A battery is a device that converts chemical energy into electrical energy, which is widely used in various fields, such as electronic equipment, transport, energy reserves, and so on. Different battery materials determine the performance characteristics of the battery, and one important parameter is the battery voltage. We will take you through the lithium-ion battery voltage chart.
Part 1. Lithium-ion battery voltage chart and definitions
The lithium-ion battery voltage chart is a comprehensive guide to understanding the potential difference between the battery’s two poles. Key voltage parameters within this chart include rated voltage, open circuit voltage, working voltage, and termination voltage.
|
Voltage Type |
Description |
Typical Value (for Lithium-ion Batteries) |
|
Rated Voltage |
Nominal value representing the theoretical design voltage of the battery. |
Varies for different materials |
|
Open Circuit Voltage |
Potential difference between the positive and negative terminals when the battery is inactive, i.e., no current is passing through. |
Around 3V |
|
Working Voltage |
Actual voltage at both ends of the battery during operation. Generally lower than the open-circuit voltage due to polarization and internal resistance. |
Less than the open-circuit voltage |
|
Termination Voltage |
Maximum charging and discharging voltage during the charging or discharging process. Falling below the discharge termination voltage can lead to rapid voltage drop, resulting in a deep discharge and potential damage to the battery. |
Depends on the specific battery model |
Rated voltage
The rated voltage is the nominal value and belongs to the theoretical voltage on behalf of the design voltage. The theoretical voltage is the maximum limit of the battery voltage, and the theoretical voltage of the battery is different for different materials.
Open circuit voltage
The open circuit voltage refers to the open circuit voltage is the potential difference between the positive and negative terminals of the battery when there is no current passing through the battery, that is, the voltage between the positive and negative terminals when the battery is not working. For example, the open-circuit voltage of lithium-ion batteries is generally around 3V, and sodium-ion batteries will be below 3V.
Working voltage
The working voltage refers to the voltage at both ends of the battery when it is working, that is, the actual voltage of the battery. Generally, the actual voltage is less than the open-circuit voltage because the battery needs to overcome the battery’s polarization and internal resistance when working.
Termination voltage
The termination voltage refers to the maximum charging and discharging voltage of the battery in the process of charging or discharging. Suppose the voltage is lower than the discharge termination voltage after the battery discharges. In that case, the voltage at both ends of the battery will drop rapidly, forming a deep discharge, so that the plate’s formation on the product’s formation in the standard charging is not easy to recover, thus affecting the life of the battery.
Part 2. Lithium-ion battery voltage chart for different materials
Different battery materials have different battery voltages caused by the differences in their chemical reaction processes and electron transfer mechanisms. The following are several common battery materials and their corresponding battery voltages:
|
Battery Type |
Positive Electrode Material |
Negative Electrode Material |
Voltage Range |
Advantages |
|
Ternary Material Batteries |
Lithium-nickel-cobalt-manganese oxide (LiNiCoMnO2) |
Graphite or other carbon materials |
2.5V to 4.2V |
Efficient charge transfer, electrical energy generation during charging and discharging, versatile applications. |
|
Lithium-Iron Phosphate Battery |
Lithium iron phosphate (LiFePO4) |
Carbon |
3.2V (rated), 3.6V to 3.65V (charging cut-off) |
High operating voltage, high energy density, long cycle life, good safety performance, low self-discharge rate, no memory effect. |
|
Lithium Cobaltate Battery |
Lithium cobalt oxide (LiCoO2) |
Graphite or other carbon materials |
3.6V to 4.2V |
Suitable for various applications, moderate voltage range. |
Ternary material batteries
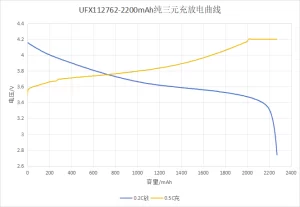
The positive electrode material of ternary material batteries is lithium-nickel-cobalt-manganese oxide (LiNiCoMnO2), composed of lithium, nickel, cobalt, and manganese. In contrast, the harmful electrode material comprises graphite or other carbon materials. Lithium ions move back and forth between the positive and negative electrodes during the charging and discharging process, generating electrical energy by charge transfer through the electrolyte medium. The voltage range of batteries made of ternary materials is between 2.5V and 4.2V.
Lithium-iron phosphate battery
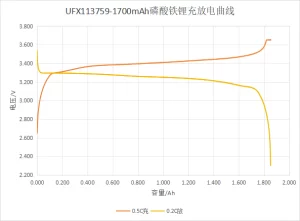
Lithium iron phosphate battery is a kind of lithium-ion battery using lithium iron phosphate (LiFePO4) as the cathode material and carbon as the anode material, with a single rated voltage of 3.2 V and a charging cut-off voltage of 3.6 V to 3.65 V. Lithium iron phosphate battery has the advantages of high operating voltage, high energy density, long cycle life, good safety performance, low self-discharge rate, and no memory effect.
Lithium cobaltate battery
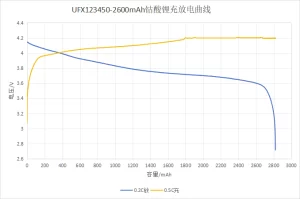
The buoyant material of a lithium cobaltate battery is lithium cobalt oxide (LiCoO2), which is composed of lithium, cobalt, and oxygen. In contrast, the harmful material is graphite or other carbon materials. Its battery voltage is usually 3.6 volts (V) to 4.2 volts (V).
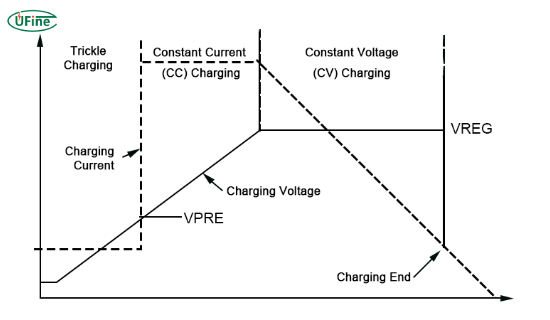
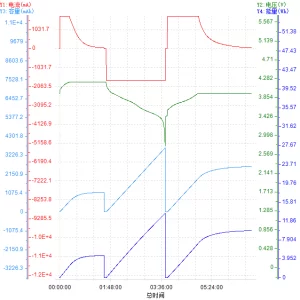
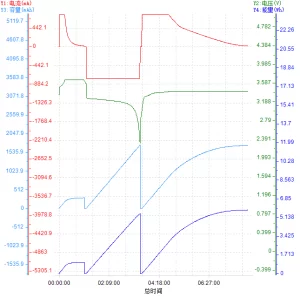
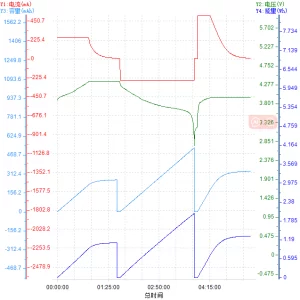
Lithium-ion battery charge and discharge curve:
1)NCM 2)LFP
3)LiCOO2
The relationship between battery voltage and capacity, the corresponding battery state:
1)NCM 804585 3.7 V 3500mAh 2)LFP 904062 3.2 V 1500mAh
3)LiCOO2 782525 4.2 V 510mAh
Part 4. Why do you need to know about lithium-ion battery voltage?
Diverse material impacts
Lithium batteries vary in their voltage ranges based on the materials used in their construction. Selecting the appropriate battery is pivotal as it directly influences equipment performance and safety. The nuanced differences in voltage among lithium battery variants necessitate precise selection to guarantee optimal functioning and mitigate potential risks associated with incompatible voltages.
Performance alignment
Battery voltage serves as a pivotal metric defining the energy output capacity of the battery. Varied applications require specific voltage ranges to operate effectively. High-powered devices demand batteries with a higher voltage for sufficient power output. In contrast, low-powered devices can function optimally with lower-voltage batteries. A comprehensive understanding of battery voltage ranges facilitates the meticulous selection of batteries, ensuring seamless device operation and peak performance across diverse usage scenarios.
Compatibility and integration
Understanding lithium-ion battery voltage is crucial for ensuring compatibility and seamless integration within devices or systems. Different devices are designed to operate within specific voltage ranges, and selecting the appropriate battery voltage ensures optimal performance and safety. Using a battery with an incompatible voltage could lead to malfunction or potential damage to the equipment.
Safety considerations
Voltage plays a significant role in the safety of lithium-ion batteries. In extreme cases, overvoltage or undervoltage scenarios can cause issues like overheating, leakage, or even explosion. Being aware of the correct voltage range helps prevent these hazardous situations, ensuring battery-powered devices’ longevity and safe operation.
Charging and discharging efficiency
It is understanding the voltage range of lithium-ion batteries aids in efficient charging and discharging processes. It helps in determining the right charging protocols and discharge rates, optimizing the battery’s performance, and prolonging its lifespan. Charging a battery with an inappropriate voltage could reduce efficiency or damage to the battery cells.
Regulatory compliance
Voltage specifications often align with industry standards and regulations. Ensuring that the battery voltage meets these standards is essential for compliance purposes, especially in regulated sectors like medical devices or aviation, where adherence to specific voltage ranges is mandatory for safety and quality standards.
Part 5. Conclusion
In short, understanding the voltage range of batteries is crucial to the proper selection and use of lithium batteries. As a company specializing in the production of high-quality lithium batteries, Ufine is committed to providing reliable battery products and LFP batteries that meet the needs of our customers. Our products have stability, reliability, and high performance to meet the needs of various application scenarios. By choosing Ufine’s lithium batteries, you can rest assured that you will be able to use them and get a quality supply of electrical energy.
Related Tags:
More Articles

Comprehensive Guide to Choosing the Right Cart Battery
Choosing the right cart battery ensures optimal performance and longevity. This guide covers cart battery types and helps you make an informed choice.
The Ultimate Guide to 18650 Button Top Battery
18650 button top batteries are popular for their high energy density and reliability. This guide covers their key features, usage, and maintenance tips.
The Power of Slim: Unveiling the Potential of Flat Lithium Ion Battery
Flat lithium-ion batteries power devices from phones to vehicles. This article explores their design, benefits, types, applications, charging, and safety.
The Comprehensive Guide to Battery Balancing and Battery Balancer
Battery balancing and balancers optimize performance, longevity, and safety. This guide covers techniques and tips for choosing the right balancer.
10 Key Facts About Drone Battery for 2024
Uncover crucial insights with "10 Key Facts About Drone Battery for 2024." Learn the latest trends and essential details on drone batteries.