Battery hookup is a crucial aspect of electrical systems, mainly when dealing with lithium-ion batteries. Whether setting up a power bank, an electric vehicle, or an off-grid solar system, understanding the proper battery hookup procedures is essential for optimal performance, safety, and longevity. This comprehensive guide will delve into battery hookup’s intricacies, importance, different connection methods, factors to consider, and tips for hooking a battery charger. So, let’s dive in and uncover the truth behind battery hookups.
Part 1. What is the battery hookup?
Battery hookup refers to connecting batteries in a circuit or system, allowing them to work together to provide electrical power. You can establish this connection using various configurations, such as series, parallel, or a combination. Proper battery hookup ensures efficient power distribution, prevents overloading or damaging batteries, and maximizes lifespan.
Importance of Proper Battery Hookup
- Optimal Performance: Correctly hooking up batteries ensures you achieve the desired voltage and current levels, enabling the system to function at its best. Improper hookups can result in underperformance or even system failure.
- Battery Longevity: Proper battery hookup helps distribute the electrical load evenly among the batteries, preventing excessive strain on specific units. This balanced distribution promotes longevity and extends the overall lifespan of the batteries.
- Safety: Incorrectly connected batteries can pose safety hazards such as short circuits, thermal runaway, or even explosions. Proper battery hookup minimizes these risks and ensures safe operation.
Part 2. How do you hook up lithium-ion batteries?
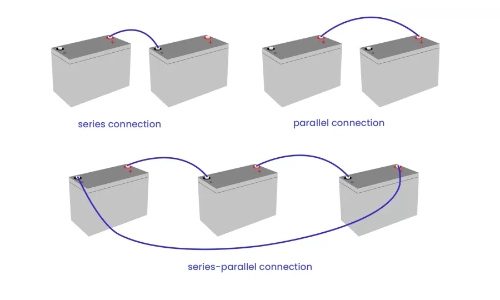
1. Batteries in Parallel
Method:
- Connect the positive terminal of one battery to the positive terminal of another and the negative terminal to the negative, creating a parallel connection.
- Ensure the voltage of each battery is the same before connecting in parallel.
Characteristics:
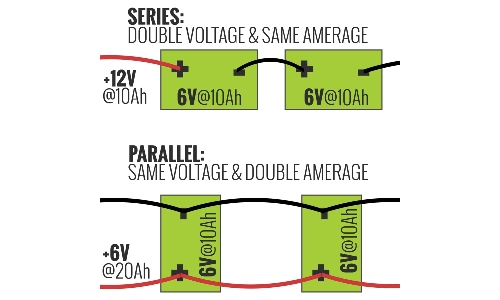
- Increases overall capacity (mAh) while maintaining voltage.
- Connecting batteries in parallel allows for longer device runtime due to increased capacity.
- It is ideal for applications where high capacity and sustained power are needed, such as electric vehicles and backup power systems.
Applications:
- Electric vehicles: Connecting lithium-ion batteries in parallel increases the total energy storage capacity, allowing longer driving distances.
- Portable electronic devices: Parallel connections provide extended usage time for devices like smartphones and laptops without increasing voltage.
2. Batteries in Series
Method:
- Connect the positive terminal of one battery to the negative terminal of another battery, linking them in series.
- Continue this connection until you achieve the desired voltage.
Characteristics:
- Increases total voltage while keeping capacity (mAh) the same as a single battery.
- Valid for applications requiring higher voltage, such as powering motors or high-performance electronics.
- Voltage adds up across batteries in series.
Applications:
- Power tools: Series connections of lithium-ion batteries provide the higher voltage needed to drive motors efficiently.
- Solar power systems: Series connections allow for voltage accumulation from multiple batteries, optimizing power storage capacity.
3. Batteries in Series and Parallel
Method:
- Combine series and parallel connections to achieve the desired voltage and capacity.
- First, connect batteries in parallel to increase capacity, then connect these parallel sets in series to increase voltage.
Characteristics:
- This configuration offers a balance between increased capacity and voltage.
- Provides flexibility in designing battery configurations for specific power requirements.
- Requires careful planning to ensure a proper balance of capacity and voltage across the entire battery array.
Applications:
- Hybrid electric vehicles: Series-parallel connections allow for both increased capacity and voltage, optimizing energy storage and power delivery for vehicle propulsion.
- Off-grid renewable energy systems: Combining series and parallel connections enables customization of battery banks to store and deliver power efficiently from sources like solar or wind.
Part 3. Do you hook up a red or black battery first?
When hooking up a battery, connecting the positive terminal (red) first and then the negative terminal (black) is generally recommended. This sequence reduces the risk of short circuits and potential sparks if the negative terminal is connected first. Connecting the positive terminal first minimizes the chances of accidental contact with metal surfaces or other conductive materials that could cause a short circuit.
Similarly, removing the negative terminal and then the positive terminal is advisable when disconnecting a battery. This order ensures the electrical circuit is interrupted correctly, reducing the risk of accidental short circuits.
Part 4. Factors to consider when hooking up batteries
- Battery Compatibility: Ensure the batteries you connect have the same voltage and capacity ratings. Mismatched batteries can lead to imbalances, reduced performance, and potential damage to the batteries and the electrical system.
- Battery Condition: It is crucial to connect batteries that are in similar states of charge. Connecting a fully charged battery to a partially discharged one can cause an imbalance, leading to inefficient charging or discharging. Ideally, all batteries should be in the same state of charge before connecting them.
- Wiring and Connections: Pay attention to the quality of wiring and connections. Ensure that the cables used for battery hookup are of the appropriate gauge to handle the current flow without excessive resistance or voltage drop. Loose or corroded connections can result in poor performance and safety hazards.
- Protection and Monitoring: Consider incorporating protective devices such as fuses, circuit breakers, or battery management systems (BMS) to safeguard the batteries and the electrical system. These devices help prevent overcharging, over-discharging, and other potentially damaging conditions.
- Ventilation: If you are hooking up batteries in an enclosed space, ensure proper ventilation to dissipate heat and prevent the buildup of potentially harmful gases. Adequate ventilation is crucial, especially when dealing with lithium-ion batteries, as they can be sensitive to temperature variations.
- Safety Precautions: Always follow safety guidelines and precautions provided by the battery manufacturer. Wear appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE) when handling batteries, and avoid short circuits or accidental contact with conductive materials.
Part 5. How to hook up a battery charger?
Here’s a general step-by-step guide for connecting a battery charger:
- Ensure the battery charger is compatible with the type and voltage of the battery you are charging. Refer to the charger’s user manual and the battery specifications for compatibility information.
- Ensure you unplug the charger from the power source before connecting.
- Identify the positive (+) and negative (-) terminals on the battery and the charger. These terminals usually have corresponding symbols or labels indicating them.
- Connect the positive clamp or cable of the charger to the battery’s positive terminal. Ensure a secure and tight connection.
- Connect the negative clamp or cable of the charger to the battery’s negative terminal. Again, ensure a secure and tight connection.
- Double-check all connections to ensure they are adequately secured and there are no loose or exposed wires.
- Plug the charger into a power outlet and turn it on, following the manufacturer’s instructions.
- Monitor the charging process and follow your battery type’s recommended charging time and procedures.
- Once the battery reaches full charge, unplug the charger from the power source before disconnecting the clamps or cables. Remove the negative clamp or cable first, followed by the positive clamp or cable.
- Store the charger in a safe place per the manufacturer’s instructions.
Part 6. Conclusion
In conclusion, when it comes to battery hookup, getting it right is crucial for optimal performance and safety. By understanding the different connection methods, considering important factors, and following proper procedures, you can ensure that your batteries work efficiently and last longer. So, whether you’re setting up a power bank or working on a renewable energy system, remember to connect those batteries like a pro and enjoy the power they provide with peace of mind.
Related Tags:
More Articles

Safe Charging Protocols for Your 11.1V LiPo Battery Charger
Safely charge your 11.1V LiPo battery by following proper rates, using safety tools, and avoiding common charging mistakes.
11.1 V LiPo Battery Airsoft: Boosting Field Performance
Upgrade your airsoft gun with an 11.1V LiPo battery for faster firing, longer runtime, and top-tier performance on the battlefield.
Batteries for Trolling Motors Lightweight vs. Leaf Blower Power
Explore the best lightweight trolling motor batteries and how they compare to leaf blower power for performance, portability, and runtime.
What Is a 2C Battery?
Learn what a 2C battery is, how C-rates affect performance, and how to calculate the number of batteries your device needs.
What Battery Does LED Strips Use?
Discover which batteries power LED strips best. Learn about voltage, capacity, battery types, and how to safely power your LED lighting projects.