lithium Ion Cell Sizes Chart: Standard Dimensions and Capacity
Below is the most comprehensive lithium ion cell sizes chart, comparing key specifications for popular models like 18650 and 21700 batteries.
Common Sizes and Dimensions
| Battery Type | Dimensions (mm) | Capacity (mAh) | Common Uses | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10440 | 10 x 44 | 250 – 350 | Mini electronics, flashlights | |
| 14500 | 14 x 50 | 700 – 1200 | LED flashlights, digital cameras | |
| 16340 | 16 x 34 | 400 – 900 | Laser lights, security cameras | |
| 18650 | 18 x 65 | 1500 – 4000 | Laptops, electric vehicles | |
| 21700 | 21 x 70 | 3000 – 6000 | E-bikes, power tools | |
| 26650 | 26 x 65 | 2400 – 6000 | High-powered flashlights, drones | |
Lithium Ion Cell Sizes Comparison: 18650 vs 21700 vs 26650
Understanding key differences between popular cell sizes:
| Cell Type | Diameter | Typical Capacity | Key Applications | Advantages |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 18650 | 18mm | 1500-4000mAh | Laptops, Power Tools | Widely available, cost-effective |
| 21700 | 21mm | 3000-6000mAh | Tesla EVs, E-bikes | Higher energy density, longer lifespan |
| 26650 | 26mm | 2400-6000mAh | Solar Storage, Drones | Maximizes capacity in limited space |
Real-World Example: Tesla’s shift from 18650 to 21700 cells increased Model 3’s battery pack energy density from 250 Wh/kg to 300 Wh/kg, extending range by 15%.
Industry Standards for Cell Sizes
The 21700 size was standardized by the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) in 2018, driving its adoption across EV manufacturers. This standardization ensures compatibility between batteries from Panasonic, LG Chem, and other major suppliers.
Why Is It Important to Follow Industry Standard Battery Sizes?
1. Improved Production Efficiency
Standard battery sizes help manufacturers streamline their production. Companies can reduce equipment costs and maintenance by focusing on specific battery models. This efficiency lowers production costs and boosts competitiveness.
2. Reduced Design and Development Costs
With standard sizes, manufacturers can use multiple production lines. This adds complexity and costs. Standardizing sizes helps reduce design changes and development costs.
3. Enhanced Compatibility
Standard battery sizes make it easier to fit batteries into devices. This reduces compatibility issues and simplifies battery replacement or upgrades for consumers.
4. Ensured Product Quality
Different sizes require different production processes and quality checks. Standardizing sizes helps maintain consistent quality and reliability and reduces quality fluctuations.
5. Industry Growth
With the rise of electric vehicles and renewable energy, battery demand is growing. Standardizing sizes supports industry growth and allows innovators to focus on new developments.
6. Easier Battery Recycling
Uniform battery sizes make recycling simpler. This helps improve recovery rates and reduces environmental impact, supporting sustainable development goals.
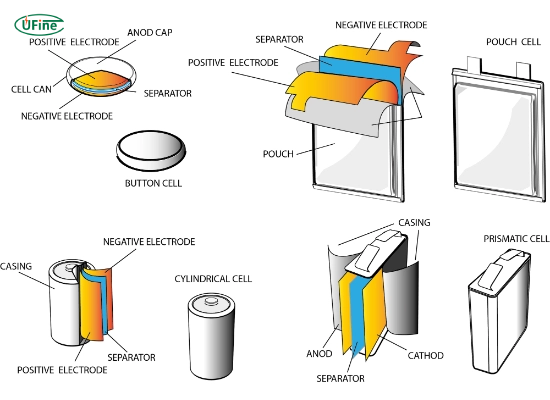
Part 3. Types of lithium-ion cells
Lithium-ion cells can be divided into several types based on their shape and construction. Each type has advantages and disadvantages, making it suitable for different applications.
Cylindrical Cells
Cylindrical cells are the most widely used type of lithium-ion battery. They are typically encased in a metal cylinder and are known for their robustness and high energy density.
Standard Sizes: 18650, 21700, 26650
Applications: Laptops, power tools, electric vehicles, and flashlights.
Advantages:
- High energy density.
- Robust construction.
Disadvantages:
Less efficient use of space in battery packs compared to prismatic cells.
Prismatic Cells
Prismatic cells are rectangular, allowing for better space utilization in battery packs. They are often used in applications where space is at a premium.
Standard Sizes: 103450, 18650 (in prismatic form)
Applications: Smartphones, tablets, and electric vehicles.
Advantages:
- Better space efficiency.
- It is easier to integrate into compact designs.
Disadvantages:
Generally lower energy density compared to cylindrical cells.
Pouch Cells
Pouch cells are flexible and lightweight, encased in a soft, foil-like material. They can be manufactured in various shapes and sizes, making them versatile for different applications.
Standard Sizes: Custom sizes based on application needs.
Applications: Wearable devices, smartphones, and drones.
Advantages:
- Lightweight and flexible.
- Customizable shapes and sizes.
Disadvantages:
Less durable than cylindrical or prismatic cells.
Button Cells
Button or coin cells are small, round batteries typically used in low-power devices.
Standard Sizes: CR2032, CR2025
Applications: Watches, remote controls, and small electronic devices.
Advantages:
- Compact and lightweight.
- Cost-effective for low-power applications.
Disadvantages:
Limited capacity and power output.
Part 4. Why do different battery specifications require different manufacturing processes?
1. Variations in Size and Shape
Batteries come in many shapes and sizes, like cylindrical or pouch types. Each design needs specific equipment and processes. For example, cylindrical batteries use winding techniques, while pouch batteries are stacked.
2. Different Capacity and Energy Density Requirements
Batteries have different needs in terms of capacity and energy. Larger-capacity batteries need precise manufacturing techniques to maximize energy density.
3. Diverse Materials and Chemical Systems
Batteries use different materials and chemicals. For instance, lithium iron phosphate batteries need different processes than lithium cobalt oxide batteries.
4. Application-Specific Needs
Different uses require different battery features. For example, electric vehicle batteries need high safety and consistency, while consumer batteries focus on energy density and cost.
5. Variations in Manufacturing Equipment and Technology
Manufacturers use different equipment. Advanced equipment makes high-performance batteries but costs more. More straightforward equipment helps smaller companies manage expenses.
Part 5. How to choose the right lithium-ion cell size?
When selecting a lithium-ion cell, consider the following factors:
- Application Requirements: Determine the energy needs of your device. Higher-capacity cells are better for devices requiring more power.
- Size Constraints: Ensure the cell fits within the physical dimensions of your device.
- Weight Considerations: For portable devices, lighter batteries are preferable.
- Cost: Different cell types and sizes come at various prices, so budget accordingly.
Still unsure which size fits your project? Learn how to Calculate Lithium Battery Capacity or explore Different Types of Lithium Batteries.
Part 6. FAQs about lithium ion cell sizes
What is the standard lithium ion cell size for laptops and EVs?
The 18650 (18mm diameter x 65mm length) remains the standard lithium ion cell size for most laptops. For electric vehicles like Tesla models, the 21700 (21mm x 70mm) has become dominant, offering 50% higher energy density than 18650 cells.
How do I know which lithium-ion cell to choose?
Consider your device’s energy requirements, physical space constraints, and weight limits. For example, drones need high-capacity 26650 cells, while compact electronics perform best with 14500 sizes.
Can lithium-ion cells be recycled?
Yes, lithium-ion cells are 95% recyclable. Major manufacturers like Ufine Battery participate in certified recycling programs to recover cobalt, nickel, and lithium materials.
What are the safety concerns with lithium-ion batteries?
Key risks include thermal runaway (fire risk) if damaged or overheated. Always use batteries with built-in protection circuits and avoid exposing them to temperatures above 60°C (140°F).
How long do lithium-ion batteries last?
Typical lifespan is 300-500 charge cycles (2-3 years). High-quality 21700 cells in EVs can last 1,000+ cycles, maintaining 80% capacity after 8 years.
Related Tags:
More Articles

High‑Capacity 3S LiPo Batteries: 5000 mAh vs. 10000 mAh
Compare 3S LiPo 5000mAh vs 10000mAh batteries by weight, power, and use. Find the best fit for your drone, RC car, or boat setup.
Top 5 Applications for Small 3S LiPo Batteries
Small 3S LiPo batteries power drones, RC gear, wearables, and robotics with high energy and low weight. Making them ideal for compact electronics projects.
Building and Charging Your Own 3S LiPo Pack: A Step‑by‑Step Guide
Learn how to build, balance, and charge a 3S LiPo battery pack safely at home with this complete DIY guide for hobbyists and beginners.
How to Choose the Right LiPo Battery Plug Type?
Discover the best LiPo battery plug types, how to choose them, and expert tips for safe usage, soldering, and maintenance.
Choosing the Right Connector for Your 3S LiPo Battery
Choosing the right 3S LiPo connector depends on current, space, and use. Learn the pros and cons of XT60, JST, EC3, and more.