Do you need clarification about choosing LiPo, Li-ion, or LiFePO4 batteries? Don’t worry; depending on your application and requirements, you must compare and analyze to select the best battery.
Each battery has unique specifications, construction, and applications. Hence, you need to know each in detail to identify the best fit.
In this guide, we will walk through all three types of batteries, LiPo, Li-ion, and LiFePO4, in terms of construction, advantages, disadvantages, and a quick comparison.
Part 1. What are LiPo batteries?
LiPo batteries, also known as Lithium Polymer batteries. They are a class of rechargeable battery that uses polymer electrolytes rather than liquid electrolytes. However, LiPo batteries are very flexible in shape and size. Thus, they are widely used in many applications due to their effectiveness.
Construction
LiPo batteries consist of multiple cells, each consisting of a positive electrode (the cathode), a negative electrode (the anode), and a separator. These properties help build contact between the electrodes. However, the electrodes are made of a lithium-based compound, namely lithium cobalt oxide or lithium manganese oxide, but the electrolyte is a polymer gel.
Advantages and limitations
The following are the critical advantages of LiPo battery:
- Ability to store large amounts of energy
- It is a small, lightweight package and best suits portable electronics and many applications.
- It can be produced in various shapes and sizes and is ideal for a wide range of devices.
- It consists of high discharge rates and is suitable for rapid power delivery.
The following are the key disadvantages of LiPo battery:
- LiPo battery is sensitive to overcharging.
- It has a limited lifespan and may experience degradation with time.
- Requires careful handling in terms of safety and storage.
Applications
The following are the primary applications of LiPo batteries:
- Consumer electronics (smartphones, tablets, laptops, and portable electronic devices)
- Remote-controlled vehicles (RC cars, boats, airplanes, and drones)
- Medical devices (portable defibrillators, infusion pumps, and patient monitors).
- Aerospace and aviation (uncrewed aerial vehicles (UAVs), satellites, and other aerospace applications)
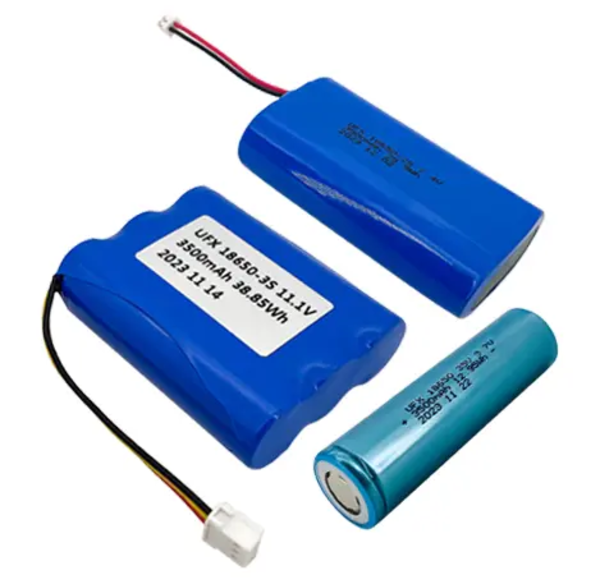
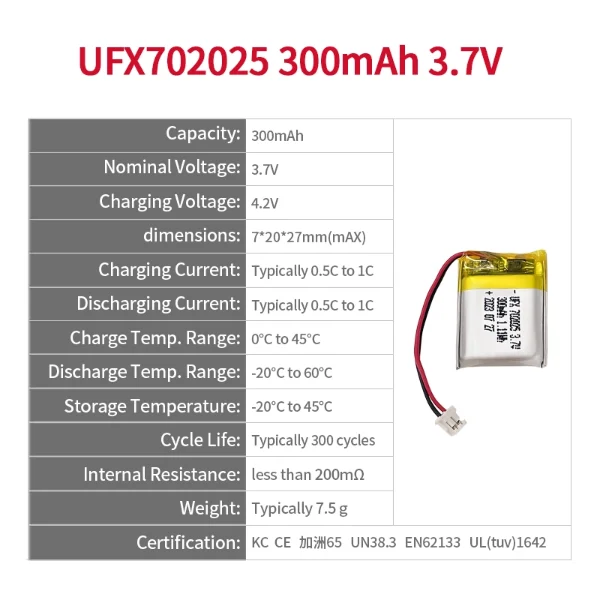
Our LiPo Battery Recommendation
Ufine 3.7 V 300mAh Lithium Ion Battery 702025
Part 2. What are li-ion batteries?
Li-ion batteries, also called Lithium-ion batteries, are a class of rechargeable batteries that use lithium ions as the preceding component of its electrolyte. Thus, they are widely used in many electronic devices as they have a high energy density, are lightweight, and have a long lifespan.
Construction
A Li-ion battery has one or more cells, each consisting of a positive electrode (cathode), a negative electrode (anode), and a separator (to prevent direct contact between the electrodes). Lithium cobalt oxide (the cathode) and graphite (the anode) are the electrodes. The electrolyte is made of lithium salt dissolved in a solvent.
Advantages and limitations
The following are the critical advantages of Li-ion battery:
- Consists of high energy density.
- It is relatively small and lightweight, making it widely used in portable electronic devices, namely smartphones, laptops, and tablets.
- Has a longer lifespan compared to other rechargeable battery chemistries.
- Possess a low self-discharge rate and retain the charge for extended periods when unused.
The following are the key disadvantages of Li-ion batteries:
- Ability to hold charge only for a limited temperature scale between 0°C and 45°C.
- It may cause performance issues or reduce lifespan if used outside its optimal temperature range.
- Proper safety concerns must be implemented to prevent thermal runaway and fire.
- Careful handling and charging techniques should be managed to avoid the cause of any accidents.
- It may cause environmental impact due to using toxic materials such as lithium and cobalt.
Applications
The following are the primary applications of Li-ion batteries:
- Consumer electronics (smartphones, laptops, tablets, digital cameras, and more! )
- Electric vehicles (EVs)
- Power auxiliary systems (air conditioning and infotainment).
- Energy storage applications (grid-scale energy storage systems and residential battery backup systems)
- Aerospace and aviation (aircraft and spacecraft such as powering onboard systems, emergency backup power, and electric propulsion systems)
Our Li-ion battery Recommendation
Ufine 18650 Li-ion Battery 3500mAh
Part 3. What are LiFePO4 batteries?
LiFePO4 batteries are also called Lithium Iron Phosphate batteries. They are another class of rechargeable battery that operates using lithium iron phosphate as the cathode material. Thus, they ensure higher safety, longevity, and stability to power many applications, including consumer electronics. Hence, they are widely used in renewable energy storage systems.
Construction
LiFePO4 battery construction is closely related to other lithium-ion batteries. However, it consists of positive and negative electrodes separated by an electrolyte. The positive electrode is produced of lithium iron phosphate (LiFePO4), the negative electrode is assembled using carbon, and the electrolyte is a lithium salt dissolved in a solvent. Thus, the purpose and inclusion of lithium iron phosphate serve to support thermal and chemical stability compared to other lithium-ion chemistries.
Advantages and limitations
The following are the critical advantages of LiFePO4 battery:
- Ensures high safety for excellent thermal and chemical stability
- Less inclined to thermal runaway and fire hazards compared to other lithium-ion chemistries.
- It has a longer lifespan compared to other lithium-ion types.
- The ability to withhold thousands of charge-discharge cycles supports minimal capacity degradation and a stable voltage output.
- They are concerned to be environmentally friendly as they contain non-toxic and abundant materials.
The following are the key disadvantages of LiFePO4 battery:
- It has less energy density comparatively to other lithium-ion chemistries
- It has a large and heavy battery pack to store the energy capacity.
- It has a higher cost compared to other lithium-ion chemistries.
Applications
The following are the primary applications of LiFePO4 battery:
- Electric vehicles (EVs) (electric drivetrain and auxiliary systems)
- Renewable energy storage (solar energy storage systems and wind energy storage systems)
- Marine and RV applications (marine and recreational vehicle (RV) applications)
- Backup power systems (backup power systems for homes, businesses, and critical infrastructure)
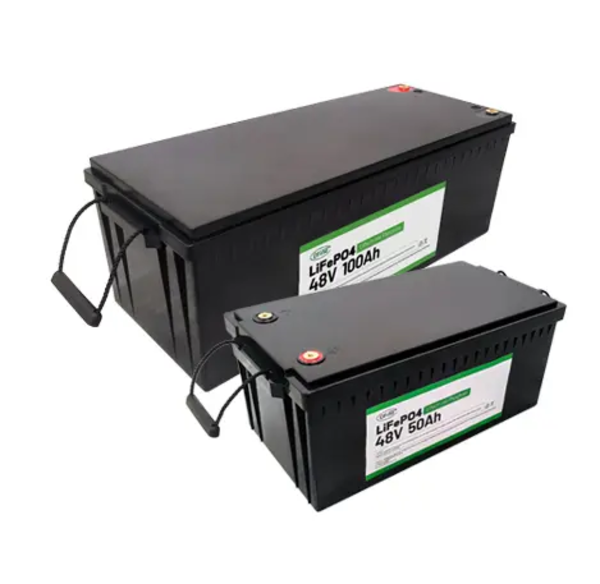
Our LiFePO4 battery Recommendation
Part 4. Li-Po VS Li-ion VS LiFePO4
Chemistry:
- Li-Po: Polymer electrolyte ensuring a flexible shape.
- Li-ion: Made of cathode materials and different anodes.
- LiFePO4: Made of cathode material and lithium iron phosphate for enhanced stability.
Safety:
- Li-Po: It is prone to swelling and thermal runaway.
- Li-ion: It has the risk of thermal runaway and fire hazards.
- LiFePO4: It is known for its high thermal and chemical stability.
Cycle Life:
- Li-Po: It consists of a moderate cycle life.
- Li-ion: It consists of a shorter cycle life compared to LiFePO4.
- LiFePO4: It consists of a longer cycle life with minimal degradation.
Voltage:
- Li-Po: 3.7V per cell.
- Li-ion: Nominal 3.6V to 3.7V per cell.
- LiFePO4: 3.2V per cell.
Energy Density:
- Li-Po: Has a high energy density.
- Li-ion: Has a higher energy density than LiFePO4.
- LiFePO4: Has a lower energy density compared to some lithium-ion types.
Applications:
- Li-Po: RC vehicles, drones, portable electronics.
- Li-ion: Consumer electronics, electric cars.
- LiFePO4: Electric cars, solar storage, backup power.
Part 5. Final thoughts
In conclusion, whether you choose Li-Po, Li-ion, or LiFePO4 batteries depends on several factors, such as safety requirements, cycle life, voltage, density, and your requirements.
Hence, identify your unique requirements and correlate them to find the best type of battery suiting your application.
Part 6. FAQs
-
Which is better, LiPo or LiFePO4?
Whether LiPo or LiFePO4 is better depends on your requirements. If you need a high-voltage battery, LiPo is the best. However, if you consider your safety, LiFePO4 is your go-to choice. -
Which is better, lithium-ion or LiFePO4 battery?
Choosing between lithium-ion or LiFePO4 batteries depends on a couple of factors, such as safety. Lithium-ion batteries are recommended as they are resistant to temperature. -
Is li-ion battery better than LiPo?
When comparing Li-Ion and LiPo batteries, it’s essential to consider your specific requirements. LiPo batteries excel in high-voltage and speed applications, while Li-Ion batteries offer superior capacity and energy density. Understanding these performance differences can guide your decision. -
Are lithium-ion and LiFePO4 chargers the same?
You can charge LiFePO4 using a lithium-ion or even an AGM charger. However, the charger should have the exact voltage to ensure compatibility with the other device.
Related Tags:
More Articles

What Is a Disk Battery? A Simple Guide for Non-Tech Users
A disk battery is a small, round cell used in watches, remotes, and other electronic devices. It delivers steady power for compact, low-drain devices.
What Battery Powers a Space Heater?
Discover the type of battery that powers space heaters and learn how to choose the right one for efficient heating in your home or office.
What Is an LR14 Battery? Learn About This C-Size Cell
The LR14 battery, also known as a C battery, delivers steady power. Learn its specs, uses, lifespan, and how it compares to other battery types.
Watch Battery Dimensions Chart: Sizes, Voltages, and Equivalents Explained
Understanding watch battery dimensions helps you choose the right size, voltage, and equivalent model to keep your watch running safely and smoothly.
How Long Can You Rely on Battery-Powered Generators?
Discover battery generator runtime & lifespan factors. Learn how to maximize performance and choose the right power solution.