- Part 1. What is a miniature battery?
- Part 2. Why ultra-thin batteries matter in modern tech?
- Part 3. Key types of miniature batteries used in thin devices
- Part 4. What makes a miniature battery ultra-thin?
- Part 5. Important factors when selecting a miniature battery
- Part 6. Common applications of ultra-thin miniature batteries
- Part 7. Engineering challenges in thin battery integration
- Part 8. Innovations driving ultra-thin battery performance
- Part 9. Environmental and safety considerations
- Part 10. Future trends in ultra-thin battery development
- Part 11. FAQs about miniature battery solutions
What is a miniature battery, and why is it key in slim device design? A miniature battery is a compact and powerful energy source that plays a vital role in powering ultra-slim electronic devices. These batteries enable the creation of smaller, thinner, and lighter products without compromising on performance. As the demand for ultra-thin electronic gadgets increases, especially in wearables, medical devices, and smart cards, the importance of ultra-thin miniature battery solutions continues to grow rapidly.
This in-depth guide examines how miniature batteries are revolutionizing the design of slim devices, the various types of batteries available, their applications, and the innovations driving the future of miniature energy storage.
Part 1. What is a miniature battery?
A miniature battery is a small-sized power cell designed for compact electronic circuits and devices. These batteries are typically coin-shaped, cylindrical, cubed, or flat and flexible. The key feature of a miniature battery is its ability to fit into products with limited space while still delivering consistent and reliable power.
Miniature batteries are available in various chemistries, including lithium-ion, silver oxide, zinc-air, and solid-state. They are used in a wide range of applications, including hearing aids, fitness trackers, smart sensors, implantable medical devices, and payment cards.
Despite their tiny size, these batteries can have high energy density, long shelf life, and advanced safety features, making them essential for modern electronics.
Part 2. Why ultra-thin batteries matter in modern tech?
Technology is becoming smaller, faster, and more integrated into daily life. From fitness bands to health monitors, there is a growing need for devices that are light, thin, and portable. Ultra-thin batteries are the backbone of this trend.
Without ultra-thin batteries, many of today’s innovations would not be possible. Devices like credit-card-sized medical wearables or flexible skin patches would be too bulky or heavy with traditional batteries. These miniature power sources allow designers to deliver compact products that offer both performance and comfort.
Ultra-thin miniature batteries also open doors to new applications such as smart contact lenses, wearable patches for drug delivery, and disposable electronics used in diagnostics.
Part 3. Key types of miniature batteries used in thin devices
A variety of miniature battery types are available, each suited to different devices and use cases. Below are the most common types used in ultra-thin devices:
Lithium-ion polymer (Li-Po)
Lithium-ion polymer batteries are known for their flexibility, high energy density, and rechargeability. They are widely used in wearables, fitness bands, and medical patches. These batteries can be formed into various shapes and sizes, making them ideal for custom designs.
Solid-state batteries
Solid-state batteries use a solid electrolyte instead of a liquid one. This allows them to be extremely thin and safe. These batteries are often as thin as 0.1 mm and are used in implantable devices, smart cards, and other sensitive electronics. They offer a longer lifespan and excellent stability.
Zinc-air batteries
Zinc-air batteries are often used in hearing aids and other low-drain devices. They are lightweight and have high energy density but are typically non-rechargeable. Their performance is powerful in environments where space is limited and long runtime is needed.
Silver oxide batteries
These batteries are commonly used in watches, small medical devices, and instrumentation tools. They provide a stable voltage output and are compact.
Each battery type offers a different balance of size, capacity, rechargeability, and cost, making it essential to match the chemistry to the device’s specific needs.
Part 4. What makes a miniature battery ultra-thin?
An ultra-thin battery is defined by its thickness, which is usually less than 1 millimeter. These batteries can be either rigid or flexible, depending on the intended application. They are often manufactured using advanced materials, such as solid electrolytes, and are built with minimal casings to reduce thickness.
Some ultra-thin batteries are even printed onto flexible substrates using roll-to-roll technology, allowing them to be integrated into paper-like electronics, e-textiles, and flexible patches.
Key characteristics of ultra-thin batteries include:
- Minimal thickness
- Lightweight construction
- High energy density
- Safety and reliability
- Customizable shapes and sizes
The ability to integrate these batteries into ultra-thin electronics is driving innovation across multiple industries.
Part 5. Important factors when selecting a miniature battery
Selecting the right miniature battery depends on several crucial technical and design considerations. These include:
Size and form factor
The physical space available for the battery is a primary concern. Some devices may require a flexible battery, while others need a rigid and flat cell. Matching the battery’s dimensions to the product’s design ensures proper integration.
Energy and power requirements
Understanding how much power the device needs and for how long is crucial. High-drain devices, such as wireless sensors, may require batteries with burst energy output, while low-power devices, like RFID tags, can operate for years on a small cell.
Rechargeability
Some applications benefit from rechargeable batteries, such as fitness trackers or medical monitors, while others use single-use batteries for simplicity and lower costs.
Environmental conditions
Batteries must perform reliably under the environmental conditions they will face. For example, implantable batteries must be biocompatible and safe within the human body, whereas outdoor sensors require resistance to humidity and temperature fluctuations.
Regulatory compliance
In medical and wearable applications, miniature batteries must often meet stringent safety and performance standards. Choosing a battery that is already certified can reduce time to market and cost.
By evaluating these factors early in the design process, engineers can ensure that the battery will meet performance expectations while fitting seamlessly within the product.
Part 6. Common applications of ultra-thin miniature batteries
Ultra-thin miniature batteries are used across a wide range of industries. Some of the most common applications include:
Medical wearables
Devices such as continuous glucose monitors, ECG patches, and drug delivery systems require thin, flexible batteries that can operate safely on or inside the human body.
Smart cards
Modern payment cards and ID cards often include displays, keypads, or security chips that require a thin battery capable of delivering short bursts of power.
Flexible electronics
Smart textiles, bendable screens, and flexible phones all rely on batteries that can conform to various shapes without compromising performance or breaking.
IoT sensors
Miniature wireless sensors used for temperature, motion, location, or air quality monitoring employ ultra-thin batteries, allowing for extended deployment with minimal maintenance.
Consumer gadgets
Devices like smart rings, slim remotes, hearing aids, and compact beauty tools all utilize space-saving batteries to deliver high performance in a compact footprint.
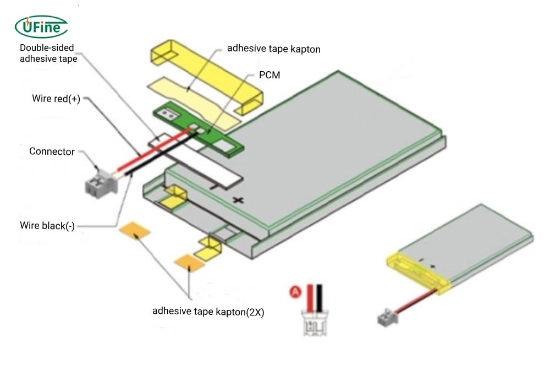
Part 7. Engineering challenges in thin battery integration
Designing and integrating miniature batteries into ultra-thin devices presents several engineering challenges:
- Thermal management is critical to avoid overheating in small enclosures.
- Battery placement must be optimized to prevent interference with other components.
- Connection and sealing must ensure the battery remains protected from moisture or contaminants.
- Capacity limitations often require creative power management strategies.
- Mechanical stress can damage thin battery layers, especially in wearable or flexible applications.
Addressing these challenges early in the design cycle helps avoid costly redesigns and ensures device reliability.
Part 8. Innovations driving ultra-thin battery performance
The field of miniature battery technology is evolving quickly. Recent innovations are making batteries safer, smaller, and more efficient:
- Printed batteries created using inkjet and screen-printing allow for integration into flexible electronics.
- 3D microbatteries increase surface area, offering more capacity in a small volume.
- Hybrid energy sources combine batteries with solar or kinetic energy harvesters for longer life.
- Biocompatible batteries made from non-toxic materials are being developed for use in implantable devices.
- AI-assisted battery management systems are helping optimize battery performance and lifespan.
These breakthroughs are opening new possibilities for next-generation electronics in healthcare, consumer tech, and industrial applications.
Part 9. Environmental and safety considerations
As miniature batteries become more widespread, their environmental and safety impact must be considered:
- Recycling programs are essential for properly handling materials like lithium and silver.
- Preventing battery leakage is crucial in medical and wearable devices.
- The safe disposal of single-use batteries helps protect the environment.
- Regulatory standards such as IEC and UL must be met for global product launches.
Designers should select batteries from reputable manufacturers that adhere to best practices for safety, sustainability, and compliance.
Part 10. Future trends in ultra-thin battery development
The future of miniature battery solutions is filled with exciting possibilities:
- Stretchable batteries will power smart clothing and athletic gear.
- Transparent batteries may be integrated into smart glasses and HUDs.
- Self-charging batteries using ambient light, motion, or thermal energy are on the horizon.
- The body can safely absorb medical-grade bio-batteries after they have performed their function.
- Modular battery systems will enable consumers to easily swap or upgrade power sources.
As innovation continues, batteries will become even thinner, smarter, and more adaptable, enabling the next generation of transformative technologies.
Part 11. FAQs about miniature battery solutions
What is the thinnest battery available today?
The thinnest batteries on the market are solid-state batteries measuring as little as 0.1 millimeters thick, making them ideal for ultra-slim electronics.
Are ultra-thin batteries rechargeable?
Yes, many ultra-thin batteries, such as lithium polymer and solid-state variants, are rechargeable. However, some types, like zinc-air, are designed for single use.
Which devices use miniature batteries?
Miniature batteries are used in hearing aids, fitness trackers, smart rings, implantable sensors, smart cards, and IoT devices.
Can ultra-thin batteries be flexible?
Many ultra-thin batteries are designed to be flexible, especially those used in wearable electronics and smart textiles. Flexibility allows them to bend with the device without breaking.
How long do miniature batteries last?
The lifespan varies by type and usage. Primary batteries may last from months to years, while rechargeable versions can provide hundreds or thousands of charge cycles.
Related Tags:
More Articles

What are Watts and Watt Hours in Battery?
Understand watt vs watt-hour in batteries, how to calculate battery watt hours, and what Wh means for car batteries, devices, and energy storage.
A Complete Guide to the Best Batteries for Flashlights
Compare the best batteries for flashlights, including AA, AAA, 18650, 21700, CR123A. See which battery offers the best brightness, runtime, and reliability.
How Long Do Rechargeable AA Batteries Last?
How long do rechargeable AA batteries last? Compare NiMH and lithium AA lifespan, recharge cycles, key factors, and performance vs alkaline batteries.
How Much Current Can a 9V Battery Really Supply?
Discover how many amps a 9V battery can supply, its actual current output, discharge rate, and capacity for alkaline, lithium, and rechargeable 9V batteries.
12V STD vs 12V AGM: Meaning, Differences, and Which Is Better
Understand what STD and AGM batteries mean, their key differences, and which 12V battery fits your needs best in 2026.