Lithium capacitors are an advanced energy storage solution that combines the benefits of supercapacitors and lithium-ion batteries. They offer fast charging, high power output, and long lifespan, making them suitable for various industries, from renewable energy to automotive applications.
But how do they work? What makes them different from other energy storage devices? And where are they used in real life?
This guide will cover everything you need about lithium capacitor technology, including its fundamentals, functionality, advantages, and real-world applications.
Part 1. What is a lithium capacitor?
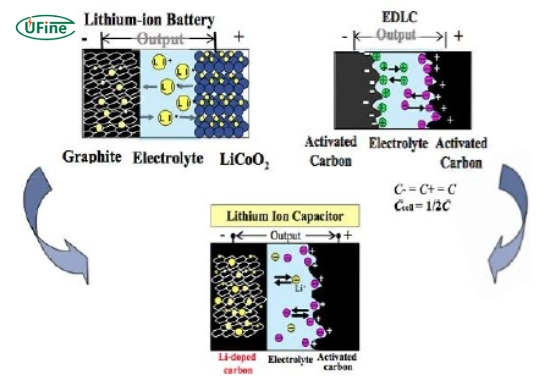
A lithium capacitor is a hybrid energy storage device that combines electrostatic charge storage (like a supercapacitor) with lithium-ion intercalation (like a battery).
Key characteristics of lithium capacitors:
- Higher energy storage than traditional capacitors
- Faster charge and discharge than lithium-ion batteries
- Longer lifespan compared to most battery technologies
- High power output for applications needing instant energy
These features make lithium capacitors ideal for industries requiring fast and reliable energy storage.
Part 2. How does a lithium capacitor work?
A lithium capacitor stores energy using two different mechanisms:
- Electrostatic energy storage: Like a supercapacitor, it stores charge on the electrode surfaces.
- Lithium-ion intercalation: Like a lithium-ion battery, it allows lithium ions to move into the electrode structure, increasing energy storage capacity.
This hybrid structure offers lithium capacitors high power density and more excellent energy storage than supercapacitors alone.
Part 3. What are the main components of a lithium capacitor?
Lithium capacitors consist of several essential parts that store and release energy efficiently.
1. Electrodes
- Positive electrode (cathode): Made of activated carbon to provide a large surface area for charge storage.
- Negative electrode (anode): Contains lithium-doped material, improving energy storage capacity.
2. Electrolyte
A lithium salt solution that helps ions move between electrodes.
3. Separator
A thin insulating layer that prevents short circuits while allowing ion movement.
4. Current collectors
Conductive materials connect the electrodes to an external circuit, allowing electricity to flow.
Each component is crucial in ensuring high efficiency, safety, and durability.
Part 4. How do lithium capacitors compare to lithium-ion batteries?
What is the difference between a lithium capacitor and a lithium-ion battery?
Although lithium capacitors and lithium-ion batteries store energy, they work differently.
- Lithium-ion batteries store energy through chemical reactions. They have a high energy density, meaning they can store energy for a long time. However, they take longer to charge and degrade over time.
- Lithium capacitors, on the other hand, store energy using both electrostatic charge and lithium-ion intercalation. They charge much faster, last longer, and are safer than lithium-ion batteries. However, they store less energy per unit of weight.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Lithium Capacitor | Lithium-Ion Battery |
|---|---|---|
| Energy Density | 10-20 Wh/kg (lower) | 150-250 Wh/kg (higher) |
| Charge Time | Seconds to minutes | 30 minutes to several hours |
| Cycle Life | 100,000+ cycles (longer) | 500-5,000 cycles (shorter) |
| Power Output | High (fast energy release) | Moderate |
| Self-Discharge Rate | Low | Higher than capacitors |
| Safety | Very safe, low risk of explosion | Higher risk of overheating |
| Temperature Range | -40°C to 85°C | -20°C to 60°C |
Key takeaway: Lithium capacitors are a great choice for long-lasting, fast-charging energy storage. Lithium-ion batteries may be better for high-energy storage for long-term use.
Artikel Terkait: A Comparison of Supercapacitors and Lithium Ion Batteries
Part 5. What are the advantages of lithium capacitors?
Lithium capacitors provide several benefits over traditional batteries and capacitors:
- Fast charging and discharging
They can fully charge in seconds or minutes, unlike lithium-ion batteries, which take hours. - Long lifespan
They can handle over 100,000 charge cycles, while most batteries last only a few thousand cycles. - High power output
They can deliver instant bursts of energy, making them useful for applications requiring rapid power delivery. - Wide operating temperature
They function between -40°C and 85°C, making them ideal for extreme environments. - Enhanced safety
They have lower risks of fire, swelling, or explosion compared to lithium-ion batteries.
Part 6. What are the disadvantages of lithium capacitors?
Despite their benefits, lithium capacitors have some drawbacks:
- Lower energy density: They store less energy than lithium-ion batteries.
- Higher cost: Advanced materials and manufacturing make them more expensive.
- Voltage limitations: They need voltage-balancing circuits to prevent overcharging.
Part 7. Where are lithium capacitors used?
Lithium capacitors are used in various industries due to their fast charge times and durability.
- Renewable energy storage
They store extra power from solar panels and wind turbines for later use. - Electric vehicles (EVs)
They help with regenerative braking, improving energy efficiency. - Backup power systems
Used in uninterruptible power supplies (UPS) to prevent power loss. - IoT and industrial sensors
Powers wireless sensors and remote monitoring devices. - Medical equipment
Provides reliable energy for implantable medical devices and emergency systems.
Part 8. How do you choose the right lithium capacitor?
When selecting a lithium capacitor, consider:
- Voltage and capacity requirements: Ensure it meets your power needs.
- Operating temperature range: Choose one that works in your environment.
- Lifespan: Look for a model with high cycle durability.
- Size and weight: Opt for a compact design if space is limited.
Part 9. How to properly maintain a lithium capacitor?
To extend the lifespan of a lithium capacitor:
- Avoid overcharging or deep discharging – Use a regulated charging system.
- Store in a cool, dry place – Reduces degradation over time.
- Regularly inspect for damage – Check for swelling, leaks, or performance drops.
Part 10. Are lithium capacitors the future of energy storage?
Lithium capacitors provide a powerful combination of speed, durability, and safety. As industries demand faster charging, longer lifespans, and safer energy solutions, these capacitors will play a more significant role in renewable energy, electric vehicles, and industrial applications.
While they won’t completely replace lithium-ion batteries, they are becoming a key component in modern energy storage systems.
Part 11. FAQs about lithium capacitor
What is the main difference between a lithium capacitor and a lithium-ion battery?
A lithium capacitor charges faster and lasts longer, while a lithium-ion battery stores more energy.
Can lithium capacitors replace lithium-ion batteries?
No, lithium capacitors cannot fully replace lithium-ion batteries. Still, they are better for fast-charging and long-life applications.
Are lithium capacitors safe?
Yes, they have low risks of overheating, swelling, or explosion.
How long do lithium capacitors last?
They last over 100,000 charge cycles, much longer than lithium-ion batteries.
Where are lithium capacitors used?
They are used in solar energy storage, electric vehicles, industrial sensors, and medical devices.
Related Tags:
More Articles

Safe Charging Protocols for Your 11.1V LiPo Battery Charger
Safely charge your 11.1V LiPo battery by following proper rates, using safety tools, and avoiding common charging mistakes.
11.1 V LiPo Battery Airsoft: Boosting Field Performance
Upgrade your airsoft gun with an 11.1V LiPo battery for faster firing, longer runtime, and top-tier performance on the battlefield.
Batteries for Trolling Motors Lightweight vs. Leaf Blower Power
Explore the best lightweight trolling motor batteries and how they compare to leaf blower power for performance, portability, and runtime.
What Is a 2C Battery?
Learn what a 2C battery is, how C-rates affect performance, and how to calculate the number of batteries your device needs.
What Battery Does LED Strips Use?
Discover which batteries power LED strips best. Learn about voltage, capacity, battery types, and how to safely power your LED lighting projects.