- Part 1. Demystifying the term “2C battery”
- Part 2. What is a 2C battery? Understanding the C-rate
- Part 3. How the 2C rate affects charging and discharging
- Part 4. Where 2C batteries are commonly used
- Part 5. Benefits of 2C-rated batteries
- Part 6. Drawbacks and limitations of 2C discharge or charging
- Part 7. How many C-rate batteries does your device need? how to calculate?
- Part 8. C-rate vs. battery capacity: what matters more?
- Part 9. Battery chemistry and 2C compatibility
- Part 10. How to know if your battery supports 2C
- Part 12. Final words
Batteries are often discussed in terms of their voltage, capacity, or chemistry. But for high-performance applications like drones, RC vehicles, and power tools, one more critical factor comes into play: the C-rate. Among these, the 2C battery is a term you’ll frequently encounter—but what does it really mean? And how do you know how many C-rate batteries your device needs?
This article will answer all these questions in depth, clarify common misconceptions, and help you understand how to size and select the right battery pack for your needs.
Part 1. Demystifying the term “2C battery”
Many consumers misunderstand the term “2C battery.” At first glance, it may seem like it refers to a physical battery size—such as the common C-cell batteries used in flashlights. However, this is not the case.
In battery terminology, “2C” is a measurement of the rate at which a battery can safely charge or discharge, relative to its total capacity. This article will unpack the concept of C-rate, explain what 2C really means, and help you apply this knowledge when selecting or configuring batteries for any high-demand device.
Part 2. What is a 2C battery? Understanding the C-rate
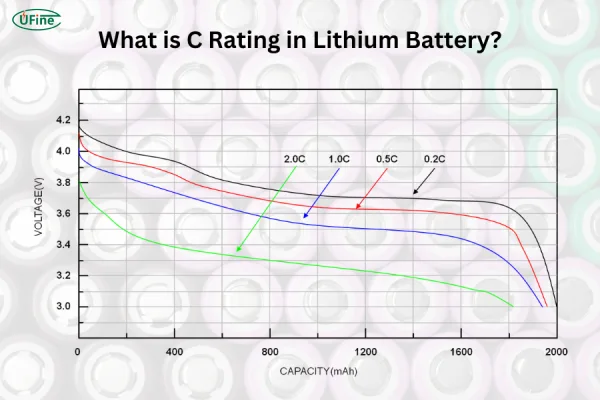
The C-rate is a unit that tells us how quickly a battery can be charged or discharged relative to its nominal capacity.
What does C Mean in Batteries?
For example:
- A 1C discharge rate means a battery can safely discharge its full capacity in 1 hour.
- A 2C discharge rate means the battery can discharge in 30 minutes, or at twice the current of its nominal capacity.
Let’s break that down with a simple formula:
Discharge/Charge Current (Amps) = Battery Capacity (Ah) × C-Rate
So, if you have a 2,000mAh (or 2Ah) battery rated at 2C, then:
2A × 2C = 4 Amps
This battery can safely deliver or receive a 4A current.
This metric becomes especially crucial in performance-critical applications like drones, electric scooters, and industrial equipment where power surges are frequent.
Part 3. How the 2C rate affects charging and discharging
The C-rate determines how fast energy can flow in or out of a battery. A 2C-rated discharge means the battery is capable of being fully depleted in 30 minutes, while a 2C-rated charge means it could be fully charged in the same time frame (provided the charger supports this speed).
However, it’s important to note:
- Just because a battery can charge at 2C doesn’t mean it should—doing so requires proper temperature monitoring and protection circuits.
- Many standard chargers only support 0.5C to 1C, so charging at 2C may require a specialized charger.
Part 4. Where 2C batteries are commonly used
2C batteries are ideal for devices that require short bursts of high power. Common applications include:
- Drones and RC cars – for powerful acceleration and responsiveness
- Power tools – which need high current to handle torque-demanding tasks
- LED flashlights and headlamps – where brightness often correlates with power draw
- Medical devices – where reliable, consistent power output is critical
- Electric scooters and hoverboards – for performance and speed
Part 5. Benefits of 2C-rated batteries
Here are some compelling advantages of using a 2C battery:
- Faster Energy Output: Perfect for motors, lights, or systems requiring a quick power burst
- Reduced Charge Time: When paired with a compatible charger, 2C batteries charge in half the time of 1C-rated ones
- Enhanced Performance: Stable high-current delivery ensures uninterrupted operation
- Versatility in System Design: Ideal for applications requiring flexibility between runtime and power draw
Part 6. Drawbacks and limitations of 2C discharge or charging
Despite their advantages, 2C batteries do come with certain trade-offs:
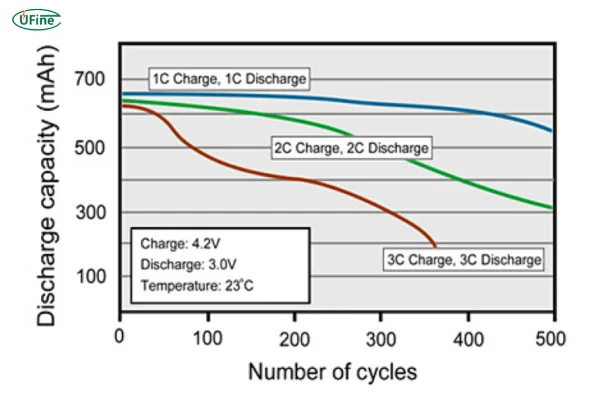
- Higher Heat Generation: Faster discharge produces more internal heat, requiring better thermal management
- Reduced Lifespan: Consistent high-rate charging/discharging may reduce the overall cycle life
- Cost Consideration: High-C-rate batteries tend to be more expensive than their lower-rated counterparts
- Increased Risk: If misused (overcharged or short-circuited), 2C batteries can pose fire or explosion risks without proper battery management systems (BMS)
Part 7. How many C-rate batteries does your device need? how to calculate?
This is a common question: How do I calculate the number of batteries needed to meet my device’s power requirements—especially when working with C-rates?
Step-by-Step Calculation:
1. Know Your Device’s Power Requirements:
- Voltage (V)
- Current draw (A)
- Runtime needed (hours)
2. Choose Battery Specifications:
- Nominal Voltage (V)
- Capacity (Ah)
- C-rate
3. Use This Formula to Estimate Required Current:
Required Current (A) = Device Load (W) ÷ Battery Voltage (V)
Then:
Number of batteries = Total Current Required ÷ (Battery Capacity × C-rate)
🔍 Example:
You have a device that consumes 40 watts and runs on 11.1V.
- Required Current = 40W ÷ 11.1V ≈ 3.6A
- You want to use a 2,000mAh (2Ah) battery rated at 2C → Max current = 2 × 2 = 4A
You only need 1 battery, as 4A > 3.6A.
If you used a 1C battery instead, it could only safely provide 2A, and you’d need at least 2 such batteries connected in parallel.
This method ensures you’re not overloading the battery, which could lead to performance loss or even hazardous failure.
Part 8. C-rate vs. battery capacity: what matters more?
It’s important to understand that C-rate and capacity are two different things:
- Capacity (Ah or mAh) tells you how much energy the battery stores
- C-rate tells you how fast the energy can be discharged or recharged
For example:
- A 2,000mAh 2C battery can discharge at 4A
- A 5,000mAh 2C battery can discharge at 10A
Choosing the right battery depends on both factors. A high-capacity battery with a low C-rate may underperform if your device needs rapid energy bursts.
Part 9. Battery chemistry and 2C compatibility
Not all battery types can safely support 2C rates. Here’s how common chemistries stack up:
Battery TypeTypical Safe C-Rate2C Compatible?Li-ion (18650)0.5C – 2CYes, with cautionLiPo1C – 30CYes, widely usedLiFePO41C – 5CYes, very stableNiMH0.5C – 1CNot recommendedAlkaline< 0.5CNot recommended
LiFePO4 and LiPo batteries are the safest and most reliable for 2C applications due to their stable internal chemistry and structural robustness.
Part 10. How to know if your battery supports 2C
Not all batteries are labeled with a clear C-rate. To verify a battery’s C-rate:
- Check Manufacturer Specifications: Always refer to the battery datasheet or product label
- Look for Markings: Many LiPo batteries include ratings like “20C” or “30C” printed on them
- Contact the Supplier: Reputable battery manufacturers like Ufine Battery provide full technical support and customization details
✅ Why Choose Ufine Battery?
If you’re sourcing high C-rate lithium batteries for your devices or applications, Ufine Battery is a trusted Chinese custom battery manufacturer. We specialize in LiPo, LiFePO4, cylindrical lithium, and ultra-thin/high-temperature/high-rate battery packs, with the capability to meet specific 2C or higher discharge needs. You can contact us for customized battery solutions designed to fit your performance, size, and safety requirements.
Part 12. Final words
A 2C battery is a powerful option for modern electronics and machines that need quick, high-current energy bursts. Understanding the C-rate is essential for safe and efficient battery usage, especially in high-performance applications.
When choosing a battery:
- Match C-rate with your device’s current draw
- Confirm battery specs through manufacturer documentation
- Use proper charging and safety systems to protect your investment
For high-quality, high-C-rate lithium battery packs, consider Ufine Battery. With years of experience in custom lithium battery design and production, Ufine offers the technical expertise and product flexibility you need—whether for consumer electronics, industrial gear, or electric mobility solutions.
Related Tags:
More Articles

고방전 배터리는 높은 전류와 발열로 배터리수명이 줄어듭니다. 구조적 한계, 사용 패턴, 충전 습관 등 실제 수명 단축 요인을 체계적으로 분석했습니다.
Capacitor vs Battery: What is the Difference?
Capacitor vs battery explained in detail. Learn the difference between capacitor and battery in energy storage, charging speed, lifespan, and real applications.
18650 Battery vs AA: Which Is Better for Your Device?
Compare 18650 vs AA batteries in capacity, voltage, rechargeability, and applications. Learn which battery type fits high-drain or everyday devices.
What is the Difference Between Battery Cell, Battery Control Module, and Battery Pack?
Compare battery cells, modules, and packs. Learn functions, design differences, control modules, and selection tips for EV, ESS, and industrial use.
How to Prevent LiPo Battery Explosion?
Can LiPo batteries explode or catch fire? Learn key causes of LiPo battery fires and proven charging, storage, and handling tips to reduce explosion risk.