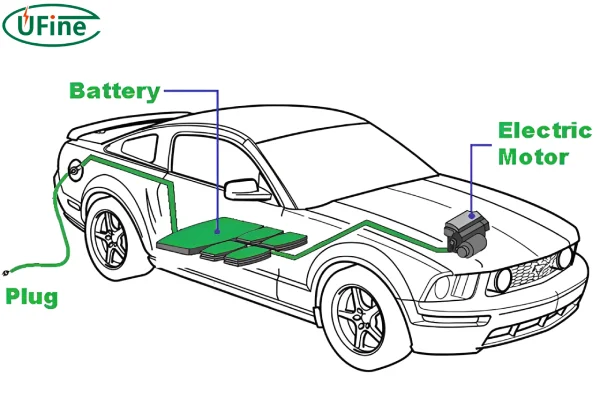
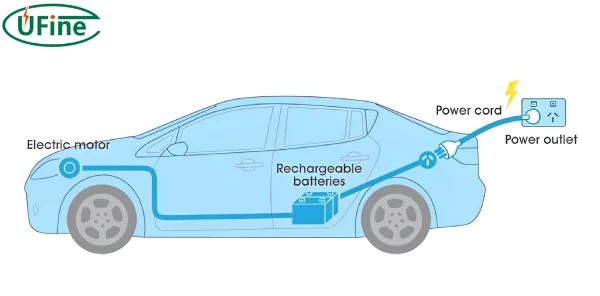
The heavier the car battery weight, the greater the mileage will generally be. At the same time, car battery weight will also affect the car’s dynamic performance, suspension, and steering components. Therefore, car battery weight is one of the critical elements that must be balanced in electric vehicle manufacturing.
Part 1. What’s inside a car battery?
Car batteries are fascinating. They might seem like simple black boxes under your car hood, but there’s a lot going on inside. Understanding their internal structure can help us see why they weigh what they do.
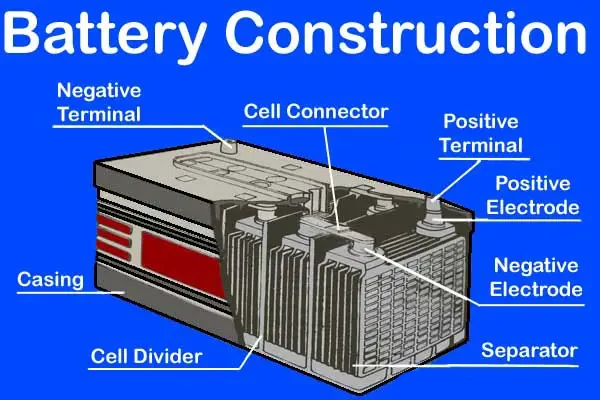
A typical car battery consists of several key components, each playing a vital role in its function and contributing to its overall weight.
- Lead Plates: These are the battery’s heavyweights, quite literally. Lead plates, also known as electrodes, are where the magic happens. They store and release energy, making them essential for the battery’s operation. The more lead plates a battery has, the heavier it will be. These plates are usually coated in lead dioxide, adding to their heft.
- Electrolyte: The electrolyte is a mixture of sulfuric acid and water. This liquid is crucial because it facilitates the chemical reactions needed to store and release energy. While the electrolyte isn’t as heavy as the lead plates, it still adds a significant amount of weight to the battery.
- Separators: To prevent the lead plates from touching and short-circuiting, batteries use separators. These are often made of fiberglass or other insulating materials. While they don’t add much weight, they’re essential for the battery’s safe operation.
- Casing: The casing holds everything together. It’s usually made of durable plastic or sometimes metal. The casing needs to be strong enough to protect the internal components but lightweight to avoid adding unnecessary weight.
So, what is the heaviest part? Definitely, the lead plates. They are the primary contributors to the car battery’s weight. The more plates a battery has, the heavier it becomes, which we’ll see when we look at different battery types.
Part 2. Car battery weight composition
Before knowing what affects car battery weight, we need to know the composition of a car battery.
The cost of an automobile battery pack system includes three parts: cell, battery management system, and pack system, including functional components, wiring harnesses, structural parts, and other components. Take Tesla as an example. The battery cost of the earliest Tesla Model accounted for a quarter of the entire vehicle. This makes their electric vehicles expensive.
For lithium-ion power batteries, the basic unit is the cell. The structure of the cell includes:
- Positive electrode: lithium compound.
- Negative electrode: carbon material.
- Electrolyte: non-aqueous liquid electrolyte.
- BMS: Car batteries also include a battery management system (BMS), which monitors the status of the battery to ensure safe performance and the normal range of output power.
Part 3. 8 types of car batteries
Not all car batteries are the same. They vary in size, weight, and technology. Let’s dive into the most common types and see how their weights compare. There are mainly the following types of car batteries
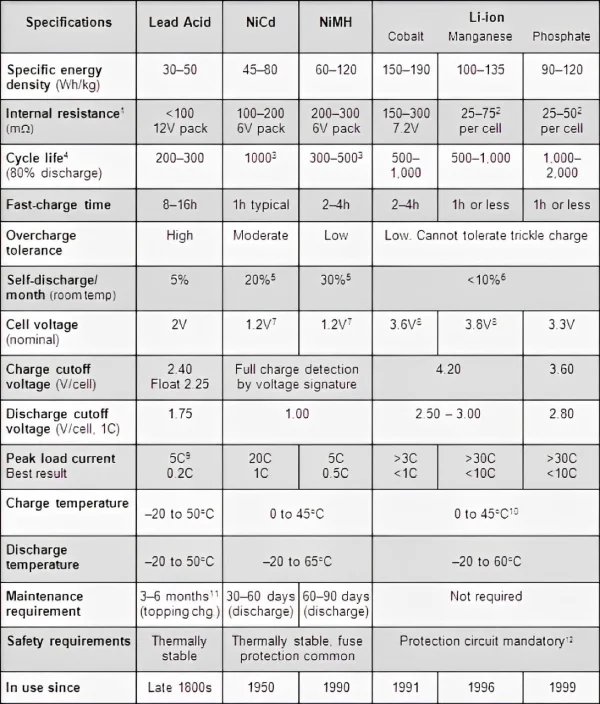
- Lithium-ion battery. Lithium-ion batteries have a higher voltage, usually 3.6V. It has a long service life and high energy density, but the cost is relatively high. Lithium-ion batteries are becoming more popular, especially in electric and hybrid vehicles. They are lighter and more efficient than lead-acid batteries but come with a higher price tag. Standard Lithium-Ion: These batteries weigh between 10 to 15 kg. The lighter weight is due to the different materials used, such as lithium and other lightweight metals. Despite their lighter weight, they provide excellent performance and can store more energy than their lead-acid counterparts.
- Ni-MH battery. The positive active material of nickel-metal hydride batteries is nickel hydroxide. The negative active material is metal hydride. The electrolyte is a potassium hydroxide solution. Nickel metal hydride batteries have low cost, mature technology, and long life but have low energy density and large size.
- Lead-acid batteries. They have been around for over a century and are known for their reliability and cost-effectiveness. Standard Lead-Acid: These are your typical car batteries. They usually weigh between 15 to 25 kg. The weight comes from the numerous lead plates and the sulfuric acid electrolyte. These batteries are widely used because they are affordable and provide sufficient power for most vehicles. The electrodes of lead-acid batteries are mainly made of lead and its oxides. The electrolyte is a sulfuric acid solution with low cost and good low temperature performance. However, lead-acid batteries have low energy density, short life, and large size. Lead-acid batteries are the most common type found in vehicles today.
- LiFePo4 battery. LiFePo4 battery uses LiFePo4 as the cathode material. LiFePo4 batteries have good thermal stability, low safety cost, and long life. But its energy density is low, and it fears low temperatures.
- Ternary lithium-ion battery. The cathode material of the ternary lithium-ion battery uses lithium nickel cobalt manganate. It has high energy density, long cycle life and good low temperature stability. But it is not stable enough at high temperatures.
- Nickel-cadmium batteries. The nickel-cadmium battery voltage is 1.2V and has a service life of 500 times. The discharge temperature of nickel-cadmium batteries is -20℃~60℃, and the charging temperature is 0℃~45℃. And it has strong overcharge resistance.
- AGM (Absorbent Glass Mat): AGM batteries are an upgraded version of the standard lead-acid battery. They have glass mats that absorb the electrolyte, making them spill-proof and more durable. However, this added technology increases the weight. AGM batteries typically weigh between 20 to 30 kg. They are often used in high-performance vehicles and those with lots of electronic features.
- There are also supercapacitors, lithium cobalt oxide batteries, graphene batteries, etc. Each battery has its unique advantages and disadvantages and is suitable for different automotive applications and needs.
As you can see, lithium-ion batteries are significantly lighter than lead-acid batteries. However, the choice of battery depends on various factors, including your vehicle’s requirements and your budget.
Part 4. What affects car battery weight?
Generally speaking, the heavier the car battery weight, the greater the driving distance. At the same time, EV battery weight will also affect the vehicle’s dynamic performance, suspension and steering components, etc. Therefore, EV battery weight is one of the key elements that must be balanced in electric vehicle manufacturing.
Therefore, we can conclude that the following factors determine car battery weight:
1. Car battery types
Car battery weight mainly depends on the type and capacity of the battery. Popular battery types currently on the market include lithium-ion batteries, nickel-cobalt-lithium manganate, and solid-state batteries.
Lithium-ion batteries are the most commonly used battery type due to their high energy density, long life, and low self-discharge rate. However, the disadvantages of lithium-ion batteries are their higher cost and limited capacity. Therefore, a larger battery capacity is needed for a longer cruising range. But this will also make the car battery weight heavier.
2. Car battery capacity
The capacity of a battery, measured in amp-hours (Ah), indicates how much charge it can store. Higher capacity batteries can power your car for longer periods without recharging. However, this increased capacity comes at a cost—more weight.
Car battery weight is directly proportional to battery capacity. In other words, the greater the capacity, the greater the weight.
A 100 Ah battery will be heavier than a 50 Ah battery because it needs more lead plates and electrolyte to store the additional charge. If your vehicle has high energy demands, you might need a higher capacity battery, which will be heavier.
3. Car battery material density
The density of the positive and negative plates of the car battery and the electrolyte will affect the car battery’s weight. Different manufacturers’ density differences in materials will also lead to different car battery weights.
Higher quality materials might weigh more but offer better performance and longevity.
For instance, thicker lead plates can store more energy and last longer but will also add to the battery’s weight. Similarly, better quality separators and casings can increase durability but also contribute to the overall mass.
4. Battery size
Size matters when it comes to batteries. Larger batteries naturally weigh more. The physical dimensions of a battery—its height, width, and length—determine how much material is used, and thus, its weight.
For example, a battery designed for a compact car will be smaller and lighter than one meant for a large SUV or truck. The larger the battery, the more lead plates and electrolyte it will contain, increasing its weight.
5. Number of cells
Car batteries consist of multiple cells, each contributing to the overall voltage and capacity. More cells mean more weight. A typical 12-volt lead-acid battery has six cells, while a 24-volt battery will have twelve.
Each cell adds weight due to the additional materials required. So, the more cells a battery has, the heavier it will be. This is especially true for batteries used in larger vehicles or those with high power requirements.
6. Car battery shell structure
The shell structure of the car battery also affects its weight to a certain extent. Some battery manufacturers use stronger casings to protect their batteries. Therefore, these car battery weights tend to be heavier.
7. Car size and weight
The size and weight of an electric vehicle also affect battery weight. For example, the capacity and weight of batteries used in large SUVs and small cars differ.
8. Others
Other factors also affect car battery weight. For example, the charging speed and charging type of electric vehicles, body materials, power systems, etc.
Part 5. Car battery weight
Different car batteries also weigh differently.
- The weight of traditional lead-acid car batteries is usually between 11 kg and 22 kg.
- For electric vehicle batteries, the weight is even heavier. Most are between 250 kg and 450 kg. The exact weight will vary based on battery type and capacity.
- The weight of car batteries will also vary depending on the capacity. For example, a 45Ah battery weighs approximately 12.5 kg. The weight of a 110Ah battery is approximately 24.5Kg. It’s important to note that these figures may vary depending on the specific battery make and model.
Compared with the weight of the engine and gearbox of fuel vehicles, the batteries of electric vehicles are much heavier. Suppose we only use battery cell density to calculate car battery weight. In that case, we can see that car battery weight is a shortcoming of electric vehicles.
Taking an 80kwh battery as an example, the total weight of the battery cells of the ternary lithium battery is 400kg. The total weight of LiFePo4 cells can reach 485 kg.
This is just the weight of the cell. Add the weight of the battery structure outside the cell, such as the battery top/bottom case, insulation layer, CMC, cooling system, and other components. The car battery weight will be even heavier.
Part 6. How does car battery weight affect a car’s performance?
The weight of a car battery doesn’t just sit there passively; it has a direct impact on your vehicle’s performance. Let’s explore how.
Fuel Efficiency
Heavier batteries can reduce fuel efficiency. The extra weight means your car’s engine has to work harder to move the vehicle, leading to increased fuel consumption. In a world where fuel efficiency is becoming increasingly important, a lighter battery can make a noticeable difference.
Handling
Weight distribution is crucial for a car’s handling. A heavier battery can alter the balance of your vehicle, particularly if it’s located in the front or back. This change in weight distribution can affect how your car handles, especially in tight corners or during quick maneuvers.
Acceleration
Extra weight can slow down acceleration. If your car is carrying a heavier battery, the engine needs to exert more power to achieve the same level of acceleration. This can be particularly noticeable in smaller cars or those with less powerful engines.
Battery Life
Heavier batteries with higher capacity might last longer. They can provide more consistent power over time and are less likely to discharge quickly. However, this comes at the cost of added weight. If you need a battery that can handle frequent short trips or lots of electronic accessories, a heavier battery with a higher capacity might be the better choice.
Part 7. Summary
In general, the EV battery weight of an electric vehicle directly impacts its performance and cruising range. Automakers need to find a balance between battery weight and performance. In the future, with further upgrades in battery technology, car battery weight will continue to be optimized. Car battery manufacturers will increase the energy density of car batteries and reduce car battery weight without sacrificing car performance and service life.
Related Tags:
More Articles

High‑Capacity 3S LiPo Batteries: 5000 mAh vs. 10000 mAh
Compare 3S LiPo 5000mAh vs 10000mAh batteries by weight, power, and use. Find the best fit for your drone, RC car, or boat setup.
Top 5 Applications for Small 3S LiPo Batteries
Small 3S LiPo batteries power drones, RC gear, wearables, and robotics with high energy and low weight. Making them ideal for compact electronics projects.
Building and Charging Your Own 3S LiPo Pack: A Step‑by‑Step Guide
Learn how to build, balance, and charge a 3S LiPo battery pack safely at home with this complete DIY guide for hobbyists and beginners.
How to Choose the Right LiPo Battery Plug Type?
Discover the best LiPo battery plug types, how to choose them, and expert tips for safe usage, soldering, and maintenance.
Choosing the Right Connector for Your 3S LiPo Battery
Choosing the right 3S LiPo connector depends on current, space, and use. Learn the pros and cons of XT60, JST, EC3, and more.