- Part 1. Are lithium batteries inherently dangerous?
- Part 2. Most common dangers associated with lithium batteries
- Part 3. Causes of lithium battery failures
- Part 4. Which lithium battery is the most dangerous?
- Part 5. How manufacturers ensure lithium battery safety
- Part 6. How to use and store lithium batteries safely
- Part 7. Are lithium batteries harmful to humans?
- Part 8. Signs that a lithium battery may be dangerous
- Part 9. How to deal with dangerous lithium batteries
- Part 9. Final thoughts
- Part 11. FAQs
Lithium batteries have changed the way we live. From powering smartphones to electric vehicles, they are small, powerful, and reliable. But with that power comes a question that many people often overlook: Is there any danger to a lithium battery?
The short answer is yes. Lithium battery dangers are real. But with proper knowledge and precautions, most risks can be minimized. This article explores these risks in depth, including why they happen, how to avoid them, and what warning signs to watch for.
Let’s dig deeper.
Part 1. Are lithium batteries inherently dangerous?
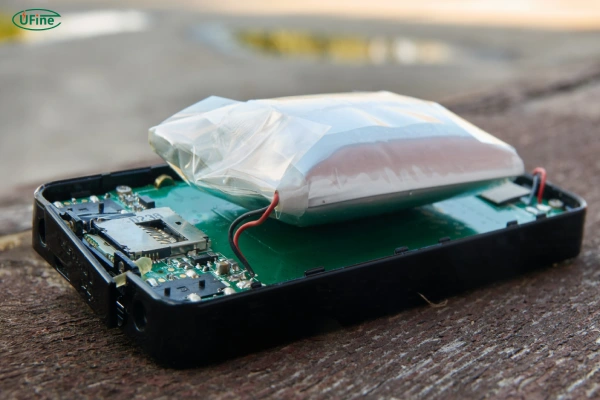

To understand whether lithium batteries are inherently dangerous, we need to look at how they work.
Lithium batteries store energy using electrochemical reactions. Inside each battery are two electrodes (a cathode and an anode), a separator, and an electrolyte. The lithium ions move between the electrodes through the electrolyte, producing energy. However, these reactions are delicate.
Here’s why lithium batteries can become dangerous:
- High Energy Density: Lithium batteries pack a lot of power in a small package. If something goes wrong, that energy is released rapidly.
- Flammable Electrolyte: The liquid electrolyte inside is often flammable. If the battery overheats, it can catch fire.
- Thermal Runaway: This is a chain reaction where increasing temperature causes further reactions, leading to explosions or fires.
- Internal Short Circuits: If the separator is damaged, the positive and negative electrodes can touch, causing a short circuit.
So yes, lithium batteries are inherently dangerous in principle—not because they are poorly designed, but because of the nature of the materials and chemistry involved.
That said, in real life, most lithium battery dangers come from external factors like damage, misuse, or poor manufacturing.
Part 2. Most common dangers associated with lithium batteries
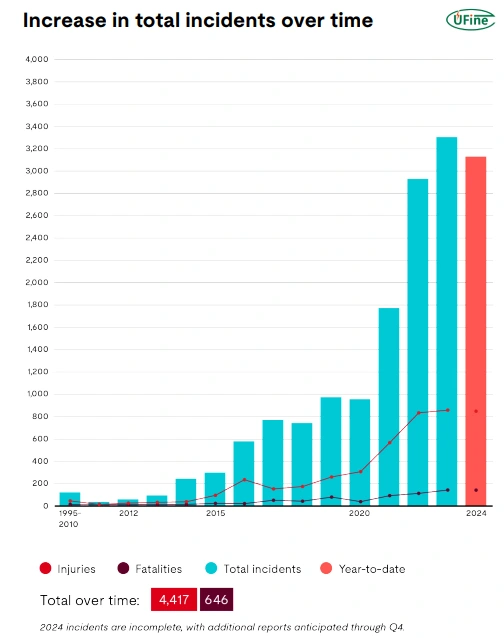
UK fire brigades are now responding to more than three lithium-ion battery fires each day, according to QBE.UK fire brigades attended 1,330 lithium-ion battery fires in 2024.This represents a 93% increase from 2022.The insurance company recorded 1,330 lithium-ion battery fires in 2024, up from 690 in 2022.
Let’s look at the most common lithium battery dangers that users should be aware of:
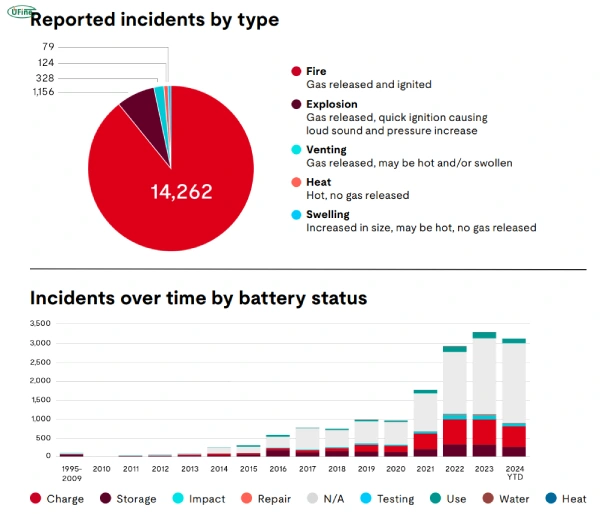
- Fires: Overheating during charging or use can lead to fire.
- Explosions: In rare cases, gases inside the battery cause it to burst violently.
- Swelling and Leaking: Internal pressure from chemical reactions can cause the battery to swell and leak hazardous material.
- Electric Shock: Though rare, handling exposed terminals may lead to shock.
Part 3. Causes of lithium battery failures
Understanding the causes of battery failure can help prevent them. Here are the key reasons why lithium batteries fail:
1. Overcharging
Overcharging a lithium battery can lead to overheating and gas buildup, eventually causing thermal runaway.
2. Physical Damage
Dropping or puncturing a battery can compromise the internal structure. Damaged cells are much more likely to catch fire.
3. High Temperatures
Storing or using batteries in hot environments (like inside a car) can increase pressure inside the battery, leading to leakage or fire.
4. Low-Quality Manufacturing
Batteries without proper protection circuits or quality control are far more likely to fail. That’s why choosing a reputable supplier is critical.
This is where Ufine Battery stands out. As a professional Chinese custom lithium battery manufacturer, Ufine Battery offers high-quality lithium polymer batteries, LiFePO4 batteries, 18650 cells, cylindrical, ultra-thin, and high-temperature lithium batteries. Our strict safety standards and reliable designs reduce risks significantly. Contact Ufine Battery to learn more or request a quote.
Part 4. Which lithium battery is the most dangerous?
There are several types of lithium batteries, and they vary in stability and risk:
1. Lithium-ion (Li-ion)
Used in phones and laptops. High energy density, moderate risk.
2. Lithium-polymer (LiPo)
Used in drones and RC models. Lighter and flexible, but more sensitive to overcharge and damage. Higher risk if misused.
3. Lithium Iron Phosphate (LiFePO4)
Used in solar systems, EVs, and energy storage. Very stable, lower risk of fire. Safer but heavier and bulkier.
LiPo batteries are generally considered the most dangerous if punctured or improperly charged. For safer applications, LiFePO4 is recommended.
Part 5. How manufacturers ensure lithium battery safety
Good battery design is essential to safety. Here’s how top manufacturers reduce lithium battery dangers:
- Battery Management Systems (BMS): Prevent overcharging, over-discharging, and overheating.
- Thermal Cutoff Switches: Disconnect power when overheating is detected.
- Current Limiters and Fuses: Prevent short circuits.
- Quality Testing: Ensures each battery meets safety standards like UL, CE, or IEC certifications.
Again, this highlights the importance of buying from reliable manufacturers like Ufine Battery, where safety is built into every cell.
Part 6. How to use and store lithium batteries safely
Your daily habits also affect safety. Follow these tips:
- Charge with the original charger only.
- Never overcharge or leave batteries charging overnight.
- Store batteries in a dry, cool place.
- Avoid metal contact: Never let battery terminals touch coins or keys.
- Inspect batteries for swelling, cracks, or heat before use.
Using fireproof charging bags and disconnecting the battery after charging are also smart precautions.
Part 7. Are lithium batteries harmful to humans?
Yes, but only in rare or extreme situations. If a battery leaks or explodes, the chemicals released can:
- Irritate skin or eyes
- Cause respiratory issues if inhaled
- Be toxic if ingested
Never open or tamper with a battery. Dispose of damaged batteries carefully to avoid exposure.
Part 8. Signs that a lithium battery may be dangerous
Watch out for these warning signs:
- Swelling or bloating
- Excess heat during charging
- Strange smell or smoke
- Cracks or leaks
- Inconsistent charge performance
If you notice any of these, stop using the battery immediately and contact a recycling center or disposal service.
Part 9. How to deal with dangerous lithium batteries
If a battery becomes dangerous:
- Unplug it immediately.
- Move it to a fire-safe area, such as outdoors or in a metal container.
- Do not throw it in household trash.
- Call your local hazardous waste center for safe disposal.
- For fire, use a Class D extinguisher or sand—never water.
Part 9. Final thoughts
So, is there any danger to a lithium battery? The answer is yes—but most of those dangers are preventable. With the right design, proper use, and smart handling, lithium battery dangers can be reduced to almost zero.
When buying batteries, trust manufacturers who prioritize safety. Ufine Battery offers custom-made, certified lithium batteries that meet rigorous safety standards. If you’re sourcing lithium batteries for your business or project, reach out to Ufine Battery for expert help and reliable solutions.
Part 11. FAQs
Can lithium batteries explode without warning?
Usually not. There are often signs like swelling or heat.
What battery type is safest?
LiFePO4 batteries are very stable and rarely catch fire.
Can I travel with lithium batteries?
Yes, in carry-on bags. Airlines have rules about size and quantity.
Can I use any charger for my lithium battery?
No. Using the wrong charger increases fire risk.
Where can I find safe lithium batteries?
Choose trusted suppliers like Ufine Battery. They provide high-quality, custom lithium battery solutions.
Related Tags:
More Articles

NiMH vs Lithium 7.2V Battery and Charger: Which Is Better?
Compare 7.2V NiMH vs Lithium batteries and chargers in 2025. Learn runtime, weight, charging, lifespan, and cost to choose the best for your device.
How to Choose the Right 7.2V Battery and Charger for Your Device?
Learn how to choose the right 7.2V battery and charger for optimal performance, safety, and longevity across RC, tools, medical, and industrial devices.
Big Square Battery Safety Standards You Must Know
Learn key safety standards for big square batteries to avoid fire risks, shipping delays, and compliance issues in EV, industrial, and energy storage projects.
Big Square Battery Applications in Solar & Industrial Equipment
Big square batteries deliver high capacity, stable output, and long life for solar, industrial, and backup power. Explore key uses and advantages.
Big Square Battery vs Cylindrical Battery: Complete 2025 Guide for EVs, ESS & Industrial Devices
Choosing the right battery is key for designers and engineers. Compare big square vs cylindrical batteries to find the best fit for your application.