In the ever-evolving world of battery technology, two types of batteries have gained significant attention for their unique properties and applications: the Tadiran lithium thionyl chloride (Li-SOCl2) battery and the lithium polymer (Li-Po) battery. While both utilize lithium-based chemistry, these power sources serve distinctly different purposes in various industries. This comprehensive article will delve into the intricacies of both battery types, exploring their working principles, advantages, disadvantages, and specific applications. By understanding the strengths and limitations of each, we can better appreciate their roles in powering our increasingly connected world.
Part 1. What is a Tadiran lithium thionyl chloride battery (Li-SOCl2)?
Tadiran lithium thionyl chloride (Li-SOCl2) batteries are renowned for their ultra-long life and high energy density. Due to their reliability and efficiency, remote wireless applications primarily use these batteries. Tadiran pioneered this technology nearly 50 years ago and has since been a leader in the industry, providing power solutions for various applications, including automatic meter reading (AMR) units, asset tracking, and infrastructure monitoring.
Advantages of Tadiran lithium thionyl chloride batteries
High Energy Density
Tadiran Li-SOCl2 batteries boast a high energy density, which allows them to deliver substantial power in a compact size. This makes them suitable for applications where space and weight are critical factors.
Long Shelf Life
These batteries have an exceptionally long shelf life, with a self-discharge rate of only about 1% per year. This means they can remain functional for many years without significant loss of capacity.
Wide Temperature Range
Tadiran Li-SOCl2 batteries can operate in extreme temperatures ranging from -55°C to +85°C, making them ideal for harsh environments.
Low Self-Discharge
The low self-discharge rate ensures that users can store the batteries without losing their charge, which is crucial for applications that require long-term reliability.
High Voltage Stability
These batteries maintain a stable voltage throughout their discharge cycle, ensuring consistent performance.
Disadvantages of Tadiran lithium thionyl chloride batteries
Non-Rechargeable
One of the primary drawbacks of Li-SOCl2 batteries is that they are not rechargeable. Once depleted, they need to be replaced, which can be a limitation for some applications.
Passivation Effect
When you first put the battery into operation, the passivation layer that forms on the lithium anode can initially impede current flow. This can cause a temporary voltage drop, although it stabilizes over time.
Applications of Tadiran lithium thionyl chloride batteries
Remote Wireless Devices
Remote wireless devices widely use Tadiran Li-SOCl2 batteries due to their long life and reliability. They are ideal for applications where replacing batteries frequently, such as remote sensors and monitoring systems, is not feasible.
Metering Systems
These batteries are commonly used in automatic meter reading (AMR) and advanced metering infrastructure (AMI) systems, providing reliable power for extended periods.
Asset Tracking
Tadiran Li-SOCl2 batteries are used in asset-tracking devices, ensuring that the equipment can be monitored and tracked over long distances and timeframes without frequent battery changes.
Part 2. How do Tadiran lithium thionyl chloride batteries work?
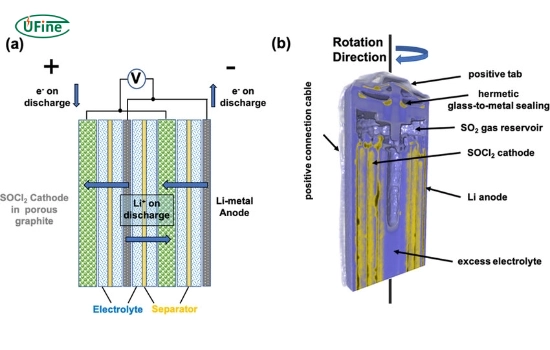
Tadiran Li-SOCl2 batteries operate on a unique electrochemical principle. The battery comprises a lithium metal anode, a liquid thionyl chloride cathode, and a porous carbon current collector. The thionyl chloride serves as both the cathode material and the electrolyte solvent.
When the battery is in use, the following reaction occurs:
4Li + 2SOCl2 → 4LiCl + S + SO2
This reaction produces lithium chloride (LiCl), sulfur (S), and sulfur dioxide (SO2). The battery gradually consumes the lithium anode while the carbon cathode reduces the thionyl chloride. A vital feature of these batteries is forming a passivation layer on the lithium anode, which helps prevent self-discharge and contributes to the battery’s long shelf life.
Part 3. What is a lithium polymer battery (Li-Po)?
Lithium polymer (Li-Po) rechargeable batteries have gained popularity in consumer electronics and the radio control industry. Li-Po batteries, known for their lightweight, high energy density, and flexible form factor, are commonly used in smartphones, tablets, drones, and other portable devices. They offer significant energy capacity and discharge rate advantages, making them ideal for high-power applications.
Advantages of lithium polymer batteries
Lightweight and Flexible
Li-Po batteries are lightweight and can be manufactured in various shapes and sizes, making them versatile for different applications. Their flexible form allows designers to use them in compact, portable devices.
High Energy Density
These batteries offer a high energy density, providing more power in a smaller package. This makes them ideal for high-performance applications such as drones and electric vehicles.
High Discharge Rates
Li-Po batteries can deliver high discharge rates, essential for applications requiring bursts of power, such as radio-controlled models and drones.
Safety
Experts generally consider Li-Po batteries safer than other lithium-ion batteries because they use a solid polymer electrolyte, which reduces the risk of leaks and explosions.
Disadvantages of lithium polymer batteries
Higher Cost
Li-Po batteries tend to be more expensive than other types, which can be a limiting factor for some users.
Shorter Lifespan
Compared to other lithium-ion batteries, Li-Po batteries have a shorter lifespan and may require more frequent replacements.
Sensitivity to Overcharging
These batteries are sensitive to overcharging and require careful management to avoid potential safety hazards.
Applications of lithium polymer batteries
Consumer Electronics
Due to their high energy density and lightweight characteristics, consumer electronics manufacturers extensively use Li-Po batteries in smartphones, tablets, and laptops.
Drones and RC Models
These batteries are popular in the radio control industry, particularly in drones and RC models, where high power and lightweight are essential.
Electric Vehicles
Electric vehicles also use Li-Po batteries, providing the necessary power and energy density for efficient performance.
Part 4. How do lithium polymer batteries work?
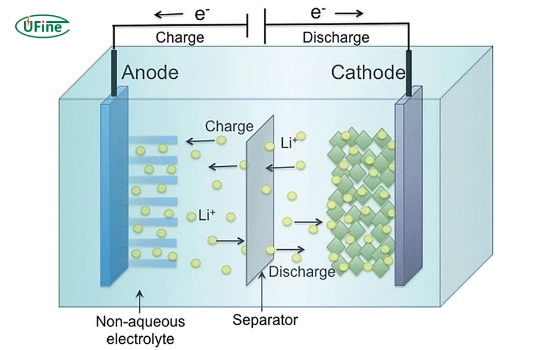
Lithium polymer batteries operate on a principle similar to other lithium-ion batteries but with a critical difference in their electrolyte. In a Li-Po battery, a solid polymer composite, such as polyethylene oxide or polyacrylonitrile, holds the lithium-salt electrolyte instead of an organic solvent.
The essential components of a Li-Po battery include:
- Positive electrode (cathode): Usually made of lithium cobalt oxide (LiCoO2) or lithium manganese oxide (LiMn2O4).
- Negative electrode (anode): Typically made of graphite.
- Polymer electrolyte: A solid polymer composite containing lithium salts.
Lithium ions move from the anode to the cathode through the polymer electrolyte during discharge, and this process is reversed during charging. The polymer electrolyte allows for a more flexible and potentially safer battery design than traditional liquid electrolyte lithium-ion batteries.
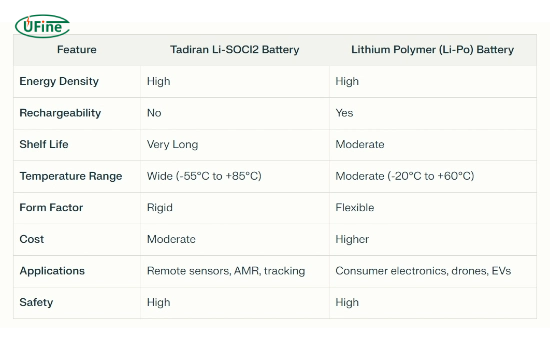
Part 5. Comparison: Tadiran lithium thionyl chloride battery vs lithium polymer battery
When comparing Tadiran Li-SOCl2 batteries with Li-Po batteries, it’s essential to consider their distinct characteristics and applications. Tadiran Li-SOCl2 batteries excel in long-term, low-power applications where battery replacement is challenging or costly. They offer unparalleled shelf life and performance in extreme temperatures, making them ideal for remote sensing and monitoring applications.
On the other hand, Li-Po batteries shine in high-power, rechargeable applications where weight and form factor are crucial. Their ability to deliver high discharge rates and withstand multiple recharges makes them perfect for consumer electronics and portable devices.
While both battery types offer high energy density, they cater to different needs regarding rechargeability, temperature range, and application specifics. The choice between the two often depends on the application’s specific requirements, including power needs, environmental conditions, and maintenance capabilities.
Here’s a detailed comparison of the two battery types:
Part 6. FAQs
-
How does the passivation layer in Li-SOCl2 batteries affect their performance?
The passivation layer in Li-SOCl2 batteries plays a crucial role in their long shelf life by preventing self-discharge. However, it can initially impede current flow when the battery is activated, causing a temporary voltage drop. This effect stabilizes over time, allowing the battery to deliver consistent performance throughout its lifespan. -
Can lithium polymer batteries be recharged?
Yes, you can recharge lithium polymer (Li-Po) batteries and use them multiple times, which makes them suitable for consumer electronics and other high-usage applications. -
How do Li-Po batteries compare to traditional lithium-ion batteries in terms of safety?
Li-Po batteries are generally considered safer than traditional lithium-ion batteries due to their solid polymer electrolyte. This design reduces the risk of leaks and thermal runaway, which can lead to fires or explosions in liquid electrolyte batteries. However, Li-Po batteries still require proper handling and charging practices to ensure safety. -
Are lithium polymer batteries safe?
Yes, Li-Po batteries are generally safe when used correctly. They use a solid polymer electrolyte, which reduces the risk of leaks and explosions compared to other lithium-ion batteries. -
Why are Li-Po batteries popular in the radio control industry?
Li-Po batteries are popular in the radio control industry because of their high energy density, lightweight, and ability to deliver high discharge rates, which are essential for powering drones and RC models.
Related Tags:
More Articles

GoPro Battery Charger Guide: Top Picks & Pro Charging Tips
Explore the best GoPro chargers, compare third-party options, and learn how to charge smarter for longer battery life.
GoPro Battery Life Comparison: How Long Does a GoPro Battery Last?
Find out how GoPro battery life varies by model and get practical advice to maximize runtime for every adventure.
What Battery Powers Your GoPro?
Learn all about GoPro batteries - compatibility, runtime, charging tips, and how to extend battery life for longer shoots.
What Is a Disk Battery? A Simple Guide for Non-Tech Users
A disk battery is a small, round cell used in watches, remotes, and other electronic devices. It delivers steady power for compact, low-drain devices.
What Battery Powers a Space Heater?
Discover the type of battery that powers space heaters and learn how to choose the right one for efficient heating in your home or office.