- Part 1. What is an alternator?
- Part 2. What is a car battery?
- Part 3. Can an alternator charge a battery?
- Part 4. How an alternator charges the battery
- Part 5. How long does it take for an alternator to charge a battery?
- Part 6. Can a completely dead battery be recharged by an alternator?
- Part 7. Signs your alternator is not charging the battery
- Part 8. Alternator vs. battery problems: how to tell the difference
- Part 9. Can you drive with a bad alternator?
- Part 10. Alternator charging myths debunked
- Part 11. Maintenance tips to ensure your alternator charges properly
- Part 12. When to consider a battery charger instead
- Part 13. Conclusion
- Part 14. FAQs
If you’ve ever had a dead battery, you might have wondered: can alternator charge battery or do you need an external charger? This question is more common than you think. Understanding how your vehicle’s alternator works can save you time, money, and roadside trouble. In this guide, we’ll explain everything you need to know about alternators, batteries, and how they work together.
Part 1. What is an alternator?
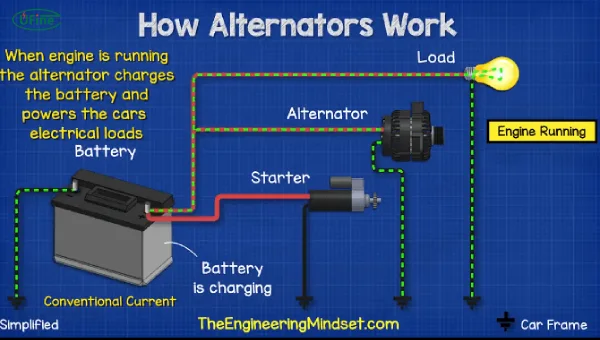
The alternator is a small but essential part of your car’s electrical system. It’s mounted to the engine and driven by the serpentine belt. Its main job? To turn mechanical energy from the engine into electrical energy for your car.
Here’s what the alternator powers:
- Headlights and interior lights
- Dashboard systems
- Power windows and seats
- Radio and infotainment system
- And most importantly—the battery
Key parts of an alternator include:
- Rotor and stator – generate electricity
- Voltage regulator – controls voltage levels
- Rectifier – converts AC to DC power
Understand DC to AC Converters: A Simple Overview
Part 2. What is a car battery?
The battery is your car’s main power storage device. It provides a strong burst of electricity to start your engine. Once the engine runs, the alternator takes over.
There are different types of batteries, but most vehicles use:
- Lead-acid starter batteries
- AGM (Absorbent Glass Mat) batteries in modern cars
Batteries power:
- The ignition system
- Your car’s electrical systems when the engine is off
- Short power surges, like when you start the engine
Part 3. Can an alternator charge a battery?
Yes! The alternator does charge your battery—but with a few caveats.
Here’s how it works:
- When your engine starts, the serpentine belt turns the alternator.
- The alternator generates electricity.
- This power goes to your battery and powers all car electronics.
- The voltage regulator ensures the battery doesn’t overcharge.
So, can alternator charge battery? Absolutely—but it’s designed to maintain the charge, not fully recharge a completely dead battery.
Part 4. How an alternator charges the battery
Let’s break down the process step-by-step:
- Engine starts → alternator begins spinning.
- The rotor inside the alternator spins inside a set of coils (stator).
- This motion creates alternating current (AC).
- The rectifier turns AC into direct current (DC), which your car uses.
- The voltage regulator adjusts the flow to keep it between 13.8V and 14.8V.
- The electricity charges the battery and powers the car at the same time.
This process continues while the engine runs.
Part 5. How long does it take for an alternator to charge a battery?
It depends.
If your battery is only slightly discharged, driving for 30 minutes at highway speed might restore most of the charge.
But if it’s deeply discharged, it could take hours—or may not recharge at all through the alternator alone.
Factors that affect charging time:
- Battery size
- Current charge level
- Alternator output (measured in amps)
- Engine RPM (higher RPM = faster charging)
- Electrical load (AC, lights, stereo, etc.)
Driving, rather than idling, is best for fast charging.
Part 6. Can a completely dead battery be recharged by an alternator?
This is where many people get confused.
If your battery is totally dead, the alternator may not be able to recharge it alone. Why?
- The alternator needs power from the battery to start operating.
- If the battery has zero voltage, the alternator can’t begin charging.
- It’s also risky—overworking the alternator can damage it.
In this case, jump-start your car and use a battery charger to restore full power. Don’t rely on the alternator alone.
Part 7. Signs your alternator is not charging the battery
Sometimes, your battery isn’t the problem—it’s the alternator. Here are signs that your alternator isn’t charging:
- Battery warning light on the dashboard
- Dim headlights or flickering interior lights
- Slow engine crank
- Unusual smells, like burning rubber (from belt slippage)
- Clicking sounds when starting
- Dead battery even after driving
Use a multimeter to test the alternator. A healthy alternator should show 13.8 to 14.8 volts with the engine running.
Part 8. Alternator vs. battery problems: how to tell the difference
Both the battery and the alternator can cause starting issues. Here’s how to know which is at fault:
SymptomLikely ProblemCar won’t start after sitting overnightBatteryCar dies while drivingAlternatorElectrical systems shut down while runningAlternatorClicking noise but no crankBattery or starter
Pro tip: If you jump-start the car and it dies soon after, the alternator is likely bad.
Part 9. Can you drive with a bad alternator?
Technically, yes—but only for a short distance.
Once the alternator fails, your car runs on battery power alone. That won’t last long—usually 30 to 60 minutes.
You risk:
- Complete loss of power
- Steering and brake failure (in modern vehicles)
- Getting stranded in unsafe areas
If you suspect your alternator is failing, don’t wait. Get it inspected or replaced immediately.
Part 10. Alternator charging myths debunked
Let’s clear up some common misconceptions:
- Myth: Revving the engine always charges faster.
- Fact: Only true up to a point. Beyond a certain RPM, charging levels off.
- Myth: If the alternator is good, the battery won’t die.
- Fact: Batteries wear out with age and can still fail, even if charged.
- Myth: You don’t need a battery charger if you have an alternator.
- Fact: A charger is better for restoring deeply discharged batteries safely.
Part 11. Maintenance tips to ensure your alternator charges properly
Prevent breakdowns by following these tips:
- Check the serpentine belt – look for cracks or wear.
- Clean battery terminals – corrosion limits charging.
- Test your battery every 6–12 months.
- Listen for unusual noises from the engine bay.
- Watch the dashboard for the battery warning light.
Part 12. When to consider a battery charger instead
An alternator is great for maintaining battery charge, but sometimes it’s not enough. Use a battery charger when:
- Battery is deeply discharged
- Car has been sitting for a long time
- You want a slow and safe recharge (trickle chargers)
- Vehicle is stored off-season (e.g., motorcycle, RV)
Battery tenders are ideal for storage—they keep the battery topped off without overcharging.
Part 13. Conclusion
So, can alternator charge battery? Yes, it can—but it has limits.
The alternator keeps your battery charged while driving. It’s essential for running your car’s electronics and maintaining battery life. However, it’s not designed to revive a completely dead battery.
Take care of both your battery and alternator through regular maintenance. Know the signs of failure. And when in doubt, use an external charger to give your battery the full attention it deserves.
Part 14. FAQs
Does the alternator charge the battery when idling?
Yes, but it’s slower than when driving. Higher RPM = faster charging.
How many volts should a healthy alternator produce?
Between 13.8V and 14.8V with the engine running.
Can a bad alternator ruin a battery?
Yes. An overcharging or undercharging alternator can damage the battery over time.
How often should I replace the alternator?
Alternators usually last 7–10 years or about 100,000 to 150,000 miles, depending on use.
Related Tags:
More Articles

고방전 배터리는 높은 전류와 발열로 배터리수명이 줄어듭니다. 구조적 한계, 사용 패턴, 충전 습관 등 실제 수명 단축 요인을 체계적으로 분석했습니다.
Capacitor vs Battery: What is the Difference?
Capacitor vs battery explained in detail. Learn the difference between capacitor and battery in energy storage, charging speed, lifespan, and real applications.
18650 Battery vs AA: Which Is Better for Your Device?
Compare 18650 vs AA batteries in capacity, voltage, rechargeability, and applications. Learn which battery type fits high-drain or everyday devices.
What is the Difference Between Battery Cell, Battery Control Module, and Battery Pack?
Compare battery cells, modules, and packs. Learn functions, design differences, control modules, and selection tips for EV, ESS, and industrial use.
How to Prevent LiPo Battery Explosion?
Can LiPo batteries explode or catch fire? Learn key causes of LiPo battery fires and proven charging, storage, and handling tips to reduce explosion risk.