In the rapidly evolving world of energy storage, two types of batteries have emerged as potential game-changers: lithium-sulfur batteries and lithium-metal batteries. Understanding the differences between these two technologies is crucial for making informed decisions about their applications and potential. This article delves into the composition, chemistry, advantages, disadvantages, and applications of both battery types, followed by a detailed comparison.
Part 1. What is a lithium-sulfur battery?
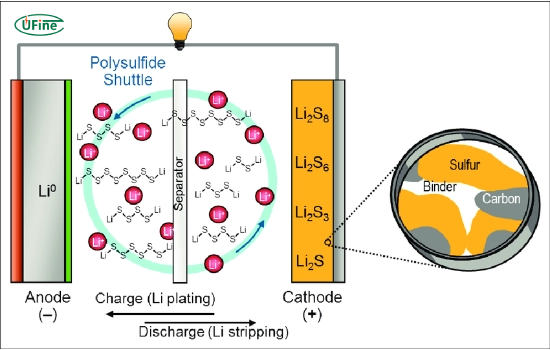
A lithium-sulfur (Li-S) battery is a rechargeable battery that uses lithium as the anode and sulfur as the cathode. The energy storage mechanism in Li-S batteries involves the redox reaction between lithium and sulfur. During discharge, lithium ions migrate from the anode to the cathode, reacting with sulfur to form lithium sulfide (Li2S).
Composition and chemistry of lithium-sulfur batteries
A lithium-sulfur battery’s composition includes a lithium metal anode and a sulfur-based cathode. The electrolyte is typically a lithium salt dissolved in an organic solvent.
Chemical reactions
The primary reactions in a Li-S battery during discharge are:
S8+16Li→8Li2S
During charging, the reverse reactions occur, converting lithium sulfide back to sulfur and lithium ions.
Advantages of lithium-sulfur batteries
- High energy density: Li-S batteries have a theoretical energy density of up to 2,600 Wh/kg, significantly higher than traditional lithium-ion batteries.
- Cost-effective materials: Sulfur is abundant and inexpensive, making Li-S batteries potentially cheaper.
- Environmental benefits: Using sulfur, a more sustainable material, offers ecological advantages over other battery chemistries.
Disadvantages of lithium-sulfur batteries
- Reduced cycle life: Li-S batteries suffer from a shorter cycle life due to the degradation of the sulfur cathode and the polysulfide shuttle effect.
- Low conductivity: Sulfur’s low electrical conductivity requires additional conductive materials, increasing the battery’s weight and complexity.
- Safety concerns: Lithium dendrite formation and electrolyte degradation pose safety risks.
Applications of lithium-sulfur batteries
People use lithium-sulfur batteries in:
- Aerospace: Their high energy density makes them suitable for applications in drones and satellites.
- Electric vehicles: Potential for use in electric cars due to their lightweight and high energy capacity.
- Military: Used in various military applications for their high energy and long-lasting power.
Part 2. What is a lithium metal battery?
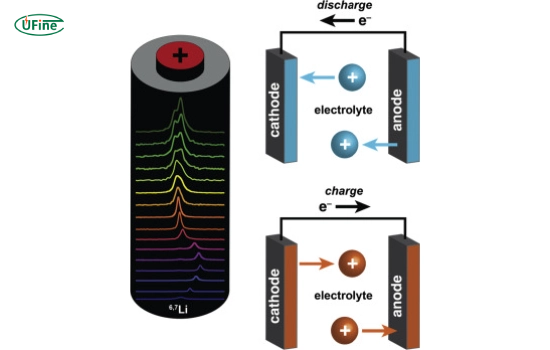
A lithium metal battery uses metallic lithium as the anode. These batteries are known for their high charge density. They are primarily used in non-rechargeable applications, although rechargeable versions are under development.
Composition and chemistry of lithium metal batteries
A lithium metal battery consists of a metallic lithium anode and various types of cathodes, such as manganese dioxide or sulfur dioxide. The electrolyte is usually a lithium salt in an organic solvent.
Chemical reactions
The typical reaction for a lithium metal battery during discharge is:
Li+MnO2→LiMnO2
In rechargeable lithium metal batteries, the reversible reaction allows users to recharge the battery.
Advantages of lithium metal batteries
- High energy density: Lithium metal batteries offer a high energy density due to metallic lithium’s high electrochemical potential.
- Lightweight: The low atomic weight of lithium contributes to a lighter battery, making it ideal for portable applications.
- High voltage: These batteries can produce up to 3.7 V, higher than many other battery types.
Disadvantages of lithium metal batteries
- High cost: Metallic lithium makes these batteries expensive to produce.
- Safety risks: Pure lithium is highly reactive, posing significant safety hazards, especially in the presence of moisture.
- Limited rechargeability: Most lithium metal batteries are non-rechargeable, and developing rechargeable versions remains a challenge
Applications of lithium metal batteries
Lithium metal batteries find applications in:
- Consumer electronics: Widely used in cameras, watches, and other small electronic devices.
- Medical devices: Manufacturers use these in pacemakers and other implantable medical devices due to their long life and reliability.
- Aerospace: Aerospace applications use it because of its high energy density and lightweight.
Part 3. Lithium-sulfur battery vs lithium metal battery
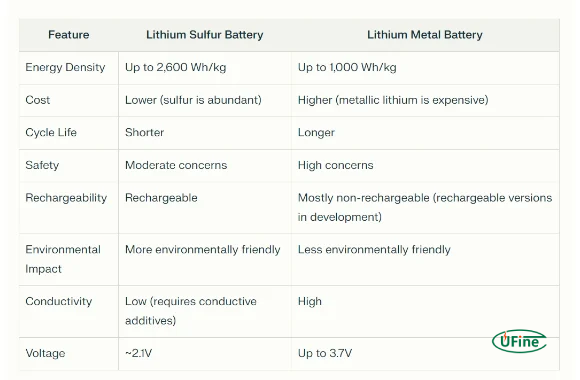
Lithium-sulfur (Li-S) and lithium metal batteries differ significantly in energy density, cost, cycle life, safety, and environmental impact:
- Energy density: Li-S batteries offer a higher theoretical energy density, making them more suitable for applications requiring high energy storage.
- Cost: Li-S batteries are generally more cost-effective due to their abundance and low sulfur cost.
- Cycle life: Lithium metal batteries typically have a longer cycle life than Li-S batteries, which suffer from degradation issues.
- Safety: Both battery types have safety concerns, but lithium metal batteries pose higher risks due to metallic lithium’s reactivity.
- Environmental impact: Li-S batteries are considered more environmentally friendly due to abundant sulfur.
- Applications: While there is some overlap, Li-S batteries focus more on high-energy applications like aerospace and electric vehicles, while manufacturers commonly use lithium metal batteries in consumer electronics and medical devices.
- Rechargeability: Engineers design Li-S batteries to be rechargeable, while most lithium metal batteries remain non-rechargeable, with rechargeable versions still under development.
Part 4. FAQs
-
What is the main advantage of lithium-sulfur batteries?
Lithium-sulfur batteries are renowned for their high energy density, which allows them to store more energy per unit weight than many other battery types. This makes them particularly advantageous for lightweight and high-capacity energy storage applications, such as electric vehicles and aerospace. -
Are lithium metal batteries rechargeable?
Designers need to create more rechargeable lithium metal batteries. Instead, they typically use these batteries in single-use applications. However, advancements in research are focusing on developing rechargeable lithium metal batteries by addressing issues like dendrite formation and stability during charging. -
Why are lithium-sulfur batteries considered environmentally friendly?
Experts consider lithium-sulfur batteries environmentally friendly because they use sulfur, which is abundant and cheaper than other materials like cobalt or nickel found in traditional batteries. Sulfur is less toxic and has a lower environmental impact during production and disposal, making it a more sustainable option. -
What are the safety concerns with lithium metal batteries?
Safety concerns with lithium metal batteries stem from the high reactivity of metallic lithium, which can react violently with moisture or air, potentially leading to fires or explosions. The formation of lithium dendrites during charging can also cause short circuits and increase the risk of thermal runaway. -
Which battery type is more cost-effective?
Lithium-sulfur batteries are generally more cost-effective due to the lower sulfur cost than metallic lithium. Simpler manufacturing processes further enhance this cost advantage, making Li-S batteries a more economical choice for high-energy applications.
Related Tags:
More Articles

LiPo Battery Discharge Rate Guide & Calculation Tips
Understand LiPo battery discharge rates, C-ratings, and how to calculate max current. Essential guide for RC, drones, and electronics users.
High‑Capacity 3S LiPo Batteries: 5000 mAh vs. 10000 mAh
Compare 3S LiPo 5000mAh vs 10000mAh batteries by weight, power, and use. Find the best fit for your drone, RC car, or boat setup.
Top 5 Applications for Small 3S LiPo Batteries
Small 3S LiPo batteries power drones, RC gear, wearables, and robotics with high energy and low weight. Making them ideal for compact electronics projects.
Building and Charging Your Own 3S LiPo Pack: A Step‑by‑Step Guide
Learn how to build, balance, and charge a 3S LiPo battery pack safely at home with this complete DIY guide for hobbyists and beginners.
How to Choose the Right LiPo Battery Plug Type?
Discover the best LiPo battery plug types, how to choose them, and expert tips for safe usage, soldering, and maintenance.