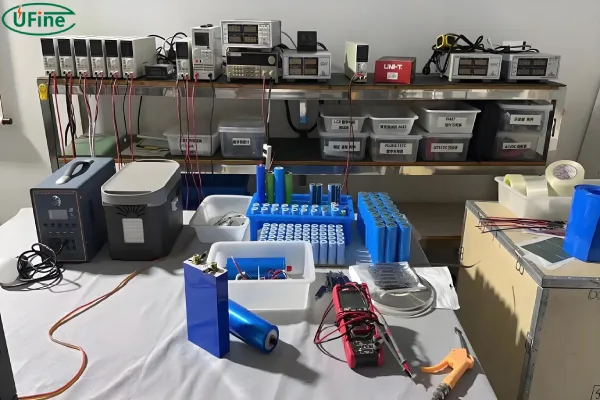
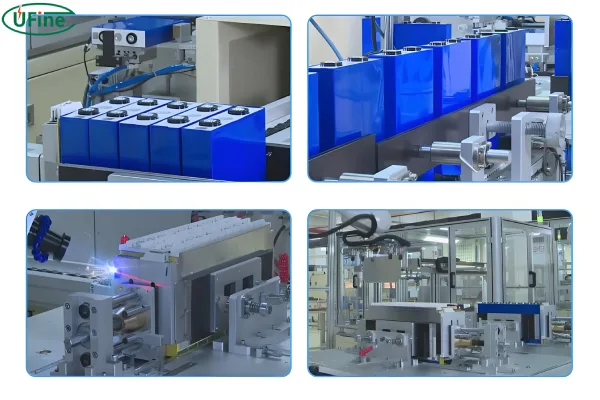
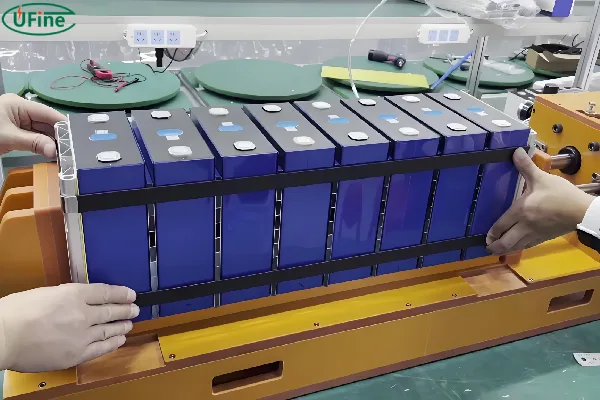
The LiFePO4 car battery is made in two main steps. The first step is the manufacture of lithium battery cells. The second step is to connect the lithium cells one by one in series or parallel, to achieve the desired voltage and capacity of the lithium battery pack for electric vehicles, as well as charging and discharging requirements.
Learn how to DIY a LiFePO4 battery with our simple guide. Save money and boost your car’s performance. Get started on your project today!
Part 1. What should you know before DIY LiFePO4 car battery?
Before embarking on a DIY LiFePO4 car battery project, it’s essential to gather specific information about both the vehicle and the battery to ensure compatibility, safety, and optimal performance. Here’s a comprehensive list of what you should know:
1. Vehicle Specifications
- Battery Type: Identify the current battery type (lead-acid, AGM, etc.) and its specifications, including voltage and capacity (Ah).
- Voltage Requirements: Determine the vehicle’s voltage system (12V, 24V, etc.) to match your LiFePO4 configuration accordingly.
- Space Constraints: Measure the physical dimensions of the existing battery space to ensure the DIY battery will fit comfortably.
- Weight Considerations: Check the weight capacity of the vehicle’s battery compartment, as LiFePO4 batteries are typically lighter than lead-acid batteries.
2. Battery Requirements
- Capacity Needs: Calculate the required amp-hour (Ah) rating based on your vehicle’s power needs. Consider how long you want the battery to last under load.
- Discharge Rate: Understand the maximum discharge rate your vehicle will require, especially for high-drain applications like electric starters or high-performance systems.
- Cycle Life: Research the expected cycle life of the LiFePO4 cells you’re considering to determine longevity and value.
3. Battery Configuration
- Series and Parallel Connections: Decide on the configuration (e.g., 4S for a 12V system) and if you need to connect cells in parallel for increased capacity.
- Cell Matching: Ensure all cells are of the same brand, model, and age to maintain performance and safety.
4. Battery Management System (BMS)
- BMS Selection: Choose a BMS compatible with your battery configuration that supports the necessary features, such as overcharge protection, over-discharge protection, and cell balancing.
- Monitoring Features: Look for BMS systems that provide real-time monitoring of voltage, current, and temperature for better safety management.
5. Charging System
- Charger Compatibility: Ensure you have a charger designed for LiFePO4 batteries, as they require specific charging profiles.
- Charging Capacity: Verify that the charger can handle the voltage and capacity of your battery pack to avoid undercharging or overcharging.
6. Safety and Regulations
- Local Regulations: Check for any local laws or regulations regarding the installation of aftermarket batteries, especially for modifications in electric or hybrid vehicles.
- Safety Features: Understand safety features required for installation, such as fuses or circuit breakers to prevent overcurrent situations.
7. Installation Process
- Connection Method: Familiarize yourself with how to safely connect the new battery to the vehicle’s electrical system, including wiring and connectors.
- Mounting Considerations: Plan for how the battery will be securely mounted to prevent movement during driving.
8. Maintenance Needs
- Maintenance Schedule: Understand any maintenance required for LiFePO4 batteries, including periodic checks of voltage and state of charge.
- End-of-Life Disposal: Research proper disposal methods for LiFePO4 batteries at the end of their life cycle.
Part 2. How do factories make LiFePO4 cells?
The basic steps of the manufacturing method of lithium battery cell are as follows:
- Stirring and mixing of raw materials: mix the electrode active materials, binder and solvent together, stir and disperse them thoroughly, and make them into slurry.
- coating of positive and negative electrode sheets: coating the slurry intermittently and uniformly on the surface of the transport collector for drying. The positive and negative pole pieces are made into rolls respectively.
- Cold pressing of positive and negative electrode sheets: after coating the positive and negative electrode sheets, the positive and negative materials are relatively loose. It is necessary to give a certain pressure to the pole piece. Compact the positive and negative materials to a certain range.
- Cutting and slitting: According to the model of battery, it is necessary to slit the positive and negative electrode sheets into corresponding widths.
- Stacking of positive and negative pole pieces: small positive and negative pole pieces and isolation film are stacked and combined to form a bare battery cell.
- Shelling, spot welding, vacuum drying: the bare core is wrapped with packaging foil and thermally encapsulated on the top and sides. In addition, and then after a high vacuum high temperature baking, a small amount of water drying, so that the lithium battery performance is guaranteed.
- Liquid injection: add the electrolyte into the cell and seal the cell completely.
- Formation: the assembled battery is given a certain current to activate its internal positive and negative substances, the battery can only be used as a power source after formation.
- Capacity Separation: In the manufacturing process, the actual capacity of the battery is inconsistent due to the process, and the battery is classified according to its capacity through certain charging and discharging tests.
- Forming: The shape of the battery cell will be done for final processing.
After the above steps, a LiFePO4 battery cell is manufactured successfully. The next step is to form the LiFePO4 cells into a LiFePO4 battery pack.
Part 3. How to diy lifepo4 cells into LiFePO4 battery pack?
It is very difficult to make a LiFePO4 cell by yourself. It requires a lot of materials and equipment. Most importantly, it is very unsafe. Therefore, it is recommended to buy a LiFePO4 cell directly and then DIY a LiFePO4 battery.
Connect the LiFePO4 battery cells one by one in series or parallel to achieve the desired LiFePO4 car battery (LiFePO4 car battery pack).
How to make a LiFePO4 car battery
LiFePO4 batteries are not only safe, but also have a lot of battery cycles. If you want to make your own 48v 20ah LiFePO4 car battery pack, you can buy LiFePO4 battery first. With 3ah 26650 LiFePO4 battery, 16 series 7 parallel can achieve 48v 20ah LiFePO4 car battery pack. then buy 16 series LiFePO4 battery protection board. Control current normal 6a, max 12a, instant 18a will be fine.
- Prepare materials, including stainless steel battery box.
- 20 LiFePO4 battery cells assembled into a string. A total of 8 strings.
- 8 strings of lithium batteries connected in parallel, and then use the spacer and tape to do a good job of insulation.
- tape fixed, series welding protection line.
- LiFePO4 car battery is very harmful if short circuit. So we should use heat shrink film to insulate the series welded lithium battery package. Connect the protection board, good insulation to prevent short circuit.
- heat shrink film wrapped battery, LiFePO4 car battery assembly is complete, put it into the car.
Part 4. Diy LiFePO4 car battery tips
1. LiFePO4 car battery inspection
Check the quality of all connections during the disassembly of the battery. Also check whether the fuse holder, charging socket, and EV lithium battery lead wire contact is normal and reliable, and tighten all connections. Those that need to be replaced should be replaced, and should focus on examining their reliability, and those that are unreliable should be replaced.
2. LiFePO4 car battery installation
LiFePO4 car battery should be installed according to the instructions in the battery box. In fact, most of the batteries inside the battery box each battery is connected in series. Use copper wire to solder each battery together with a soldering iron.
Finally, there are two output terminals, positive and negative, which are soldered to the two terminals of the output socket. Be careful not to connect the reverse, must correspond to the positive and negative poles on the charger.
3. LiFePO4 car battery trial
After installing the LiFePO4 car battery, use a multimeter to measure the voltage of the battery output port. The actual voltage of the battery should be 2~5V higher than the standard voltage, and it can be put into normal operation only after it is normal.
Pary 5. Safety tips for DIY LiFePO4 batteries
When working on DIY LiFePO4 (Lithium Iron Phosphate) batteries, safety should always be your top priority. Here are key safety tips to consider:
1. Use Quality Components
- High-Quality Cells: Choose reputable brands for LiFePO4 cells to ensure reliability and safety.
- Certified BMS: Use a Battery Management System (BMS) that has built-in protections against overcharge, over-discharge, and short circuits.
2. Work in a Safe Environment
- Ventilation: Work in a well-ventilated area to avoid the accumulation of harmful gases.
- Fire Safety: Keep a fire extinguisher rated for electrical fires nearby when assembling or testing batteries.
3. Wear Protective Gear
- Safety Goggles: Protect your eyes from potential splashes or sparks.
- Gloves: Wear insulated gloves to protect against electrical shocks and sharp edges.
4. Handle with Care
- Avoid Short Circuits: Be cautious with tools and components to prevent short-circuiting the cells, which can cause overheating and fires.
- Secure Connections: Ensure all connections are tight and well-insulated to prevent arcing.
5. Monitor Charging
- Use Compatible Chargers: Always use chargers specifically designed for LiFePO4 batteries.
- Watch for Overheating: Monitor the battery during charging for any signs of overheating.
6. Balance Cells
- Check Voltage Levels: Ensure all cells are at similar voltage levels before assembly to prevent imbalances that could lead to overheating or damage.
- Balance Charging: Use a BMS that offers balance charging to keep all cells at the same level during use.
7. Store Properly
- Avoid Extreme Temperatures: Store batteries in a cool, dry place, avoiding both extreme heat and cold.
- Charge to Partial Levels: Store batteries at a 40-60% charge level for long-term storage.
8. Regular Maintenance
- Inspect Periodically: Regularly check the battery and connections for signs of wear, corrosion, or damage.
- Test Functionality: Use a multimeter to ensure the battery is functioning properly and all cells are balanced.
9. Educate Yourself
- Research: Familiarize yourself with lithium battery technology, chemistry, and safety procedures before starting your project.
- Follow Guidelines: Adhere to best practices and manufacturer guidelines for assembly, charging, and usage.
10. Have an Emergency Plan
- Know Emergency Procedures: Familiarize yourself with what to do in case of a fire or other emergencies related to battery failure.
- Keep Emergency Contacts Handy: Have access to local emergency services and know who to contact in case of an incident.
Related Tags:
More Articles

Stick Up Cam Battery Life: What to Expect and How to Improve It
How long does Stick Up Cam battery last? Learn about battery types, charge time, tips to extend battery life, and how to replace it—simple and easy to follow.
Best Security Camera Batteries: Complete Buying Guide
Find the best security camera battery for your needs. Learn about types, lifespan, charging tips, and how to avoid common battery problems.
ICR18650 Battery Explained: Chemistry, Use Cases, and Limitations
The ICR18650 battery is widely used in electronics. Learn its chemistry, uses, pros, and cons to see if it's right for your device or project.
A Detailed Exploration of Wireless Keyboard Battery
Learn how to choose, maintain, and troubleshoot wireless keyboard batteries. Discover why lithium batteries are the best choice for long-lasting performance.
Best Rechargeable Batteries for Solar Lights: Lithium vs NiMH vs NiCd Compared
Compare lithium-ion, NiMH, and NiCd batteries to find the best rechargeable option for solar lights based on performance, cost, and lifespan.