- Part 1. What is a miniature battery?
- Part 2. Why are miniature batteries important?
- Part 3. What are the main types of miniature batteries?
- Part 4. What are the sizes and shapes of miniature batteries?
- Part 5. How do miniature batteries work?
- Part 6. What are the advantages of using miniature batteries?
- Part 7. What devices use miniature batteries?
- Part 8. How to choose the right miniature battery?
- Part 9. How to store and dispose of miniature batteries safely?
- Part 10. What are the safety concerns with miniature batteries?
- Part 11. FAQs about miniature battery
What is a miniature battery? A miniature battery is a compact and powerful energy source designed to fit into small electronic devices such as watches, hearing aids, calculators, and medical tools. These batteries are essential to modern technology, offering reliable and long-lasting power in a tiny form. In this article, we will explore the definition of miniature batteries, their various types, their working mechanism, key characteristics, and their significance in daily life. If you’re looking to understand how these small power cells function and how to choose the right one, keep reading.
Part 1. What is a miniature battery?
A miniature battery is a small-sized electrochemical power cell that stores and delivers electrical energy to devices with limited internal space. These batteries are renowned for their compact design, lightweight structure, and ability to maintain a consistent voltage for extended periods.
Miniature batteries are specially designed for use in electronic devices that cannot accommodate large battery formats. Despite their size, they are engineered with precision to deliver reliable power. They are commonly found in gadgets like digital watches, remote controls, hearing aids, medical sensors, and compact cameras.
Part 2. Why are miniature batteries important?
Miniature batteries play a vital role in modern electronics. They are designed to deliver efficient power in limited spaces. As devices become smaller and more portable, the demand for compact and reliable batteries continues to grow.
These batteries are crucial because they:
- Allow advanced technology to be compact and mobile
- Enable the development of wearable and implantable medical devices
- Offer long shelf life and dependable energy output
- Reduce maintenance by providing extended battery life
- Support critical applications in healthcare and security systems
Without miniature batteries, the miniaturization of consumer electronics and medical devices would not be possible.
Part 3. What are the main types of miniature batteries?
There are several types of miniature batteries, classified based on their chemical composition, voltage, and rechargeability. Each type is designed for specific uses.
1. Alkaline batteries
- Voltage: 1.5 Volts
- Common uses: Toys, remote controls, flashlights
- Chemistry: Zinc anode and manganese dioxide cathode in an alkaline electrolyte
- Zn + 2MnO₂ + 2H₂O → Zn(OH)₂ + 2MnOOH
Alkaline batteries are affordable and widely available, but they typically have a shorter lifespan compared to other types.
2. Silver oxide batteries
- Voltage: 1.55 Volts
- Used in: Watches, hearing aids, calculators
- Chemistry: Zinc anode and silver oxide cathode in an alkaline electrolyte
- Zn + Ag₂O → ZnO + 2Ag
These batteries offer a very stable output voltage and a long shelf life, making them ideal for precision instruments.
3. Lithium coin batteries
- Voltage: 3 Volts
- Used in: Car remotes, fitness trackers, digital thermometers
- Chemistry: Lithium anode and manganese dioxide cathode with organic electrolyte
Chemical reaction:
- Li + MnO₂ → LiMnO₂
Lithium batteries offer high energy density, low self-discharge, and excellent performance in extreme temperatures.
4. Zinc-air batteries
- Voltage: 1.4 Volts
- Used in: Hearing aids, medical devices, pagers
- Chemistry: Zinc anode and oxygen from the air as the cathode
Chemical reaction:
- 2Zn + O₂ → 2ZnO
Zinc-air batteries are lightweight and provide high energy output, but they begin to drain once exposed to air.
5. Rechargeable miniature batteries
There are two main types of rechargeable miniature batteries:
Lithium-ion (Li-ion)
- Used in: Wireless earbuds, small medical devices
- Voltage: Varies, usually 3.7 Volts
- Chemistry: Lithium cobalt oxide cathode and graphite anode
Chemical reaction:
- Lithium ions move from the anode to the cathode during discharge and reverse during charging.
Nickel-metal hydride (NiMH)
- Used in: Electric toothbrushes, handheld devices
- Voltage: 1.2 Volts
- Chemistry: Nickel oxide hydroxide and hydrogen-absorbing alloy
Chemical reaction:
- Hydrogen is stored and released via oxidation and reduction at the electrodes.
Rechargeable batteries are ideal for frequently used devices, offering hundreds of charge cycles.
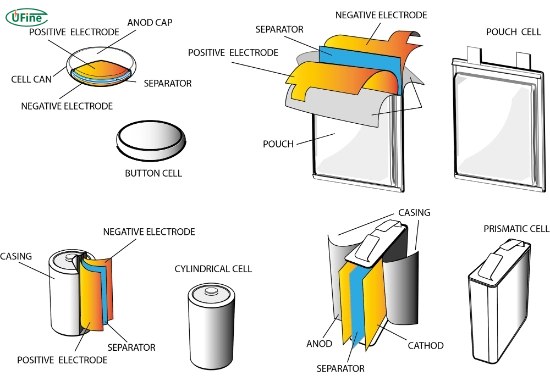
Part 4. What are the sizes and shapes of miniature batteries?
Miniature batteries are available in various shapes and sizes to meet the needs of different devices. The most common formats include:
- Button cells: Flat and round, often used in watches and hearing aids
- Coin cells: Similar to button cells but often larger in diameter
- Cylindrical cells: Small tubes used in flashlights and medical devices
- Prismatic cells: Thin, rectangular shapes for sleek electronics
Each battery type is labeled with a code indicating its size. For example, CR2032 means the battery is 20 millimeters in diameter and 3.2 millimeters thick.
Part 5. How do miniature batteries work?
Miniature batteries operate through a controlled chemical reaction that generates electrical energy. Inside each battery, there are three key components:
- Anode: The negative side where oxidation occurs
- Cathode: The positive side where reduction occurs
- Electrolyte: A medium that allows ions to move between electrodes
When the battery is connected to a device, electrons flow from the anode to the cathode through the external circuit. This movement of electrons powers the device. The electrolyte ensures that charged particles within the battery move efficiently to complete the internal circuit.
Each battery type utilizes a distinct chemical reaction to generate energy, which affects its voltage, lifespan, and performance.
Part 6. What are the advantages of using miniature batteries?
Miniature batteries offer several benefits that make them ideal for small electronic devices:
- Compact size: Perfect for devices with limited space
- Lightweight: Adds minimal weight to the device
- Long shelf life: Some can last more than five years without use
- Stable voltage: Essential for sensitive electronics like medical devices
- Low maintenance: Especially true for non-rechargeable types
- Variety: Available in different chemistries and sizes for different needs
These features make miniature batteries essential in fields like healthcare, security, and consumer electronics.
Part 7. What devices use miniature batteries?
Miniature batteries power a wide range of personal and professional devices:
- Wristwatches
- Hearing aids
- Calculators
- Fitness trackers
- Remote controls
- Blood glucose monitors
- Digital thermometers
- Car key fobs
- Compact flashlights
- Medical implants
Each device requires a specific battery type, determined by its size, voltage, and energy needs.
Part 8. How to choose the right miniature battery?
Choosing the correct miniature battery involves several considerations:
- Check the device manual: Always follow the manufacturer’s recommendations
- Identify the battery size and type: Look for model codes like CR2032 or SR626SW
- Choose the right chemistry: Depending on whether you need stable voltage, long life, or rechargeability
- Evaluate usage patterns: Frequent use may benefit from a rechargeable battery
- Consider environmental conditions: Some batteries perform better in cold or hot temperatures
Using the wrong battery can damage the device or result in poor performance.
Part 9. How to store and dispose of miniature batteries safely?
Storage tips:
- Store in a cool and dry place
- Keep batteries in their original packaging
- Avoid mixing different types of batteries
- Keep away from children and pets
Disposal tips:
- Do not throw batteries in household trash
- Use battery recycling bins or hazardous waste centers
- Follow local regulations for battery disposal
- Protect battery terminals with tape before disposal to prevent short circuits
Proper disposal is necessary to prevent environmental harm and safety risks.
Part 10. What are the safety concerns with miniature batteries?
While miniature batteries are generally safe, there are some risks:
- Swallowing hazard: Button cells can be swallowed by children or pets and cause serious internal injuries
- Leakage: Damaged batteries can leak chemicals that may harm devices or skin
- Fire risk: Rechargeable batteries can overheat if improperly charged
- Short circuits: Contact with metal can cause the battery to short and heat up
To prevent accidents, always store and handle batteries with care, and never attempt to open or puncture them.
Part 11. FAQs about miniature battery
What is the lifespan of a miniature battery?
The lifespan depends on the battery type and usage. Silver oxide and lithium batteries can last 3 to 10 years, while alkaline or zinc-air batteries may last from a few months to a year.
Can I use a different type of battery if the size is the same?
No. Even if the size fits, the voltage and chemistry must match the device’s requirements. Using the wrong type can cause damage or reduce performance.
Are miniature batteries toxic?
Some contain toxic materials like mercury or lithium. Always handle with care and keep away from children. Proper disposal is essential to prevent environmental harm.
How can I tell when it’s time to replace a miniature battery?
Signs include slower device response, dim screens, or complete device failure. Some devices show a low-battery warning before the battery dies.
Can rechargeable miniature batteries be used in all devices?
Not always. Some devices are not designed for rechargeables due to voltage differences. Always check the device manual before switching to a rechargeable battery.
Related Tags:
More Articles

What are Watts and Watt Hours in Battery?
Understand watt vs watt-hour in batteries, how to calculate battery watt hours, and what Wh means for car batteries, devices, and energy storage.
A Complete Guide to the Best Batteries for Flashlights
Compare the best batteries for flashlights, including AA, AAA, 18650, 21700, CR123A. See which battery offers the best brightness, runtime, and reliability.
How Long Do Rechargeable AA Batteries Last?
How long do rechargeable AA batteries last? Compare NiMH and lithium AA lifespan, recharge cycles, key factors, and performance vs alkaline batteries.
How Much Current Can a 9V Battery Really Supply?
Discover how many amps a 9V battery can supply, its actual current output, discharge rate, and capacity for alkaline, lithium, and rechargeable 9V batteries.
12V STD vs 12V AGM: Meaning, Differences, and Which Is Better
Understand what STD and AGM batteries mean, their key differences, and which 12V battery fits your needs best in 2026.