When choosing the right battery for your energy needs, the debate often concerns tubular versus flat plate batteries. Both types have unique characteristics, advantages, and drawbacks, making them suitable for different applications. This article will explore the key differences between these two battery types, helping you decide based on your specific requirements. Whether you’re looking for a battery for your home, business, or vehicle, understanding the nuances of tubular and flat plate batteries is crucial.
Part 1. What are tubular batteries?
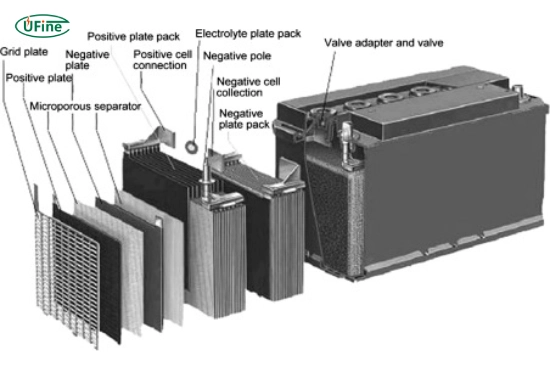
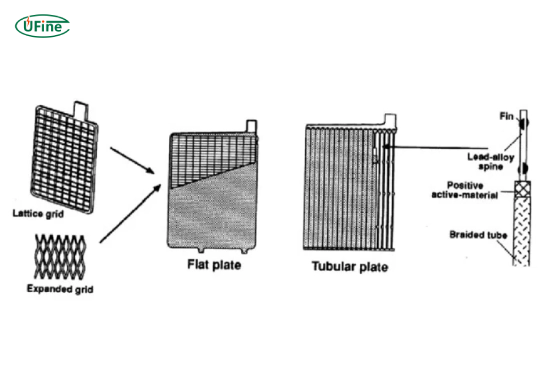
Tubular batteries are a type of lead-acid battery designed with a unique tubular plate structure. This design enhances their performance and longevity, making them a popular choice for applications that require deep cycling capabilities.
Key Characteristics of Tubular Batteries
- Construction: Tubular batteries feature tubular plates enclosed in a robust plastic casing. This design allows for better electrolyte distribution and minimizes the risk of short circuits.
- Durability: These batteries are known for their robust construction, which makes them resistant to physical damage and corrosion.
- Maintenance: Tubular batteries typically require regular maintenance, including topping up with distilled water to ensure optimal performance.
How Do Tubular Batteries Work?
Tubular batteries operate on the same principle as traditional lead-acid batteries but with a more advanced design. The active material inside the tubes undergoes a chemical reaction during the charging and discharging cycles, allowing the battery to store and release energy efficiently.
Key Processes:
- Charging: When charged, lead dioxide (PbO2) forms on the positive plates, while spongy lead (Pb) forms on the negative plates.
- Discharging: During discharge, these materials react with sulfuric acid (H2SO4) to produce lead sulfate (PbSO4), releasing electrical energy.
Part 2. What are flat plate batteries?
In contrast, flat plate batteries have a more traditional design, with flat plates arranged parallel within the battery casing. This design has been widely used for various applications due to its simplicity and effectiveness.
Key Characteristics of Flat Plate Batteries
- Construction: Flat plate batteries consist of flat lead plates immersed in an electrolyte solution. The flat design allows for efficient energy transfer but may lead to quicker wear.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Flat plate batteries are generally more affordable than their tubular counterparts, making them an attractive option for budget-conscious consumers.
- Maintenance: Like tubular batteries, flat plate batteries also require maintenance but may have slightly different upkeep needs.
How Do Flat Plate Batteries Work?
Flat plate batteries utilize a chemical reaction similar to tubular batteries but with a different internal structure. The flat plates create a larger surface area for the chemical reactions, facilitating energy storage and release.
Key Processes:
- Charging: The positive plate becomes lead dioxide, while the negative plate turns spongy lead during charging.
- Discharging: The reaction with sulfuric acid produces lead sulfate, generating electrical energy that can be used to power devices.
Part 3. Performance comparison: tubular vs. flat plate batteries
When comparing tubular and flat plate batteries, performance is a crucial factor to consider. Here’s how they stack up against each other:
Depth of Discharge
- Tubular Batteries: They can handle deeper discharges (up to 80%) without significantly affecting their lifespan.
- Flat Plate Batteries: Typically recommended for shallower discharges (around 50%), as deeper discharges can lead to reduced performance and lifespan.
Cycle Life
- Tubular Batteries: Known for their long cycle life, tubular batteries can last anywhere from 1200 to 1500 cycles depending on usage conditions.
- Flat Plate Batteries: These usually offer a shorter cycle life, averaging around 600 to 800 cycles.
Charge Retention
- Tubular Batteries: They excel in charge retention and can hold their charge longer when not in use.
- Flat Plate Batteries: While they perform adequately in charge retention, they may need to match the longevity of tubular designs.
Part 4. Applications of tubular batteries
Tubular batteries are particularly suited for applications that demand high reliability and deep cycling capabilities. Here are some common uses:
Renewable Energy Systems
Many homeowners and businesses use tubular batteries in solar energy systems because they can handle deep discharges and have long-cycle lives.
Uninterruptible Power Supplies (UPS)
For critical systems requiring backup power during outages, tubular batteries provide reliability and keep operations running smoothly.
Electric Vehicles
Some electric vehicles use tubular batteries to endure repeated charging and discharging cycles without significant degradation.
Part 5. Applications of flat plate batteries
Flat plate batteries also have their place in various applications:
General Purpose Use
These batteries are often used in applications where cost is a primary concern, such as in basic backup power systems or low-drain devices.
Automotive Applications
Flat plate batteries are commonly found in conventional vehicles due to their lower price point and sufficient performance for starting engines.
Small Solar Systems
Flat plate batteries can be a practical choice for smaller solar setups or off-grid applications with less demanding energy needs.
Part 6. Cost considerations: tubular vs. flat plate batteries
When it comes to cost, both types of batteries have different price points:
Initial Investment
Tubular Batteries: Generally more expensive upfront due to their advanced technology and longer lifespan.
Flat Plate Batteries: These are more budget-friendly initially but may require replacement sooner than tubular options.
Long-Term Costs
While tubular batteries may have a higher initial cost, their longer lifespan and lower maintenance needs often result in lower long-term costs than flat plate batteries.
Part 7. Maintenance requirements: tubular vs. flat plate batteries
Both types of batteries require maintenance but differ in terms of frequency and complexity:
Tubular Battery Maintenance
- Water Level Checks: Regularly check and top up with distilled water.
- Cleaning Terminals: Keep terminals clean from corrosion.
- Equalization Charging: Equalization charging is performed periodically to balance cell voltages.
Flat Plate Battery Maintenance
Water Level Checks: Water level checks are similar to those with tubular batteries.
Terminal Maintenance: Regular cleaning is also necessary here.
Avoid Overcharging: Be cautious with charging practices to prolong battery life.
Part 8. Environmental impact: tubular vs. flat plate batteries
Considering the environmental impact is essential when choosing between these two battery types:
Tubular Batteries
These batteries have a longer lifespan, meaning fewer units must be produced over time, potentially reducing environmental waste.
Flat Plate Batteries
While they may be less durable, advancements in recycling technologies are helping mitigate the environmental impact of flat plate battery disposal.
Part 9. User experiences and reviews: tubular vs. flat plate batteries
Understanding user experiences can provide valuable insights into the performance of both battery types:
Tubular Battery Reviews
Many users praise tubular batteries for their longevity and reliability in demanding applications like solar power systems and UPS setups.
Flat Plate Battery Reviews
Users often appreciate the affordability of flat plate batteries but note that they may need replacement sooner than expected under heavy-use conditions.
Part 10. FAQs
-
What is the lifespan of a tubular battery?
The average lifespan of a tubular battery ranges from 5 to 10 years, depending on usage and maintenance practices. -
Are flat plate batteries good for solar power systems?
While they can be used in solar systems, tubular batteries are generally preferred because they can effectively handle deeper discharges. -
Can I use a flat plate battery in an electric vehicle?
Flat plate batteries can be used in electric vehicles; however, they may not perform as well as tubular options under rigorous cycling conditions. -
How often should I maintain my battery?
Both types should be checked at least every few months; however, more frequent checks may be necessary depending on usage conditions. -
Which battery type is more cost-effective?
While flat plate batteries have a lower initial cost, tubular batteries often prove more cost-effective in the long run due to their durability and longer lifespan.
Related Tags:
More Articles

LiPo Battery Discharge Rate Guide & Calculation Tips
Understand LiPo battery discharge rates, C-ratings, and how to calculate max current. Essential guide for RC, drones, and electronics users.
High‑Capacity 3S LiPo Batteries: 5000 mAh vs. 10000 mAh
Compare 3S LiPo 5000mAh vs 10000mAh batteries by weight, power, and use. Find the best fit for your drone, RC car, or boat setup.
Top 5 Applications for Small 3S LiPo Batteries
Small 3S LiPo batteries power drones, RC gear, wearables, and robotics with high energy and low weight. Making them ideal for compact electronics projects.
Building and Charging Your Own 3S LiPo Pack: A Step‑by‑Step Guide
Learn how to build, balance, and charge a 3S LiPo battery pack safely at home with this complete DIY guide for hobbyists and beginners.
How to Choose the Right LiPo Battery Plug Type?
Discover the best LiPo battery plug types, how to choose them, and expert tips for safe usage, soldering, and maintenance.