Lithium-ion batteries have completely transformed our daily lives. Think about it: they power our smartphones, laptops, electric cars, and even some of our home appliances. But have you ever wondered where these batteries came from or how they evolved to become such an integral part of our technology? In this article, we’ll take a deep dive into the complete history of lithium-ion batteries, from the early research and key figures to the major milestones and future trends. So, let’s get started!
Part 1. 3 Key Figures
First, let us take a look at some key figures in the development of lithium-ion batteries.
1. John B. Goodenough
John B. Goodenough is often hailed as the father of the lithium-ion battery. Born in 1922, Goodenough’s contributions to science have been monumental. In the early 1980s, while working at the University of Oxford, he discovered that lithium cobalt oxide could be used as a cathode material in batteries. This discovery was groundbreaking because it provided a stable and lightweight solution that could store a significant amount of energy. Goodenough’s work laid the essential foundation for the lithium-ion batteries we use today.
2. Stanley Whittingham
Stanley Whittingham, another key figure in the development of lithium-ion batteries, made his mark in the 1970s. He was researching alternative energy storage solutions at Exxon when he stumbled upon the concept of intercalation. This process involves inserting lithium ions into a host material, which was a critical breakthrough for battery technology. Whittingham’s pioneering work earned him a share of the Nobel Prize in Chemistry in 2019, alongside Goodenough and Akira Yoshino.
3. Akira Yoshino
Akira Yoshino, a Japanese chemist, took the work of Goodenough and Whittingham and made it commercially viable. In 1985, Yoshino developed the first practical lithium-ion battery using Goodenough’s lithium cobalt oxide cathode and a carbon anode. This combination made the battery safe, stable, and rechargeable. Sony soon recognized the potential of Yoshino’s invention and released the first commercial lithium-ion battery in 1991. Yoshino’s work was instrumental in bringing lithium-ion batteries to the masses.
Part 2. Major events
The development of lithium-ion batteries is marked by several key events and milestones that have shaped their evolution over the years.
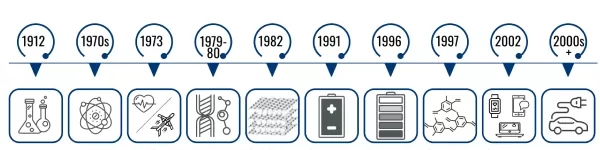
1970s: Whittingham’s Initial Research
In the 1970s, Stanley Whittingham’s research on lithium batteries laid the foundation for future developments. His discovery of intercalation was a critical breakthrough that would later be built upon by other researchers.
1980: Goodenough’s Cathode Discovery
In 1980, John B. Goodenough’s discovery of lithium cobalt oxide as a cathode material was a game-changer. This stable and high-energy solution provided the necessary groundwork for creating practical lithium-ion batteries.
1985: Yoshino’s Commercially Viable Battery
In 1985, Akira Yoshino developed the first commercially viable lithium-ion battery using Goodenough’s cathode and a carbon anode. This innovation made it possible to bring lithium-ion batteries to the market.
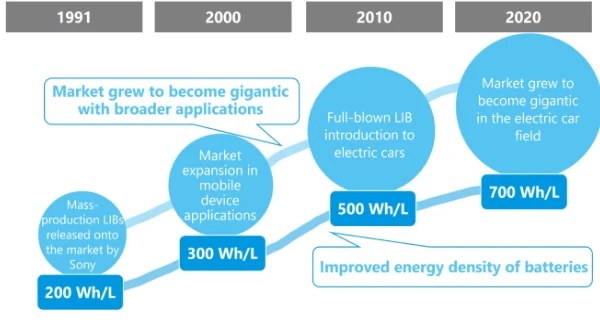
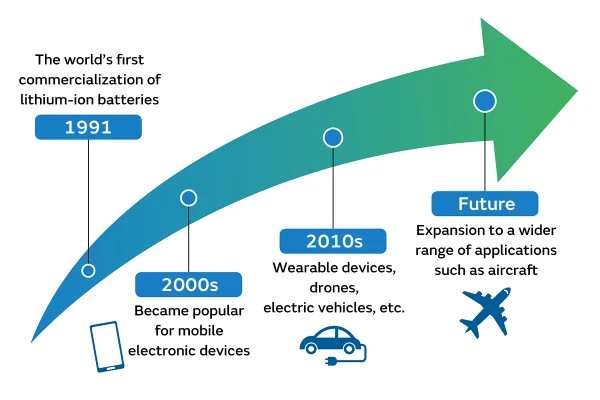
1991: Sony’s Commercial Release
In 1991, Sony released the first commercial lithium-ion battery, revolutionizing consumer electronics. This milestone marked the beginning of the widespread adoption of lithium-ion batteries in various applications, from portable electronics to electric vehicles.
2000s: Advances in Battery Technology
The 2000s saw significant advances in battery technology, leading to the development of high-capacity and safer lithium-ion batteries. Researchers focused on improving energy density, charging speed, and safety features to meet the growing demands of modern technology.
Part 3. Lithium-ion battery materials history
In 1970
M.S. Whittingham used titanium sulfide as the anode material and metallic lithium as the cathode material to create the first lithium battery. The anode material of lithium batteries is usually manganese dioxide or thionyl chloride. The cathode is lithium. This kind of battery has voltage after assembly and does not need to be charged.
Li-ion batteries are developed from lithium batteries. For example, the button batteries used in cameras in the past were lithium batteries. This kind of battery can also be recharged, but its cycle performance is not good. Lithium crystals are easily formed during the charge and discharge cycle, causing an internal short circuit in the battery. Therefore, charging this kind of battery is generally prohibited.
In 1982
R.R. Agarwal and J.R. Selman of the Illinois Institute of Technology discovered that lithium ions have the property of being embedded in graphite. This process is rapid and reversible. At the same time, the safety risks of lithium batteries made of metallic lithium have attracted much attention. Therefore, people try to use the characteristics of lithium ions embedded in graphite to make rechargeable batteries. The first usable lithium-ion graphite electrode was successfully trial-produced by Bell Laboratories.
In 1983
M. Thackeray, J. Goodenough, and others discovered that manganese spinel is an excellent cathode material. This material is low-cost, stable, and has excellent electrical and lithium conductivity properties. Its decomposition temperature is high, and its oxidizing property is much lower than lithium cobalt oxide. Even if there is a short circuit or overcharge, the danger of burning or explosion can be avoided.
Part 4. Lithium-ion battery development history
- In 1985, Sony devoted itself to researching and developing lithium-ion batteries.
- In 1987, “the era of mobile phones is coming,” mobile phone batteries using nickel-chromium batteries needed to be charged once a day. And the battery volume accounts for half of the phone.
- In 1988, Sony applied for the first lithium battery patent and named the new product Li-ion battery. Although Sony’s cooperation in applying for the patent was similar to Goodenough’s earlier paper, Goodenough did not pursue it.
- In 1989, A.Manthiram and J.Goodenough discovered that cathodes using polymeric anions would produce higher voltages.
- In 1990, the old rival of lithium-ion batteries, nickel-metal hydride batteries, came online. Nickel metal hydride batteries are mostly standard AA and AA batteries. The cycle life of nickel-metal hydride batteries with 50% DOD is not as good as the 100% DOD life of lithium-ion batteries. The energy density of nickel metal hydride is inherently lower than that of lithium batteries, and the DOD is even less than half. In addition to high-rate charge and discharge, nickel-metal hydride batteries are inferior to lithium-ion batteries.
- In 1990, the industry leader in lead-acid batteries appeared.
- In 1991, after six years of research and development, Sony’s first lithium-ion battery product was launched.
- In 1992, Japan’s Sony Corporation invented a lithium battery using carbon material as the cathode and lithium-containing compounds as the anode. During the charge and discharge process, no metallic lithium exists, only lithium ions. This is a lithium-ion battery. Later, lithium-ion batteries revolutionized consumer electronics. This type of battery, which uses lithium cobalt oxide as the cathode material, is still the main power source for portable electronic devices.
- In 1994, lithium-ion batteries became available to the public. Lithium-ion batteries initially existed only in Sony’s products. But this deadlock was broken by Dell in 1994. Dell laptops start using lithium-ion batteries.
- In 1995, lithium-ion batteries eliminated shape restrictions, and Sanyo launched the aluminum-cased lithium-ion battery 103450.
- In 1995, one million lithium-ion batteries were burned in the Sony Koriyama project fire. Therefore, the safety issue of lithium-ion batteries has been put on the agenda.
Part 5. Lithium battery application history
- In 1996, Padhi and Goodenough discovered phosphates with an olivine structure, such as lithium iron phosphate (LiFePO4). It is safer than traditional cathode materials, is particularly resistant to high temperatures, and its overcharge resistance far exceeds that of traditional lithium-ion battery materials. Therefore, it has become the current mainstream cathode material for power lithium batteries with high current discharge.
- In 1996, lithium iron phosphate was successfully developed. Goodenough again made a splash by proposing the commercialization of lithium iron phosphate.
- In 1997, Japan’s first lithium-ion battery pure electric vehicle, Prairie JoyEV, was produced.
- In 1998, Academician Chen Liquan, the father of China’s lithium battery, built the first production line using a complete set of Chinese equipment.
- In 1999, eight Japanese companies led by Panasonic launched their first polylithium products. It is called the first year of polymer lithium-ion batteries by the Japanese.
- In 1999, South Korea entered the lithium-ion battery market, and LG Chem completed South Korea’s first battery product.
- In 2000, BYD won an order from Moto. In the past, BYD took only three years to rank first in the world in its cadmium-nickel battery business. In 2000, it invested heavily in lithium battery research and development and received an order from Motorola.
- In 2004, graphene was successfully developed.
- In 2004, CATL became an iPod supplier.
- In 2004, China’s lithium battery industry emerged. China’s annual output of lithium-ion batteries is 800 million units, accounting for 38% of the global share, second only to Japan.
- In 2006, BYD launched its first electric car, the F3e. Due to insufficient policies and inadequate charging facilities, F3e was not put on the market. In the 2006 Sony battery safety incident, a Dell laptop caught fire at an international conference. Sony spent $440 million to recall 10 million batteries.
- In 2008, China, Japan, and South Korea were divided into three parts. With the rise of Korean companies such as LG and Samsung, the international lithium battery market is divided into three parts: Japan, South Korea, and Korea.
- In 2011, China’s megawatt energy storage stations were connected to the grid. In the field of energy storage, lithium-ion batteries have an application stage in addition to electric vehicles. This is also the world’s first-megawatt energy storage station using lithium iron phosphate as the cathode.
- In 2012, the Tesla Model S was launched.
- In 2012, 4.35 V lithium cobalt oxide products were launched.
- In 2012, Panasonic’s high energy density 18650 battery took the lead. Relying on using NCA materials, Panasonic has mass-produced conventional voltage batteries with the highest energy density, 18650-3400mAh. According to data from the National Bureau of Statistics, by 2013, China’s annual output of lithium-ion batteries had approached 4.768 billion, becoming an important battery producer worldwide.
- In 2014, drone production exploded. Global sales of civilian drones reached 390,000, a year-on-year increase of 50%. The broad applications of drones drive the sales of drone batteries.
- In 2016, Sony sold its battery division. Due to Panasonic’s dominance of the high-end passenger car battery market and the cost war between LG, Samsung, and Chinese manufacturers, Sony’s battery division, which has been losing money continuously, has no hope of turning around, so it resold the battery division to Murata Manufacturing.
- In 2017, the price of lithium cobalt oxide skyrocketed.
- In 2017, the 94-year-old Goodnough, the father of lithium batteries, came out again and led the team to develop solid-state batteries. After completing 1,200 cycles, it can be tried at 20-60 degrees, triggering a revolution in the lithium battery industry.
- In 2018, hydrogen fuel cells impacted the lithium battery market.
- In 2019, three people who contributed significantly to lithium ions won the Nobel Prize in Chemistry.
- In 2020, BYD officially releases blade battery
- In 2021, Mercedes-Benz announced the use of lithium iron phosphate batteries
- In 2022, the overall global lithium-ion battery shipments will be 957.7GWh, a year-on-year increase of 70.3%. China’s lithium-ion battery shipments reached 660.8GWh, a year-on-year increase of 97.7%, exceeding the global average growth rate, and accounting for 69.0% of the total global lithium-ion battery shipments.
- In 2023, global lithium battery shipments will be 1,192Gwh, a year-on-year increase of 24.9%. It is expected to exceed 1,500GWh in 2024. It is expected that the world will reach 6331GWh in 2030, with an average annual compound growth rate of 26.9% from 2023 to 2030, and global lithium battery shipments will maintain rapid growth. Global lithium battery shipments will maintain rapid growth from 2023 to 2030, mainly because automotive power batteries and energy storage batteries, which account for a large proportion of lithium batteries, will maintain rapid growth.
Part 6. The Current development
Today, lithium-ion batteries are more advanced than ever before. They are used in a wide range of applications, from consumer electronics to electric vehicles and renewable energy storage. Let’s explore some of the current developments in lithium-ion battery technology.
Improved Energy Density
One of the most significant advancements in lithium-ion batteries is the improvement in energy density. Modern lithium-ion batteries can store more energy in a smaller and lighter package, making them ideal for portable devices and electric vehicles. This improvement has been achieved through advances in materials and battery design.
Faster Charging
Another area of significant progress is charging speed. Researchers have developed new charging techniques and materials that allow lithium-ion batteries to charge much faster than before. This advancement is particularly important for electric vehicles, where fast charging is essential for widespread adoption.
Enhanced Safety
Safety has always been a critical concern for lithium-ion batteries. Recent developments have focused on enhancing the safety features of these batteries. Innovations such as solid-state electrolytes and advanced thermal management systems have made lithium-ion batteries safer and more reliable.
Environmental Considerations
As the demand for lithium-ion batteries continues to grow, so does the focus on environmental sustainability. Researchers are working on developing more eco-friendly materials and improving recycling methods to reduce the environmental impact of lithium-ion batteries. This includes finding alternatives to cobalt, which is often associated with ethical and environmental concerns.
Part 7. Future development trends
The future of lithium-ion batteries looks incredibly promising, with several exciting trends and innovations on the horizon.
Solid-State Batteries
Solid-state batteries are considered the next big thing in battery technology. Unlike traditional lithium-ion batteries, which use liquid electrolytes, solid-state batteries use solid electrolytes. This change enhances safety, energy density, and longevity. Solid-state batteries are expected to play a significant role in the future of electric vehicles and portable electronics.
Faster Charging and Longer Lifespan
Researchers are continuously working on ways to improve the charging speed and lifespan of lithium-ion batteries. New materials and technologies are being developed to allow batteries to charge in minutes rather than hours and to last significantly longer. These advancements will make lithium-ion batteries even more convenient and cost-effective.
Sustainability and Recycling
Sustainability is becoming a key focus in the development of lithium-ion batteries. Efforts are being made to create more environmentally friendly batteries by using sustainable materials and improving recycling processes. This includes developing closed-loop recycling systems that can recover valuable materials from used batteries and reuse them in new ones.
Integration with Renewable Energy
As the world shifts towards renewable energy sources, lithium-ion batteries are playing a crucial role in energy storage. Future developments will focus on integrating lithium-ion batteries with renewable energy systems to provide reliable and efficient energy storage solutions. This integration will help stabilize the grid and support the widespread adoption of renewable energy.
Part 8. Final thoughts
Throughout the history of battery development, we can see three characteristics of the current development of the world’s battery industry. First, green and environmentally friendly batteries are developing rapidly, including lithium-ion batteries, nickel-hydrogen batteries, etc. The second is the transformation from primary to storage batteries, which aligns with the sustainable development strategy. Third, batteries are further developing in small, light, and thin directions.
Among commercial rechargeable batteries, lithium-ion batteries have the highest specific energy. In particular, polymer lithium-ion batteries can make rechargeable batteries thinner. Precisely because lithium-ion batteries have high volume-specific and mass-specific energy, are rechargeable and non-polluting, and have the three major characteristics of the current development of the battery industry, they are growing rapidly in developed countries.
The development of telecommunications and information markets, especially the extensive use of mobile phones and laptops, has brought market opportunities to lithium-ion batteries. Among lithium-ion batteries, polymer lithium-ion batteries will gradually replace liquid electrolyte lithium-ion batteries and become the mainstream of lithium-ion batteries due to their unique advantages in safety. Polymer lithium-ion batteries are known as the “batteries of the 21st century”. They will open up a new era of batteries with very optimistic development prospects.
Part 9. FAQs
-
Are lithium batteries environmentally friendly?
Lithium batteries are generally considered environmentally friendly due to their higher energy efficiency, longer lifespan, and lower greenhouse gas emissions than traditional battery chemistries. -
What about the cost of lithium batteries?
The cost of lithium batteries can vary depending on factors such as battery capacity, chemistry, and market demand. Technological advances and increased production have led to a gradual decrease in cost over the years. -
What is the price of lithium batteries?
The price of lithium batteries varies depending on factors such as battery capacity, brand, and supplier. It is best to check with specific manufacturers or retailers for current pricing information. -
Are lithium batteries rechargeable?
Yes, lithium batteries are rechargeable. They are commonly used in various applications, including portable electronics, electric vehicles (EVs), and renewable energy storage systems, where their rechargeability is a key advantage.
Related Tags:
More Articles

Comprehensive Guide to Choosing the Right Cart Battery
Choosing the right cart battery ensures optimal performance and longevity. This guide covers cart battery types and helps you make an informed choice.
The Ultimate Guide to 18650 Button Top Battery
18650 button top batteries are popular for their high energy density and reliability. This guide covers their key features, usage, and maintenance tips.
The Power of Slim: Unveiling the Potential of Flat Lithium Ion Battery
Flat lithium-ion batteries power devices from phones to vehicles. This article explores their design, benefits, types, applications, charging, and safety.
The Comprehensive Guide to Battery Balancing and Battery Balancer
Battery balancing and balancers optimize performance, longevity, and safety. This guide covers techniques and tips for choosing the right balancer.
10 Key Facts About Drone Battery for 2024
Uncover crucial insights with "10 Key Facts About Drone Battery for 2024." Learn the latest trends and essential details on drone batteries.